Chapter: Business Science : Human Resource Management : The Concept of Best FIT Employee
Importance of Human resource planning
Importance of Human resource
planning
1
Definition of HRP
2
Nature of Human resource planning
3
Importance of Human resource planning
4
HRP Process
5
Requisites for successful HRP
6
Barriers to HRP
1 Concept of Human resource planning:
Human resource planning is important for helping both
organizations and employees to prepare for the future. The basic goal of human
resource planning is to predict the future and based on these predictions,
implement programmes to avoid anticipated problems. Very briefly humans
resource planning is the process of examining an organization‘s or individual‘s
future human resource needs for instance, what types of skills will be needed
for jobs of the future compared to future human resource capabilities (such as
the types of skilled employees you already have) and developing human resource
policies and practices to address potential problems for example, implementing
training programmes to avoid skill deficiencies.
1 Definition
of HRP:
According to Vetter, ―HRP is
the process by which management determines how the organization should move from its current man power
position to desired manpower position. Through planning, management strives to
have the right time, doing things which result in both the organization and
individual receiving maximum long run benefits‖.
According to Gordon Mc Beath, ―HRP is
concerned with two things: Planning of manpower requirements and Planning of Manpower supplies‖.
According to Beach, ―HRP is a
process of determining and assuming that the organization will have an adequate number of qualified persons,
available at proper times, performing jobs which meet the needs of the
enterprise and which provides satisfaction for the individuals involved‖
HRP is a Four-Phased Process.
The first
phase involves the gathering and analysis of data through manpower inventories
and forecasts,
The
second phase consists of establishing manpower objectives and
policies and gaining top management
approval of these.
The third
phase involves designing and implementing plans and promotions to enable the organization to achieve its manpower
objectives.
The
fourth phase is concerned with control and evaluation of
manpower plans to facilitate progress in
order to benefit both the organization and the individual. The long run view
means that gains may be sacrificed in the short run for the future grounds. The
planning process enables the organization to identify what its manpower needs
is and what potential manpower problems required current action. This leads to
more effective and efficient performance.
2 Nature of Human resource planning:
It is the process of analyzing and identifying the
availability and the need for human resources so that the organization can meet
its objectives. The focus of HR planning is to ensure that the organization has
the right number of human resources, with the right capabilities, at the right
times, and in the right places. In HR planning, an organization must consider
the availability and allocation of people to jobs
over long
periods of time, not just for the next month or the next year1.
HRP is a
sub system in the total organizational planning. Actions may include shifting
employees to other jobs in the organization, laying off employees or otherwise
cutting back the number of employees, developing present employees, and/or
increasing the number of employees in certain areas. Factors to consider
include the current employees‘ knowledge, skills, and abilities and the
expected vacancies resulting from retirements, promotions, transfers, and
discharges. To do this, HR planning requires efforts by HR professionals
working with executives and managers.
3 Objectives of Human Resource Planning:
1.
To ensure optimum utilization of human resources
currently available in the organization.
2.
To assess or forecast the future skill requirement
of the Organization.
3.
To provide control measures to ensure that
necessary resources are available as and when required.
4.
A series of specified reasons are there that
attaches importance to manpower planning and forecasting exercises. They are
elaborated below:
To link
manpower planning with the organizational planning
To
determine recruitment levels.
To
anticipate redundancies.
To
determine optimum training levels.
To
provide a basis for management development programs.
To cost
the manpower.
To assist
productivity bargaining.
To assess
future accommodation requirement.
To study
the cost of overheads and value of service functions.
To decide
whether certain activity needs to be subcontracted, etc.
HRP is
the subsystem in the total organizational planning. Organizational planning
includes managerial activities that set the company‘s objective for the future
and determines the appropriate means for achieving those objectives. The importance of HR is elaborated on the
basis of the key roles that it is playing in the organization.
1.
Future
Personnel Needs: Human resource planning is significant because it
helps to determine the future
personnel needs of the organization. If an organization is facing the problem
of either surplus or deficiency in staff strength, then it is the result of the
absence of effecting HR planning. All public sector enterprises find themselves
overstaffed now as they never had any planning for personnel requirement and
went of recruitment spree till late 1980‘s. The problem of excess staff has
become such a prominent problem that many private sector units are resorting to
VRS ‗voluntary retirement scheme‘. The excess of labor problem would have been
there if the organization had good HRP system. Effective HRP system will also
enable the organization to have good succession planning.
Part of Strategic Planning: HRP has
become an integral part of strategic planning of strategic planning. HRP provides inputs in strategy formulation process in
terms of deciding whether the organization has got the right kind of human
resources to carry out the given strategy. HRP is also necessary during the
implementation stage in the form of deciding to make resource allocation
decisions related to organization structure, process and human resources. In
some organizations HRP play as significant role as strategic planning and HR
issues are perceived as inherent in business management.
