Chapter: Digital Communication : Baseband Transmission
Important Short Questions and Answers: Baseband Transmission
BASEBAND
TRANSMISSION
1. What is
meant by transparency with respect to line codes
The line
code is said to be transparent if the synchronization between the transmitter
and receiver is maintained for any type of input data sequence.
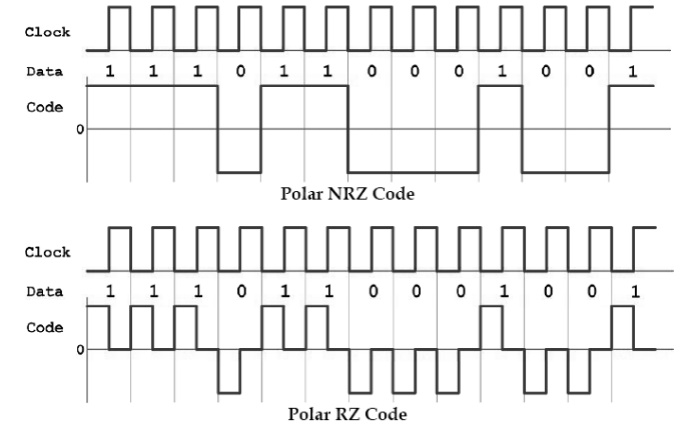
2. Draw the NRZ and RZ code for the digital data
10110001
[OR]
Draw the RZ bipolar line code format for the
information {10110}
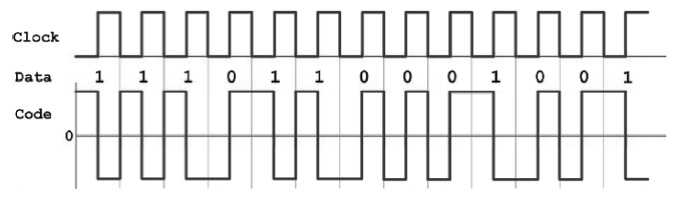
3. What is Manchester code? Draw the Manchester format
for the data stream 10110?
In
Manchester code each bit of data is signified by at least one transition.
Manchester encoding is therefore considered to be self-clocking, which means
that accurate clock recovery from a data stream is possible. In addition, the
DC component of the encoded signal is zero. Although transitions allow the
signal to be self-clocking, it carries significant overhead as there is a need
for essentially twice the bandwidth of a simple NRZ or NRZI encoding
4. State any four desirable properties of line code
· The PAM
signal should have adequate timing content,
·
The PAM signal should immune to channel noise and
interference
·
The PAM signal should allow error detection and
error correction
·
The PAM signal should be transparent to digital
data being transmitted.
5.
What is
intersymbol interference in baseband binary PAM systems?
In
baseband binary PAM, symbols are transmitted one after another. These symbols
are separated by sufficient time durations. The transmitter, channel and
receiver acts as a filter to this baseband data. Because of the filtering
characteristics, transmitted PAM pulses are spread in time.
6. What is correlative coding?
Correlative
level coding is used to transmit a baseband signal with the signalling rate of
2Bo over the channel of bandwidth Bo. This is made physically possible by
allowing ISI in the transmitted in controlled manner. This ISI is known to
receiver. .The .correlative .coding .is .implemented .by .duobinary .signalling
.and modified duobinary signalling.
7. Define Duobinary baseband PAM systemK
Duobinary
encoding reduces the maximum frequency of the baseband signal. The word „duo‟
means to double the transmission capacity of the binary system. Let the PAM
signal ak represents kth bit. Then the encoder the new waveform as Ck =ak
+ ak-1
Thus two
successive bits are added to get encoded value of the kth bit. Hence Ck becomes
a correlated signal even though ak is
not correlated. This introduces intersymbol interference in the controlled
manner to reduce the bandwidth.
8. What are eye pattern?
Eye
pattern is used to study the effect of ISI in baseband transmission.
1) Width of
.eye .opening defines the .interval over .which the .received wave can be
sampled without error from ISI.
2.) The
sensitivity of the system to timing error is determined by the rate of closure
of the eye as the sampling time is varied.
3) Height
of the eye opening at sampling time is called margin over noise.
9. How is eye pattern obtained on the CRO?
Eye
pattern can be obtained on CRO by applying the signal to one of the input
channels and given an external trigger of 1/Tb Hz. This makes one sweep of beam equal to Tb seconds.
10.
Why do
you need adaptive equalization in a switched telephone network.
In
switched telephone network the distortion depends upon 1) Transmission
characteristics of individual links.
2) Number
of links in connection.
Hence
fixed pair of transmit and receive filters will not serve the equalization
problem. The transmission characteristics keep on changing. Therefore adaptive
equalization is used.
11.
What are
the necessity of adaptive equalization?
Most of
the channels are made up of individual links in switched telephone network,the
distortion induced depends upon
1 )
transmission characteristics of individual links
2) number
of links in connection
12. Define the principle of adaptive equalization?
The
filters adapt themselves to the dispersive effects of the channel that is .the
.cofficients of the filters are changed contineously according to the received
data .The filter cofficients are changed in such a way that the distortion in
the data is reduced.
13. Define the term ISI?
Ans. The
presence of outputs due to other bits interference with the output of required
bit . This effect is called inter symbol interference (ISI).
14. Write the performance of data transmission
system using eye pattern technique?
The width
of the eye opening defines .the interval over which the received wave can can
be .sampled without error from inter symbol interference .
The
sensitivity of the system to timing error is determined by the rate of closure of
the eye as the sampling time is varied.
