Chapter: Digital Communication : Digital Modulation Scheme
Important Short Questions and Answers: Digital Modulation Scheme
DIGITAL MODULATION SCHEME
1.Define QAM and draw its constellation diagram. ?
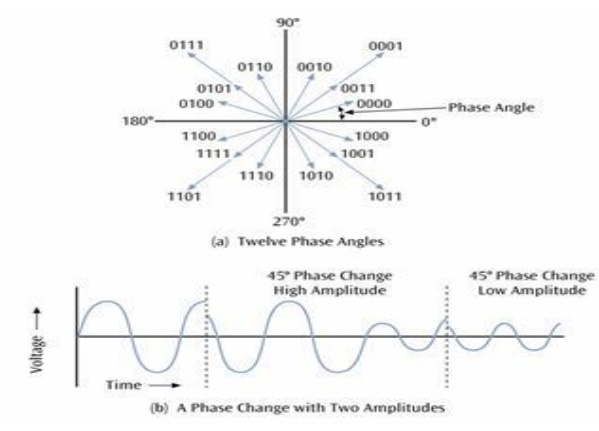
2. A binary frequency shift keying system employs
two signaling frequencies 1f and 2f. The lower frequency 1f is 1200 Hz and
signaling rate is 500 Baud. Calculate 2f. ?
For
binary FSK baud=fb
Fb=500Hz
Consider
the FN modulation index(h) of 1 in FSK
Fm-fs/Fb
=h=1
Fm-fs=fb
Fs=f1=1200HZ
Fm-1200Hz=500Hz
Fm=1700Hz,f2=fm=1700Hz.
3. Draw the PSK waveform for 011011.
4. What is meant by coherent detection system?
In
coherent ASK, correlation receiver is used to detect the signal. Locally
generated carrier is correlated with incoming Ask signal. The locally generated
carrier is in exact phase either transmitted carrier. Coherent Ask is also
called synchronous ASK.
5. Why is PSK always preferable over ASK in coherent
detection?
ASK is
on-off signaling where as the modulated carrier is continuously transmitted in
PSK. Hence peak power requirement is more in ASK, where it is reduces in PSK.
6. Differentiate between coherent and non-coherent
detection
In
coherent detection the local carrier generated at the receiver is phase locked
with the carrier at the transmitter. Hence it is also called synchronous
detection. In non coherent detection the local carrier generated at the
receiver not be phase locked with the carrier at the transmitter. It is simple,
but it has higher probability of error.
7. What are the drawbacks of binary PSK system?
It is
difficult to detect +b(t) and –b(t) because of squaring in the receiver
Problem, of ISI and inter channel interference are present.
8. A BPSK system makes errors at the average rate
of 1000 errors per delay. Data rate is 1 kbps . The single-sided noise power
spectral density is 10-20 W/Hz. Assuming the system to be wide sense
stationary,
what is the average bit error probability?
24*60*60=86400sec 86.4*106
Bir error probability Pe=100/86.4*106 =1.1157*10-6
9. What is meant by DPSK?
In DPSK,
the input sequence is modified. Let input sequence be d(t) and output Sequence
be b(t). Sequence b(t) changes level at the beginning of each interval in which
d(t)=1 and it does not changes level when d(t)=0.
When b(t)
changes level, phase of the carrier is changed. And as stated above, b(t)
changes t=its level only when d(t) =1. This means phase of the carrier is
changed only if d(t)=1. Hence the technique is called Differential PSK.
10. Explain coherent detection?
In
coherent detection, the local carrier generated at the receiver is phase locked
with the carrier at the transmitter. The detection is done by correlating
received noisy signal and locally generated carrier. The coherent detection is
a synchronous detection.
11. Bring out the difference between
coherent & non coherent binary modulation scheme.
a. Coherent detection:
In this
method the local carrier generated at the receiver is phase locked with the
carrier At the transmitter. Hence it is called synchronous detection
b. Non coherent detection:
In this
method, the receiver carrier need not be phase locked with transmitter carrier.