3.
Creating
Highly Talented Personnel: Even though India has a great pool of educated unemployed, it is the discretion of HR
manager that will enable the company to recruit the right person with right
skills to the organization. Even the existing staff hope the job so frequently
that organization face frequent shortage of manpower. Manpower planning in the
form of skill development is required to help the organization in dealing with
this problem of skilled manpower shortage
4.
International
Strategies: An international expansion strategy of an
organization is facilitated to a
great extent by HR planning. The HR department‘s ability to fill key jobs with
foreign nationals and reassignment of employees from within or across national
borders is a major challenge that is being faced by international business.
With the growing trend towards global operation, the need for HRP will as well
will be the need to integrate HRP more closely with the organizations strategic
plans. Without effective HRP and subsequent attention to employee recruitment,
selection, placement, development, and career planning, the growing competition
for foreign executives may lead to expensive and strategically descriptive
turnover among key decision makers.
5.
Foundation
for Personnel Functions: HRP provides essential information for designing
and implementing personnel
functions, such as recruitment, selection, training and development, personnel
movement like transfers, promotions and layoffs.
6.
Increasing
Investments in Human Resources: Organizations are making
increasing investments in human
resource development compelling the increased need for HRP. Organizations are
realizing that human assets can increase in value more than the physical
assets. An employee who gradually develops his/ her skills and abilities become
a valuable asset for the organization. Organizations can make investments in
its personnel either through direct training or job assignment and the rupee
value of such a trained, flexible, motivated productive workforce is difficult
to determine. Top officials have started acknowledging that quality of work
force is responsible for both short term and long term performance of the
organization.
7.
Resistance
to Change: Employees are always reluctant whenever they hear
about change and even about job
rotation. Organizations cannot shift one employee from one department to
another without any specific planning. Even for carrying out job rotation
(shifting one employee from one department to another) there is a need to plan
well ahead and match the skills required and existing skills of the employees.
8.
Uniting
the Viewpoint of Line and Staff Managers: HRP helps to unite the viewpoints of line and staff managers. Though HRP
is initiated and executed by the corporate staff, it requires the input and
cooperation of all managers within an organization. Each department manager
knows about the issues faced by his department more than anyone else. So
communication between HR staff and line managers is essential for the success
of HR Planning and development.
9.Succession Planning: Human
Resource Planning prepares people for future challenges. The ‘stars‘ are picked up, trained,
assessed and assisted continuously so that when the time comes such trained
employees can quickly take the responsibilities and position of their boss or
seniors as and when situation arrives.
10.Other
Benefits: (a) HRP helps in judging the effectiveness of manpower policies and programmes of management. (b) It
develops awareness on effective utilization of human resources for the overall
development of organization. (c) It facilitates selection and training of
employees with adequate knowledge, experience and aptitudes so as to carry on
and achieve the organizational objectives (d) HRP encourages the company to
review and modify its human resource policies and practices and to examine the
way of utilizing the human resources for better utilization.
4 HRP Process:
HRP
effectively involves forecasting personnel needs, assessing personnel supply
and matching demand – supply factors through personnel related programmes. The
HR planning process is influenced by overall organizational objectives and
environment of business.
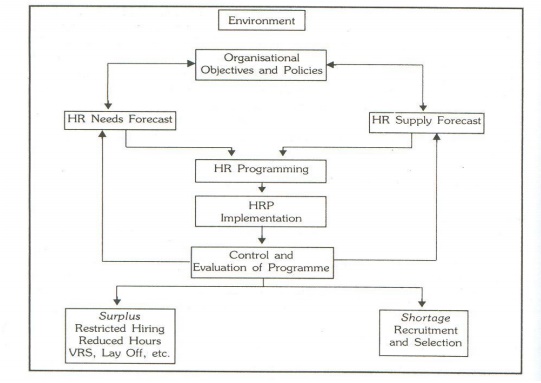
The HRP Process
Environmental Scanning:
It refers
to the systematic monitoring of the external forces influencing the
organization. The following forces are essential for pertinent HRP.
Economic
factors, including general and regional conditions. Technological changes
Demographic
changes including age, composition and literacy,
Political
and legislative issues, including laws and administrative rulings Social
concerns, including child care, educational facilities and priorities.
By
scanning the environment for changes that will affect an organization, managers
can anticipate their impact and make adjustments early.
Organizational Objectives and
Policies: HR plan is usually derived from the organizational objectives. Specific requirements in terms of
number and characteristics of employees should be derived from organizational
objectives
Once the
organizational objectives are specified, communicated and understood by all
concerned, the HR department must specify its objective with regard to HR
utilization in the organization.
