Chapter: Physics : Dielectric Materials
Important Questions and Answers: Dielectric Materials
DIELECTRIC MATERIALS
1.
Define dielectric constant?
It is the ratio between
the absolute permittivity of the medium (ε)and the permittivity of free space
(ε0).
Dielectric constant εr = Absolute permittivity (ε) /
Permittivity of free space (ε0)
2. Define polarization of a dielectric
material.
The process of the
producing electrical dipoles inside the dielectric by the application an external
electrical field is called polarization in dielectrics.
Induced dipole moment
(µ) = αE E →Applied electrical field
α → Polarizability
3. Name
the four polarisation mechanisms. i. Electronic
polarisation.
ii.
Ionic polarisation.
iii.
Orientational polarisation.
iv.
Space- charge polarisation.
v.
4. What
is electronic polarisation?
Electronic polarisation means production
of electric dipoles by the applied electric field .It is due to shifting of
charges in the material by the applied electric field.
5. What is ionic polarisation?
Ionic polarisation is
due to the displacement of cations (negative ions) and anions (positive ions)
in opposite direction due to the application of an electrical field. This
occurs in an ionic solid.
6. What is orientation polarisation?
When an electrical
field is applied on the dielectric medium with polar molecules, the dipole
align themselves in the field direction and thereby increases electric dipole
moment.
Such a type of
contribution to polarisation due to the orientation of permanent dipoles by the
applied field is called orientation polarisation.
7. What is space- charge polarisation?
In some materials
containing two or more phases, the application of an electrical field causes
the accumulation of charges at the interfaces between the phases or at the
electrodes.
As
result of this, polarisation is produced. This type of polarisation is known as
space
charge polarisation.
8. Define dielectric loss and loss
tangent.
When a dielectric
material is subjected to an A.C voltage, the electrical energy is absorbed by
the material and is dissipated in the form of heat. This dissipation of energy
is called
dielectric loss.
In a perfect insulator,
polarisation is complete during each cycle and there is no consumption of energy
and the charging current leads the applied voltage by 900. But for
commercial dielectric,
this phase angle is less than 900 by an angle and is called
dielectric loss angle. Tan is taken as measure of dielectric loss and is known
as loss tangent.
9. Define dielectric breakdown and
dielectric strength.
Whenever the electrical
field strength applied to a dielectric exceeds a critical value, very large
current flows through it. The dielectric loses its insulating property and
becomes conducting. This phenomenon is known as dielectric breakdown.
The
electrical field strength at which dielectric breakdown occurs is known as
dielectric
Strength.
10.
Mention the various breakdown
mechanisms.
i)
Intrinsic breakdown and avalanche
breakdown
ii)
Thermal breakdown
iii)
Chemical and Electrochemical breakdown
iv)
Discharge break down
v)
Defect breakdown
11.
What is intrinsic breakdown?
For a dielectric, the
charge displacement increases with increasing electrical field strength. Beyond
a critical value of electrical field strength, there is an electrical breakdown
due to physical deterioration in the dielectric material.
12. What is thermal breakdown?
When an electrical
field is applied to a dielectric material, some amount of hear is produced.
This heat must be dissipated from the material.
In some cases, the
amount of hear produced is very large as compared to the heat dissipated. Due
to excess of heat the temperature inside the dielectric increases and may
produce local melting in the dielectric material.
During this process, a
large amount of current flows through the material and causes their dielectric
to breakdown. This type of breakdown is known as thermal breakdown.
13. What is chemical and electrochemical
breakdown?
Electro chemical
breakdown is similar to thermal breakdown. When the temperature of a dielectric
material increases, mobility of ions increases and hence the electrochemical
reaction may take place.
This leads to leakage
current and energy loss in the material and finally dielectric breakdown occurs.
14.
What is discharge break down?
Discharge breakdown
occurs when a dielectric contains occluded gas bubbles. When this type of
dielectric is subjected to electric field; the gases present in the material
will easily ionize and thus produces large ionization current.
The gaseous ions bombard the solid dielectric. This
causes electrical deterioration and leads to dielectric breakdown.
15. What is defect breakdown?
The surface of the
dielectric material may have defects such as cracks, porosity and blowholes.
Impurities like dust or moisture may collect at these discontinuities
(defects). This will lead to a breakdown in a dielectric material.
16. What are requirements of good
insulating materials?
The good insulating materials should have
i)
High electrical resistivity to reduce
leakage current.
ii)
High dielectrical strength to with stand
higher voltage.
iii)
Smaller dielectric loss
iv)
Sufficient mechanical strength.
17 Compare active and
passive dielectrics.
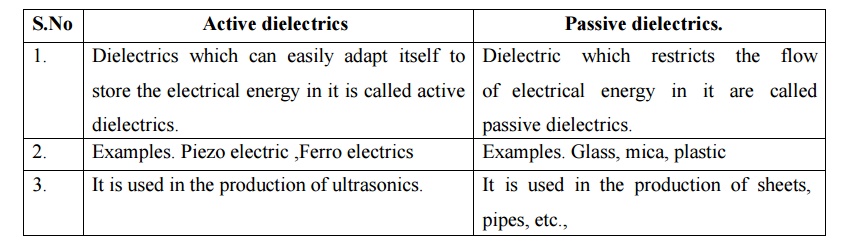
S.No Active dielectrics
1. Dielectrics
which can easily adapt itself to store the electrical energy in it is called
active dielectrics.
2. Examples.
Piezo electric ,Ferro electrics
3. It is used
in the production of ultrasonics.
Passive dielectrics.
Dielectric
which restricts the flow of electrical energy in it are called passive
dielectrics.
Examples.
Glass, mica, plastic
It is used in
the production of sheets, pipes, etc.,
18.
What are ferro-electric materials? Give examples.
Materials which exhibit electronic
polarization even in the absence of the applied electrical field are known as
ferro-electric materials.
Example.
Barium
Titanate (BaTiO3)
Potassium
Dihydrogen Phosphate (KH2PO4)
17.
What are the differences between
polar and non-polar molecules?
Ppppppppp
S.No Polar molecule
1.
These molecules have permanent dipole moments even in the absence of an applied
field.
2.
The polarization of polar molecules is highly temperature dependent.
3. These molecules do not have symmetrical
structure and they do not have centre of
symmetry.
4.
For this kind of molecules, there is absorption or emission in the infrared
range.
5.
Examples: CHCl3,HCl
Non-polar molecules
1.
These molecules do not have permanent dipole moments
2.
The polarization of polar molecules is temperature independent.
3.
These molecules have symmetrical structure and they have centre of symmetry.
4.
For these molecules, there is no absorption or emission in the infrared range.
5.
Examples: CCl4, CO2
20.
What is meant by pyro-electricity?
It
means that, the creation of electronic polarization by thermal stress.
Related Topics