Chapter: Physics : Dielectric Materials
Important Short Questions and Answers: Dielectric Materials
SHORT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
1.What is a dielectric material? State their
property.
Dielectrics are the insulating materials having
electric dipole moment permanently or temporarily by applying the electric
field. These are mainly used to store electrical energy and used as electrical
insulators. All dielectrics are electrical insulators. But all electrical
insulators need not to be dielectrics. Dielectrics are non-metallic materials of
high specific resistance and have negative temperature coefficient of
resistance.
2.Define electric flux density (D) or Electric
Displacement Vector.
The number of electric lines passing through
the unit area of cross section.
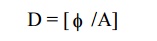
Unit: Coulomb / m²
3.Define Permittivity
It is the ratio of electric displacement vector in a dielectric medium to the applied electric field strength. ε= D / E
4.Define Dielectric constant or Relative
Permittivity
It is
the ratio of permittivity of the medium to the permittivity of the free space.
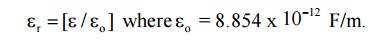
5. Define Dipole moment
Dipole
moment is defined as the product of charge and distance.
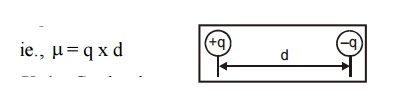
Unit : Coulomb meter.
6.Define Polarization, Polarization vector and
Polarisability
Polarization
The separation
of negative and positive charges is called polarization. i.e., the process of
producing electric dipoles by an electric field is called polarization.

Polarization
vector
If is
the average dipole moment per molecule and N is the number of molecules per
unit volume then the polarization of the solid is given by the polarization
vector P and it can be written as

The
polarization vector is the dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric
material.
Polarisability
The
polarization depends on electric field.
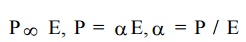
the
proportionality constant is called as polarisability.
7. Define Electronic
Polarization.
Electronic
polarization occurs due to the displacement of positively charged nucleus and
negatively charged electron in opposite directions by an external electric
field. It creates a dipole moment in the dielectric. This is called electronic
polarization.
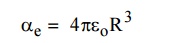
8.What is ionic polarization.
The
displacement of cations (+ve) and anions (-ve) in opposite directions is called
ionic polarization. It occurs in ionic solids in the presence of electric field
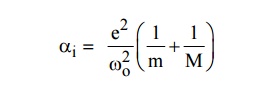
9.
Define orientation polarization.
When an
electric field is applied on the dielectric medium with polar molecules, the
electric field tries to align these dipoles along its field direction, due to
that there is a resultant dipole moment in that material and this process is
called orientation polarization.
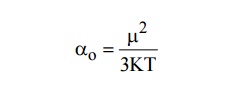
10. What is Space charge polarization?
The
space charge polarization occurs due to the diffusion of ions along the field
direction giving rise to redistribution of charge in the dielectrics. Normally
this type of polarization occurs in ferrites and semiconductors and it is very
small when compared to other types of polarization.
11.What are polar and non-polar molecules?
Molecules
which are having permanent dipole moment even in the absence of an applied
field are called polar molecules. Example: H2 O, HC, CO.
Molecules
which do not have permanent dipole moment, but they have induced dipole moment
in the presence of applied electric field are called non - polar molecules.
Example:
O2 , H2 ,
N2
12. Define Local or internal or Lorentz field.
In a dielectric material, the field acting at
the location of an atom is called local field or internal field [ Ei
]
The internal field E must be equal to the sum
of applied field and the field due to location of the atom by the dipoles of
all other atoms
ie, Ei = E + The field due to all
other dipoles.
13. Define Dielectric Loss and Dielectric
breakdown.
When a
dielectric material is subjected to an alternating electric field, some amount
of energy is absorbed by the material and is dissipated in the form heat. This
loss of energy is called Dielectric loss.
When a
dielectric material loses its property and permids the flow of a large current,
it is said to be dielectric breakdown.
14.What is optical absorption and infrared
absorption in a dielectric?
The
dielectric losses in the optical region, associated with the electrons are
referred to as optical absorption. This absorption leads to color of materials.