HR Demand Forecast:
Demand
forecasting is the process of estimating the future quantity and quality of
people required to meet the future needs of the organization. Annual budget and
long-term corporate plan when translated into activity into activity form the
basis for HR forecast.
For eg:
in the case of a manufacturing company, the sales budget will form the basis for
production plan giving the number and type of products to be produced in each
period. This will form the basis uponwhich the organization will decide the
number of hours to be worked by each skilled category of workers. Once the
number hours required is available organization can determine the quality and
quantity of personnel required for the task.
Demand
forecasting is influenced by both internal factors and external factors:
external factors include-competition, economic climate, laws and regulatory
bodies, changes in technology and social factors whereas internal factors are
budget constraints, production level, new products and services, organizational
structure and employee separations.
Demand
forecasting is essential because it helps the organization to 1. Quantify the
jobs, necessary for producing a given number of goods, 2. To determine the
nature of staff mix required in the future, 3. To assess appropriate levels in
different parts of organization so as to avoid unnecessary costs to theorganization,
4. To prevent shortages of personnel where and when, they are needed by the
organization. 5. To monitor compliances with legal requirements with regard to
reservation of jobs.
Techniques
like managerial judgment, ratio- trend analysis, regression analysis, work
study techniques, Delphi techniques are some of the major methods used by the
organization for demand forecasting.
HR Supply Forecast:
Supply
forecast determines whether the HR department will be able to procure the
required number of workers. Supply forecast measures the number of people
likely to be available from within and outside an organization, after making
allowance for absenteeism, internal movements and promotions, wastage and
changes in hours, and other conditions of work.
Supply
forecast is required because it is needed as it 1. Helps to quantify the number
of people and positions expected to be available in future to help the
organization realize its plans and meet its objectives 2. Helps to clarify the
staff mixes that will arise in future 3. It assesses existing staffing in
different parts of the organization. 4. It will enable the organization to
prevent shortage of people where and when they are most needed. 5. It also
helps to monitor future compliance with legal requirements of job reservations.
Supply
analysis covers the existing human resources, internal sources of supply and
external sources of supply.
HR Programming:
Once an organization‘s personnel demand and supply
are forecasted the demand and supply need to be balanced in order that the
vacancies can be filled by the right employees at the right time.
HR Plan Implementation:
HR
implementation requires converting an HR plan into action. A series of action
are initiated as a part of HR plan implementation. Programmes such as
recruitment, selection and placement, training and development, retraining and
redeployment, retention plan, succession plan etc when clubbed together form
the implementation part of the HR plan.
Control and Evaluation:
Control
and evaluation represent the final phase of the HRP process. All HR plan
include budgets, targets and standards. The achievement of the organization
will be evaluated and monitored against the plan. During this final phase
organization will be evaluating on the number of people employed against the
established (both those who are in the post and those who are in pipe line) and
on the number recruited against the recruitment targets. Evaluation is also
done with respect to employment cost against the budget and wastage accrued so
that corrective action can be taken in future.
5 Requisites for Successful HRP
1.
HRP must be recognized as an integral part of
corporate planning
2.
Support of top management is essential
3.
There should be some centralization with respect to
HRP responsibilities in order to have co-ordination between different levels of
management.
4.
Organization records must be complete, up to date
and readily available.
5.
Techniques used for HR planning should be those
best suited to the data available and degree of accuracy required.
6.
Data collection, analysis, techniques of planning
and the plan themselves need to be constantly revised and improved in the light
of experience.
6 Barriers to HRP
Human Resource Planners face significant barriers while
formulating an HRP. The major barriers are elaborated below:
1)
HR practitioners are perceived as
experts in handling personnel matters, but are not experts in managing
business. The personnel plan conceived and formulated by the HR practitioners
when enmeshed with organizational plan, might make the overall strategic plan
of the organization ineffective.
2)
HR information often is incompatible
with other information used in strategy formulation. Strategic planning efforts
have long been oriented towards financial forecasting, often to the exclusion
of other types of information. Financial forecasting takes precedence over HRP.
4)
Conflict may exist between short term
and long term HR needs. For example, there can be a conflict between the
pressure to get the work done on time and long term needs, such as preparing
people for assuming greater responsibilities. Many managers are of the belief
that HR needs can be met immediately because skills are available on the market
as long as wages and salaries are competitive. Therefore, long times plans are
not required, short planning are only needed.
5)
There is conflict between
quantitative and qualitative approaches to HRP. Some people view HRP as a
number game designed to track the flow of people across the department. Others
take a qualitative approach and focus on individual employee concerns such as
promotion and career development. Best result can be achieved if there is a
balance between the quantitative and qualitative approaches.
6)
Non-involvement of operating managers
renders HRP ineffective. HRP is not strictly an HR department function.
Successful planning needs a co-ordinated effort on the part of operating
managers and HR personnel.
Related Topics