Chapter: Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Fundamentals and Applications : Recombinant Human Deoxyribonuclease I
In Vivo Activity in CF Sputum - Pharmacology - Recombinant Human Deoxyribonuclease I
In Vivo Activity in CF Sputum
In vivo confirmation of the proposed mechanism of action for rhDNase I
has been obtained from direct characterization of apparent DNA size (Fig. 7)
and measurements of enzymatic and immunoreactive (ELISA) activity of rhDNase I
(Fig. 8) in sputum from CF patients (Sinicropi et al., 1994a). Sputum samples
were obtained one to six hours post-dose from adult CF patients after
inhalation of 5 to 20 mg of rhDNase I.
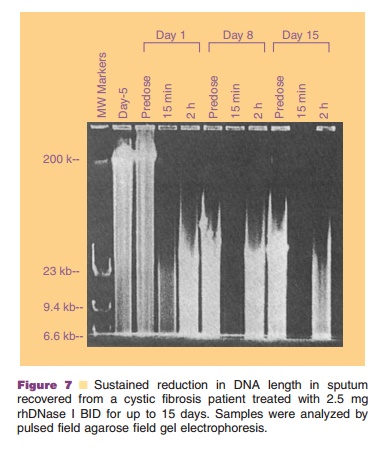
rhDNase I therapy produced a sustained reduction in DNA size in
recovered sputum (Fig. 7), in good agreement with the in vitro data.
Inhalation of the therapeutic dose of rhDNase I produced sputum levels
of rhDNase I which have been shown to be effective in vitro (Fig. 8) (Shak,
1995).
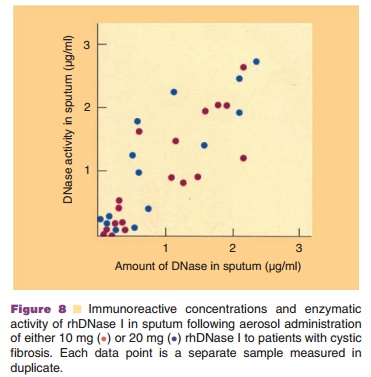
The recovered rhDNase I was also enzymatically active. Enzymatic
activity was directly correlated with rhDNase I concentrations in the sputum.
Viscoelasticity was reduced in the recovered sputum, as well. Furthermore,
results from scintigraphic studies in using twice daily 2.5 mg of rhDNase I in
CF patients suggested possible reductions in pulmonary obstruction and
increased rates of mucociliary sputum clearance from the inner zone of the lung
compared to controls (Laube et al., 1996). This finding was not confirmed in a
cross-over design study using once daily dosing, suggesting that improvement of
mucociliary clearance may require higher doses (Robinson et al., 2000).
Related Topics