Chapter: Principles of Compiler Design : Code optimization
Important Short Questions and Answers: Code optimization
1.
How the quality of object program is measured?
The quality of an object program is
measured by its Size or its running time. For large computation running time is
particularly important. For small computations size may be as important or even
more.
2.
What is the more accurate term for code optimization?
The
more accurate term for code optimization would be “code improvement”
3.
Explain the principle sources of optimization.
Code optimization techniques are
generally applied after syntax analysis, usually both before and during code
generation. The techniques consist of detecting patterns in the program and
replacing these patterns by equivalent and more efficient constructs.
4.
What are the patterns used for code optimization?
The patterns may be local or global and
replacement strategy may be a machine dependent or independent
5.
What are the 3 areas of code
optimization?
·
Local optimization
·
Loop optimization
·
Data flow analysis
6.
Define local optimization.
The
optimization performed within a block of code is called a local optimization.
7.
Define constant folding.
Deducing at compile time that the value
of an expression is a constant and using the constant instead is known as
constant folding.
8.
What do you mean by inner loops?
The most heavily traveled parts of a
program, the inner loops, are an obvious target for optimization. Typical loop
optimizations are the removal of loop invariant computations and the
elimination of induction variables.
9. What is code motion?
Code
motion is an important modification that decreases the amount of code in a
loop.
10.
What are the properties of
optimizing compilers?
·
Transformation must preserve the meaning
of programs.
·
Transformation must, on the average,
speed up the programs by a measurable amount
·
A Transformation must be worth the
effort.
11.
Give the block diagram of
organization of code optimizer.
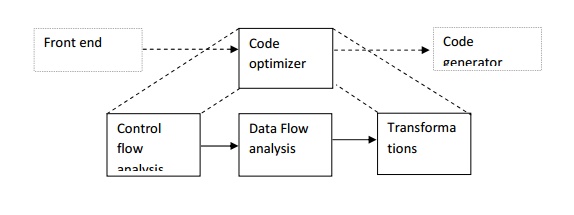
12.
What are the advantages of the
organization of code optimizer?
a.
The operations needed to implement high
level constructs are made explicit in the intermediate code, so it is possible
to optimize them.
b.
The intermediate code can be independent
of the target machine, so the optimizer does not have to change much if the
code generator is replaced by one for a different machine
13.
Define Local transformation &
Global Transformation.
A transformation of a program is called
Local, if it can be performed by looking only at the statements in a basic
block otherwise it is called global.
Give
examples for function preserving transformations.
·
Common subexpression elimination
·
Copy propagation
·
Dead – code elimination
·
Constant folding
15.
What is meant by Common
Subexpressions?
An occurrence of an expression E is
called a common subexpression, if E was previously computed, and the values of
variables in E have not changed since the previous computation.
16. What is meant by Dead Code?
A variable is live at a point in a
program if its value can be used subsequently otherwise, it is dead at that
point. The statement that computes values that never get used is known Dead
code or useless code.
17.
What are the techniques used for
loop optimization?
i)
Code motion
ii)
Induction variable elimination
iii)
Reduction in strength
18.
What is meant by Reduction in
strength?
Reduction in strength is the one which
replaces an expensive operation by a cheaper one such as a multiplication by an
addition.
19. What is meant by loop invariant
computation?
An expression that yields the same
result independent of the number of times the loop is executed is known as loop
invariant computation.
20. Define data flow equations.
A
typical equation has the form
Out[S]
= gen[S] U (In[S] – kill[S])
and
can be read as, “ the information at the end of a statement is either generated
within
the statement, or enters at the beginning and is not
killed as control flows through the statement”. Such equations are called data
flow equations.
29.
What are the two standard storage
allocation strategies?
The two standard allocation strategies are
1.
Static allocation.
2.
Stack allocation
30.
Discuss about static allocation.
In static allocation the position of an activation
record in memory is fixed at run time.
31.
Write short notes on activation
tree. Nov/Dec 2007
·
A tree which depicts the way of control
enters and leaves activations.
·
In an activation tree
i.
Each node represents an activation of an
procedure
ii.
The root represents the activation of
the main program.
iii.
The node for a is the parent of the node
for b , if and only if control flows from activation a to b
iv.
Node for a is to the left of the node
for b, if and only if the lifetime of a occurs before the lifetime of b.
32.
Define control stack.
A
stack which is used to keep track of live procedure actions is known as control
stack.
33. Define heap.
A
separate area of run-time memory which holds all other information is called a
heap.
34. Give the structure of general
activation record
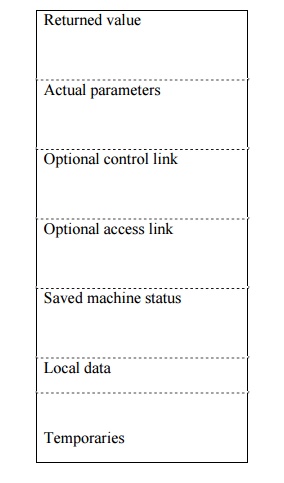
Returned
value
Actual
parameters
Optional
control link
Optional
access link
Saved
machine status
Local
data
Temporaries
35. Discuss about stack allocation.
In stack allocation a
new activation record is pushed on to the stack for each execution of a
procedure. The record is popped when the activation ends.
36.
What are the 2 approaches to
implement dynamic scope?
·
Deep access
·
Shallow access
37.
What is padding?
Space
left unused due to alignment consideration is referred to as padding.
38.
What are the 3 areas used by
storage allocation strategies?
· Static allocation
Stack allocation
·
Heap allocation
39.
What are the limitations of using
static allocation?
·
The size of a data object and constraints
on its position in memory must be known at compile time.
·
Recursive procedure are restricted,
because all activations of a procedure use the same bindings for local name
·
Data structures cannot be created
dynamically since there is no mechanism for storage allocation at run time
40.
Define calling sequence and return
sequence.
·
A call sequence allocates an activation
record and enters information into its fields
·
A return sequence restores the state of
the machine so that calling procedure can continue execution.
41.
When dangling reference occurs?
·
A dangling reference occurs when there
is storage that has been deallocated.
·
It is logical error to use dangling
references, since the value of deallocated storage is undefined according to
the semantics of most languages.
42.
Define static scope rule and
dynamic rule
·
Lexical or static scope rule determines
the declaration that applies to a name by a examining the program text alone.
·
Dynamic scope rule determines the
declaration applicable to name at runtime, by considering the current
activations.
43.
What is block? Give its syntax.
·
A block is a statement containing its
own data declaration.
·
Syntax:
{
Declaration statements
}
44.
What is access link?
·
An access link is a pointer to each
activation record which obtains a direct implementation of lexical scope for
nested procedure.
45.
What is known as environment and
state?
·
The term environment refers to a
function that maps a name to a storage location.
·
The term state refers to a function that
maps a storage location to the value held there.
46.
How the run-time memory is
sub-divided?
·
Generated target code
·
Data objects
·
A counterpart of the control stack to
keep track of procedure activations
Related Topics