Hence it is called envelope detection.
12. Write the expression for bit error rate for
coherent binary FSK. Bit error rate for coherent binary FSK is
given as,
Pe = 1/2erfc√0.6E/No
13.
What is
Signal constellation diagram?
Suppose
that in each time slot of duration T seconds, one s2(t), . . sM(t)
is transmitted with equal probability, 1/M For geometric representation, the
signal si (t), = 1, 2, ..., M, is applied to a bank of correlators.
The correlator outputs define the signal vector si. The set of message points
corresponding to the set of transmitted signals {si(t))} i=1..M is
called a signal constellation.
14.
What is
meant by memory less modulations?
When the
digital symbol modulates amplitude, phase or frequency of the carrier without
any reference to previous symbol, it is called memory less modulations.
Eg.:ASK,PSK,FSK,QPSK etc.
15.Define QPSK.
·
In QPSK two successive bits in the data sequence
are grouped together.This combination of two bits forms four distinct
symbols.When the symbol is changed to next symbol the phase of the carrier is
changed by 450(or π/4).
·
Because of combination of two bits there will be
four symbols.Hence the phase shift will be π/4, 3π/4, 5π/4 or 7π/4.
QPSK
reduces amplitude variations and required transmission bandwidth.
DIGITAL MODULATION SCHEME –
IMPORTANT TERMS
QAM :
QAM is a
combination of ASK and PSK

Coherent detection system:
In
coherent ASK, correlation receiver is used to detect the signal. Locally
generated carrier is correlated with incoming Ask signal. The locally generated
carrier is in exact phase either transmitted carrier. Coherent Ask is also
called synchronous ASK.
ASK
ASK is
on-off signaling where as the modulated carrier is continuously transmitted in
PSK. Hence peak power requirement is more in ASK, where it is reduces in PSK.
Binary PSK system:
It is
difficult to detect +b(t) and –b(t) because of squaring in the receiver
Problem, of ISI and inter channel interference are present.
DPSK:
In DPSK,
the input sequence is modified. Let input sequence be d(t) and output Sequence
be b(t). Sequence b(t) changes level at the beginning of each interval in which
d(t)=1 and it does not changes level when d(t)=0.
When b(t)
changes level, phase of the carrier is changed. And as stated above, b(t)
changes t=its level only when d(t) =1. This means phase of the carrier is
changed only if d(t)=1. Hence the technique is called Differential PSK.
Coherent detection:
In
coherent detection, the local carrier generated at the receiver is phase locked
with the carrier at the transmitter. The detection is done by correlating
received noisy signal and locally generated carrier. The coherent detection is
a synchronous detection.
Non coherent detection:
In this
method, the receiver carrier need not be phase locked with transmitter carrier.
Hence it is called envelope detection.
Bit error rate for coherent binary FSK.
Bit error
rate for coherent binary FSK is given as,
Pe = 1/2erfc√0.6E/No
Signal constellation diagram:
Suppose
that in each time slot of duration T seconds, one s2(t), . . sM(t)
is
transmitted
with equal probability, 1/M For geometric representation, the signal si
(t), i = 1, 2, ..., M, is applied to a bank of correlators. The correlator
outputs define the signal vector si. The set of message points corresponding to
the set of transmitted signals {si(t))} i=1..M is called a signal
constellation.
Memory less modulations:
When the
digital symbol modulates amplitude, phase or frequency of the carrier without
any reference to previous symbol, it is called memory less modulations.
Eg.:ASK,PSK,FSK,QPSK etc.
QPSK.
·
In QPSK two successive bits in the data sequence
are grouped together.This combination of two bits forms four distinct
symbols.When the symbol is changed to next symbol the phase of the carrier is
changed by 450(or π/4).
·
Because of combination of two bits there will be
four symbols.Hence the phase shift will be π/4, 3π/4, 5π/4 or 7π/4.
QPSK
reduces amplitude variations and required transmission bandwidth.
Related Topics