15.What is the necessity of equalization?
When the
signal is passed through the channel distortion is introduced in terms of 1)
amplitude 2) delay this distortion creates problem of ISI. The detection of the
signal also become difficult this distraction can be compensated with the help
of equalizer.
16.What is raised cosine spectrum?
In the
raised cosine spectrum, the frequency response P(f) decreases towards zero
gradually That is there is no abrupt transition.
17. What is nyquist Bandwidth?
The B.is
called nyquist bandwidth. .The nyquist bandwidth is the minimum transmission
bandwidth for zero ISI.
18.
Give two
applications for Eye pattern.
·
To determine an interval over which the received
wave van be sampled without error due ot ISI.
·
To determine the sensitivity of the system to
timing error
·
The margin over the noise is determined from eye
pattern
19.What are the information that can be obtained
from eye pattern regarding the signal quality?
·
To determine an interval over which the received
wave van be sampled without
·
error due ot ISI.
·
To determine the sensitivity of the system to
timing error
·
The margin over the noise is determined from eye
pattern
20. A 64 kbps binary PCM polar NRZ signal is passed
through a communication system with a raised-cosine filter with roll-off factor
0.25. Find the bandwidth of a filtered PCM signal.
Fb=64lpbs
B0=FB/2=32kpbs
α=0.25
B=B0(1+α)=30*103(1+0.25)=40kHz
BASEBAND TRANSMISSION
Line codes:
The line
code is said to be transparent if the synchronization between the transmitter
and receiver is maintained for any type of input data sequence.
Manchester code:
In
Manchester code each bit of data is signified by at least one transition.
Manchester encoding is therefore considered to be self-clocking, which means
that accurate clock recovery from a data stream is possible. In addition, the
DC component of the encoded signal is zero. Although transitions allow the
signal to be self-clocking, it carries significant overhead as there is a need
for essentially twice the bandwidth of a simple NRZ or NRZI encoding
Properties of line code:
The PAM
signal should have adequate timing content,
The PAM
signal should immune to channel noise and interference
The PAM
signal should allow error detection and error correction
The PAM
signal should be transparent to digital data being transmitted.
Intersymbol interference:
In
baseband binary PAM, symbols are transmitted one after another. These symbols
are separated by sufficient time durations. The transmitter, channel and
receiver acts as a filter to this baseband data. Because of the filtering
characteristics, transmitted PAM pulses are spread in time.
correlative coding:
Correlative
level coding is used to transmit a baseband signal with the signalling rate of
2Bo over the channel of bandwidth Bo. This is made physically possible by
allowing ISI in the transmitted in controlled manner. This ISI is known to
receiver. .The .correlative .coding .is .implemented .by .duobinary .signalling
.and modified duobinary signalling.
Duobinary baseband PAM system
Duobinary
encoding reduces the maximum frequency of the baseband signal. The word „duo‟
means to double the transmission capacity of the binary system. Let the PAM
signal ak represents kth bit. Then the encoder the new waveform as Ck =ak
+ ak-1
Thus two
successive bits are added to get encoded value of the kth bit. Hence Ck becomes
a correlated signal even though ak is
not correlated. This introduces intersymbol interference in the controlled manner
to reduce the bandwidth.
Eye pattern:
Eye
pattern is used to study the effect of ISI in baseband transmission. 1) Width
of .eye .opening defines the .interval over .which the .received
wave can
be sampled without error from ISI.
2.) The
sensitivity of the system to timing error is determined by the rate of closure
of the eye as the sampling time is varied.
3) Height
of the eye opening at sampling time is called margin over noise.
Eye
pattern can be obtained on CRO by applying the signal to one of the input
channels and given an external trigger of 1/Tb Hz. This makes one sweep of beam equal to Tb seconds.
Adaptive equalization:
In
switched telephone network the distortion depends upon
1) Transmission
characteristics of individual links.
2) Number of
links in connection.
Hence
fixed pair of transmit and receive filters will not serve the equalization
problem. The transmission characteristics keep on changing. Therefore adaptive
equalization is used.
Most of
the channels are made up of individual links in switched telephone network,the
distortion induced depends upon 1 ) transmission characteristics of individual
links.2) number of links in connection
Principles of adaptive equalization:
The
filters adapt themselves to the dispersive effects of the channel that is .the
.cofficients of the filters are changed contineously according to the received
data .The filter cofficients are changed in such a way that the distortion in
the data is reduced.
ISI:
The
presence of outputs due to other bits interference with the output of required
bit . This effect is called inter symbol interference (ISI).
The width
of the eye opening defines .the interval over which the received wave can can
be .sampled without error from inter symbol interference .
The
sensitivity of the system to timing error is determined by the rate of closure
of the
eye as the sampling time is varied.
Equalization:
When the
signal is passed through the channel distortion is introduced in terms of 1)
amplitude 2) delay this distortion creates problem of ISI. The detection of the
signal also become difficult this distraction can be compensated with the help
of equalizer.
Raised cosine spectrum:
In the
raised cosine spectrum, the frequency response P(f) decreases towards zero
gradually That is there is no abrupt transition.
Nyquist Bandwidth:
The B.is
called nyquist bandwidth. .The nyquist bandwidth is the minimum transmission
bandwidth for zero ISI.
Applications for Eye pattern.
·
To determine an interval over which the received
wave van be sampled without error due ot ISI.
·
To determine the sensitivity of the system to
timing error
·
The margin over the noise is determined from eye
pattern.
Related Topics