The dielectric losses in the infra-red region, associated with the ionic
vibrations are referred to as Infrared absorption.
15. Define Dielectric breakdown and what are its
types?
When a dielectric material loses its property
and permits the flow of a large current, it is known a dielectric breakdown.
Types
Intrinsic
breakdown.
Thermal
breakdown.
Electrochemical
breakdown.
Defect
breakdown.
Discharge
breakdown.
16. What are Ferro electric materials?
Materials which exhibit electric polarization
even in the absence of electric field are known as Ferro electric materials.
Crystalline dielectric materials which posses a
permanent electric polarization are called ferroelectric materials have
electric dipole moment even in the absence of any field. Normally they are
anisotropic crystals which exhibit spontaneous polarization.
Examples : Parium Titanate [Ba TiO3 ],
Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate [K H2 P O4 ],
Lithium Niobate [LiNb O3 ] and Rochelle salt.
17. What are the differences between polar and
non - polar molecules?
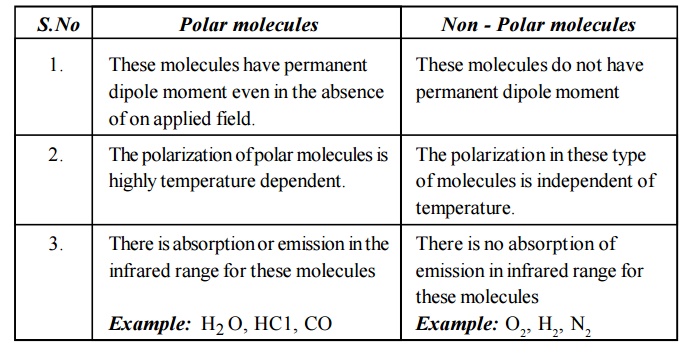
Polar
molecules
These
molecules have permanent dipole moment even in the absence of on applied field.
The
polarization of polar molecules is highly temperature dependent.
There is
absorption or emission in the infrared range for these molecules
Example:
H2 O, HC1, CO
Non - Polar molecules
These
molecules do not have permanent dipole moment
The
polarization in these type of molecules is independent of temperature.
There is
no absorption of emission in infrared range for these molecules
Example:
O2, H2, N2
18. Compare active and passion dielectrics.
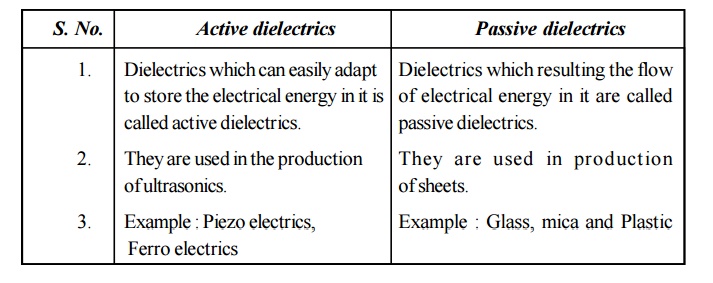
Active dielectrics
Dielectrics
which can easily adapt to store the electrical energy in it is called active
dielectrics.
They are
used in the production of ultrasonics.
Example
: Piezo electrics, Ferro electrics
Passive dielectrics
Dielectrics
which resulting the flow of electrical energy in it are called passive
dielectrics.
They are
used in production of sheets.
Example
: Glass, mica and Plastic
19. What are the applications of ferroelectric
materials?
Ferroelectric
materials are used to make pressure transducers, ultrasonic transducers,
microphones and gas filters.
They are
used as memory cores in computers.
They are
used to measure and control temperature.
Ferroelectric
ceramics are used as capacitors to store electrical energy
They are
used to make very good infrared detectors.
Rochelle
salt is used in devices like microphones, strain gauges, phonograph pickups and
SONAR devices.
In
optical communication, the ferroelectric crystals are used for optical
modulation.
Ferro
electric materials are used to produce ultrasonics
Electrets
are also used to bond the fractured bones in human body.
They are
used as frequency stabilizers and crystal controlled oscillators.
Related Topics