Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 14 : Integrating Python with MySql and C++ : Importing C++ Programs In Python
Importing C++ Programs In Python: Book Back Questions and Answers
Computer Science : Integrating Python with MySql and C++ : Importing C++ Programs In Python
Evaluation
Part – I
Choose the best answer (1 Marks)
1. Which of the following is not a scripting language?
(A) JavaScript
(B) PHP
(C) Perl
(D) HTML
2. Importing C++ program in a Python program is called
(A) wrapping
(B) Downloading
(C) Interconnecting
(D) Parsing
3.The expansion of API is
(A) Application Programming Interpreter
(B) Application Programming Interface
(C) Application Performing Interface
(D) Application Programming Interlink
4.A framework for interfacing Python and C++ is
(A) Ctypes
(B) SWIG
(C) Cython
(D) Boost
5.Which of the following is a software design technique to split your code into separate parts?
(A) Object oriented Programming
(B) Modular programming
(C) Low Level Programming
(D) Procedure oriented Programming
6.The module which allows you to interface with the Windows operating system is
(A) OS module
(B) sys module
(c) csv module
(d) getopt module
7. getopt() will return an empty array if there is no error in splitting strings to
(A) argv variable
(B) opt variable
(c) args variable
(d) ifile variable
8.Identify the function call statement in the following snippet.
if __name__ =='__main__':
main(sys.argv[1:])
(A) main(sys.argv[1:])
(B) __name__
(C) __main__
(D) argv
9.Which of the following can be used for processing text, numbers, images, and scientific data?
(A) HTML
(B) C
(C) C++
(D) PYTHON
10. What does __name__ contains ?
(A) c++ filename
(B) main() name
(C) python filename
(D) os module name
Part - II
Answer the following questions (2 Marks)
1. What is the theoretical difference between Scripting language and other programming language?
Ans. (i) The theoretical difference between the two is that
scripting languages do not require the compilation step and are rather
interpreted.
(ii) For example,
normally, a C++ program needs to be compiled before running whereas, a
scripting language like JavaScript or Python need not be compiled.
(iii) A scripting language requires an interpreter while a programming language requires a compiler. A given language can be called as a scripting or programming language depending on the environment they are put to use.
2. Differentiate compiler and interpreter.
Ans.
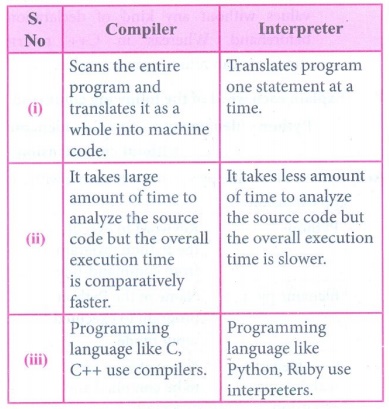
s. No
Compiler
(i) Scans the entire program and translates it as a whole into
machine code.
(ii) It takes large amount of time to analyze the source code
but the overall execution time is comparatively faster.
(iii) Programming language like C, C++ use compilers.
Interpreter
(i) Translates program one statement at a time.
(ii) It takes less amount of time to analyze the source code but
the overall execution time is slower.
(iii) Programming language like Python, Ruby use interpreters.
3. Write the expansion of (i) SWIG (ii) MinGW
(i) SWIG - Simplified Wrapper Interface Generator
(ii) MINGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
4. What is the use of modules?
Ans. (i) The use of modules to break down large programs into small
manageable and organized files.
(ii) Modules provide reusability of code. Define our most used
functions in a module and import it, instead of copying their definitions into
different programs.
5. What is the use of cd command. Give an example.
Ans. ‘cd’ command refers to change directory and absolute path refers
to the couple path.
(Eg) “cd c:\program files\open office 4\program”
Part – III
Answer the following questions (3 Marks)
1. Differentiate PYTHON and C++
Ans.
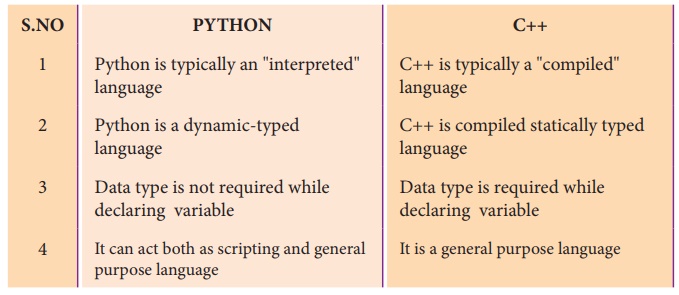
PYTHON
(i) Python is typically an "interpreted" language
(ii) Python is a dynamic-typed language
(iii) Data type is not required while declaring variable
(iv) It can act both as scripting and general purpose language
C++
(i) C++ is typically a "compiled" language
(ii) C++ is compiled statically typed language
(iii) Data type is required while declaring variable
(iv) It is a general purpose language
2. What are the applications of scripting language?
Ans. (i) To automate certain tasks in a program
(ii) Extracting information from a data set
(iii) Less code intensive as compared to traditional programming
language
(iv) can bring new functions to applications and glue complex
systems together
3. What is MinGW? What is its use?
Ans. (i) MinGW refers to a set of runtime header files, used in
compiling and linking the code of C, C++ and FORTRAN to be run on Windows
Operating System.
(ii) MinGw-W64 (version of MinGW) is the best compiler for C++
on Windows. To compile and execute the C++ program, need ‘g++’ for Windows. MinGW allows to
compile and execute C++ program dynamically through Python program using g++.
