Chapter: Digital Communication : Baseband Transmission
Equalising Filter
EQUALISING FILTER
Adaptive equalization
• An equalizer is a filter that compensates for the dispersion effects of a channel. Adaptive equalizer can adjust its coefficients continuously during the transmission of data.
Pre channel equalization
· requires feed back channel
· causes burden on transmission.
Post channel equalization
Achieved prior to data transmission by training the filter with the guidance of a training sequence transmitted through the channel so as to adjust the filter parameters to optimum values.
Adaptive equalization
It consists of tapped delay line filter with set of delay elements, set of adjustable multipliers connected to the delay line taps and a summer for adding multiplier outputs.
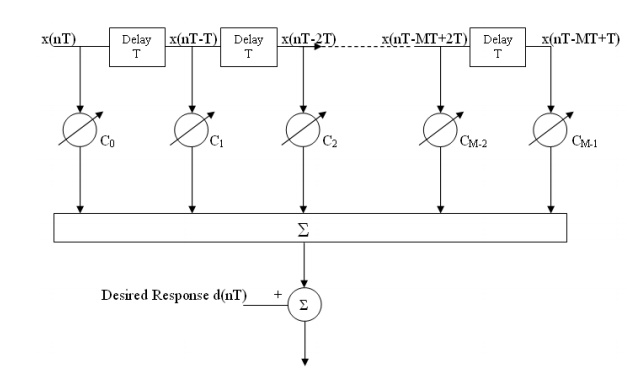
The output of the Adaptive equalizer is given by
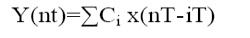
Ci is weight of the ith tap Total number of taps are M .Tap spacing is equal to symbol duration T of transmitted signal In a conventional FIR filter the tap weights are constant and particular designed response is obtained. In the adaptive equaliser the Ci's are variable and are adjusted by an algorithm.
Two modes of operation
1. Training mode
2. Decision directed mode
Mechanism of adaptation
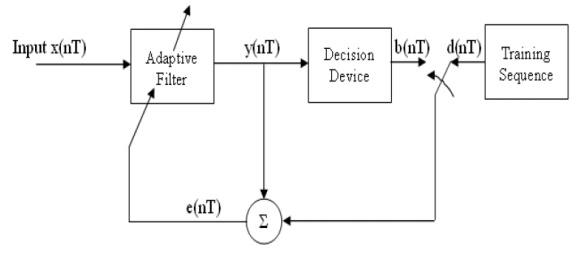
Training mode
A known sequence d(nT) is transmitted and synchronized version of it is generated in the receiver applied to adaptive equalizer. This training sequence has maximal length PN Sequence, because it has large average power and large SNR, resulting response sequence (Impulse) is observed by measuring the filter outputs at the sampling instants. The difference between resulting response y(nT) and desired response d(nT)is error signal which is used to estimate the direction in which the coefficients of filter are to be optimized using algorithms.
Related Topics