(iii) Python program that contains the C++ coding can be
executed only through minGW-w64 project’ run terminal. The run terminal open
the command-line window through which Python program should be executed.
4. Identify the module ,operator, definition name for the following welcome.display()
Ans. Welcome.display()
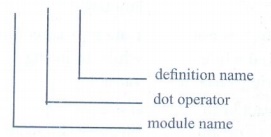
5. What is sys.argv? What does it contain?
Ans. sys.argv is the list of command-line arguments passed to the
Python program, argv contains all the items that come along via the command-line
input, it's basically an array holding the command-line arguments of the
program.
Part – IV
Answer the following questions (5 Marks)
1. Write any 5 features of Python.
Ans.
(i) Python uses Automatic Garbage Collection whereas C++ does
not.
(ii) C++ is a statically typed language, while Python is a
dynamically typed language.
(iii) Python runs through an interpreter, while C++ is
pre-compiled.
(iv) Python code tends to be 5 to 10 times shorter than that
written in C++.
(v) In Python, there is no need to declare types explicitly
where as it should be done in C++
(vi) In Python, a function may accept an argument of any type,
and retifrn multiple values without any kind of declaration beforehand. Whereas
in C++ return statement can return only one value.
2. Explain each word of the following command.
Python <filename.py> -<i> <C++ filename without cpp extension>
Python <filename.py> -i <C++ filename without cpp
extension>
Python : Keyword to execute the Python program from command-line
filename.py- i : Name of the Python program to executed input
mode
C++ filename without cpp extension : Name of C++ file to be
compiled and executed
3. What is the purpose of sys,os,getopt module in Python. Explain
Ans. This module provides access to some variables used by the
interpreter and to functions that interact strongly with the interpreter,
sys.argv :
(i) sys.argv is the list of command-line arguments passed to the
Python program, argv contains all
the items that come along via the command-line input, it's basically an array
holding the command-line arguments of the program.
(ii) To use sys.argv,
you will first have to import sys.
The first argument, sys.argv[0], is always the name of the program as it was
invoked, and sys.argv[l] is the first argument you pass to the program (here it
is the C++ file).
OS:
(i) The OS module in
Python provides a way of using operating system dependent functionality.
(ii) The functions that the OS
module allows you to interface with the Windows operating system where Python
is running on.
os.system():
(i) Execute the C++ compiling command (a string contains Unix, C
command which also supports C++ command) in the shell (Here it is Command
Window).
(ii) For Example to compile C++ program g++ compiler should be invoked. To do so the following command is
used.
os.system (‘g++’ + <varaiable_namel> ‘-<mode>’ +
<variable_name2>
getopt module:
(i) The getopt module of Python helps you to parse (split)
command-line options and arguments.
(ii) This module provides two functions to enable command-line
argument parsing.
getopt.getopt method :
(i) This method parses command-line options and parameter list.
Following is the syntax for this method -
(ii) <opts>,<args>=getopt.getopt(argv, options, [long_options])
4. Write the syntax for getopt() and explain its arguments and return values
Ans. getopt.getopt method: This
method parses command-line options and parameter list. Following is the syntax
for this method –
<opts>,<args>=getopt.getopt(argv, options, [long_options])
Here is the detail of the parameters -
(i) argv : This is
the argument list of values to be parsed (splited). In our program the complete
command will be passed as a list.
(ii) options : This
is string of option letters that the Python program recognize as, for input or
for output, with options (like ‘i’ or o’) that followed by a colon (:). Here
colon is used to denote the mode.
(iii) long_options :
This parameter is passed with a list of strings. Argument of Long options
should be followed by an equal sign ('='). In our program the C++ file name
will be passed as string and ‘f also will be passed along with to indicate it
as the input file.
getopt() method returns value
consisting of two elements. Each of these values are
stored separately in two different list (arrays) opts and args. Opts
contains list of splitted strings like mode, path and args contains any string
if at all not splitted because of wrong path or mode, args will be an empty
array if there is no error in splitting strings by getopt().
For example, The Python code which is going to execute the C++
file p4 in command line will have the getopt() method like the following one.
opts, args = getopt.getopt (argv, "i:",['ifile='])
Where opts contains : [('-i', ‘c:\\pyprg\\p4')]
-i:- : option nothing
but mode should be followed by :
'c:\\pyprg\\p4' : value nothing
but the absolute path of C++ file.
In our examples since the entire command line commands are
parsed and no leftover argument, the second
argument args will be empty []. If args is displayed using print() command
it displays the output as [].
5. Write a Python program to execute the following c++ coding
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ cout<<“WELCOME”; return(0);
}
The above C++ program is saved in a file welcome.cpp
Ans.
#Now select File→New in Notepad and type the Python program as
main.py
# Program that compiles and executes a .cpp file
# Python main.py -i welcome
import sys, os, getopt
def main(argv):
cpp_file = "
exe_file = "
opts, args = etopt.getopt(argv, "i:",['ifile='])
for o, a in opts:
if o in ("-i", "-ifile"):
cpp_file = a + '.cpp'
exe_file = a + '.exe'
run(cpp_file, exe_file)
def run(cpp_file, exe_file):
print("Compiling" + cpp_file)
os.system('g++' + cpp_file + '-o' + exe_ file)
print("Running" + exe_file)
print("………………….. ")
print
os.system(exe_file)
print
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv[1:])
Related Topics