Meaning, Objectives, Procedure, Intermediaries - Import Trade | 11th Commerce : Chapter 26 : Export and Import Procedures
Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 26 : Export and Import Procedures
Import Trade
Import Trade
Meaning
Import trade refers to purchasing goods
and service from a foreign country. For Example Purchase of chemicals by an
Indian company from France is termed as import. Domestic purchaser of goods is
termed as importer and overseas seller is called exporter.
Objectives of Import Trade
Objectives of import trade have been
highlighted hereunder.
1. Achieving Rapid Industrialization
Developing countries can achieve rapid
industrialisation by importing advanced technology scarce raw materials,
capital goods like machinery equipment, etc., and talents from other countries.
2. Meeting Consumer Demand
Certain goods are either
not available or cannot be
manufactured / produced adequately to meet the growing demand in home country.
Hence import is necessary to meet the short supply of those goods.
3. Upgrading Standard of Living of the People
Consumers are able to use a wide variety
of goods like cell phone, car laptop. television audio system, washing machine,
perfume, soaps, etc., manufactured in foreign countries and enhance their
standard of living through import trade.
4. Meeting Shortage Situation
During famine, earthquake, flood
draught, tsunami, abnormal price-increase situations and so on food grains,
vegetables and other essential
commodities are imported from foreign countries and bad situation arising from
the above situations are thus overcome.
5. Strengthening Defence
Many countries around the world import
defence equipments for its armed force. Such imports enable the country to
ensure its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
Import Procedure
Import procedure varies from country to
country depending upon the foreign trade policy of a country. Government of
India has framed rules and regulations for the import. The import procedures
has been clearly spelt out of Government of India. Following are the procedures
of import trade.
1. Obtaining Import License
Importer has to secure Import and Export
Code (IEC) from the Director General of Foreign Trade or its Regional
Authority. The Indian Institute classification (ITC)–Harmonized System
(HS) classified the goods into three categories, namely
Restricted, Canalised and Prohibited. Goods not specified in the above
categories can be freely imported without any restrictions. Import license is
not required to import the goods not mentioned in the above
classification. An import license is valid for 24 months for capital goods and
18 months for other goods.

Importer has to submit the copy of IEC
to customs authorities at the time of clearance of goods. The second copy of
IEC is used to obtain foreign exchange from RBI.
2. Trade Enquiry
Having obtained IEC, the intending
importer has to make enquiry from exporter or his agents. Importer makes
request by e-mail or postal mail to supply the details given below.
a.
Specification of goods like size,
design, quality etc.,
b.
Quantity goods available
c.
Price per unit
d.
Terms of shipping
e.
Terms of payments i.e. Letter of credit
Documents against Acceptance (D/A)or Documents against Payment (D/P)
f.
Probable delivery time
g.
Validity of offer period
Importer responds to enquiry by sending proforma
invoice
3. Obtaining Foreign Exchange
Since importer has to settle import
bills in foreign currency, he has to obtain foreign exchange. Importer has to
provide IEC code in the form supplied by authorized dealer to get foreign
exchange.. The importer has to submit an application along with necessary
documents to the Exchange Control Department of RBI. After scrutinising the
said application, the Reserve Bank of India will sanction the release of
foreign exchange.
4. Placing an Indent Order
Importer places an order
either directly or through an indent houses. The indent
contains the details like type of goods, design of goods, price, quantity,
grade, packing instructions, insurance, delivery mode, desired delivery period,
mode of period, mode of shipment, etc.,
5. Opening Letter of Credit(L/C)
Where foreign exporter does not know
Indian importer, he may like to ensure the creditworthiness of the unknown
importer. In such a case, exporter may advise the importer to arrange for
letter of credit in his favour..Letter of credit is a document under which
issuing bank undertakes to make payment on behalf of the importer or to the
order of importer in exchange for specified documents from exporters bank. The
letter of credit is issued only for financially sound importer. Exporter’s bank
eventually sends the document to issuing bank which releases the payment.
6. Receiving Shipping Document
The importer collects shipping documents
along with the advice note of
shipment of goods from the exporters.
Advice note contains a written message through which exporter informs the
importer about the dispatch of goods and advise him to make agreement for
taking delivery of goods on arrival of goods at the port of destination. The
captain of the ship informs the dock authorities about the arrival of goods on
a document called Import General Manifest. The customs authorities in turn
inform the importer concerned about the arrival of goods at the port.
7. Appointment of Clearing Agents
There are lot of formalities involved in
clearing the goods imported from the port. Normally importer does not feel
comfortable with completing the formalities by himself. In this case he may
delegate the task of clearing the imported goods from the port of discharge to
clearing agent who is well-versed in this job. The latter performs the job for
a fee. The importer sends all the documents to the clearing agent to enable him
to take delivery of goods after fulfilling the customs formalities prescribed
in this regard.
8. Fulfillment of Customs Formalities
Clearing agent engaged by the importer
performs the following activities in connection with taking delivery of goods
from the port.
i.
Getting Endorsement for Delivery
The clearing agent gets bill of lading
endorsed by importer in his favour to enable him to take delivery of goods and
approaches the shipping company. Where the freight is not paid, the clearing
agent pays it. The shipping company may give a separate delivery order after
collecting the freight charges or it may simply endorse on the bill of lading
by the importer or by his agent itself as a proof payment of freight charges.
ii.
Payment of Dock Dues
The clearing agent submits two copies of
filled in Application form to “Landing and Shipping Dues Office. This office
levies charges on all the imported goods. The clearing agent has to pay Dock
charges by Dock challan. After paying dock charges ‘Landing and Shipping Due
Office stamps on the application form itself with wordings like Dock charges
paid’ or it may issue a separate receipt called Post Trust Dues Receipt.
iii.
Preparation of Bill of Entry
Bill of Entry is prepared in triplicate
in order to pay custom duty. This document contains the details like name and
address of importer, the name of the ship, full description of the goods,
number of packages, importer and exporter code (IEC) name of the exporting
country and custom duty payable. Bill of Entry is issued in three colours. The
black form is meant for non-dutiable goods while the blue form is meant for the
goods within the country and the violet is
intended for re-export. Import
duty is calculated on the basis of details given in the bill of entry by
customs authorities. Where the importer / clearing agent does not know
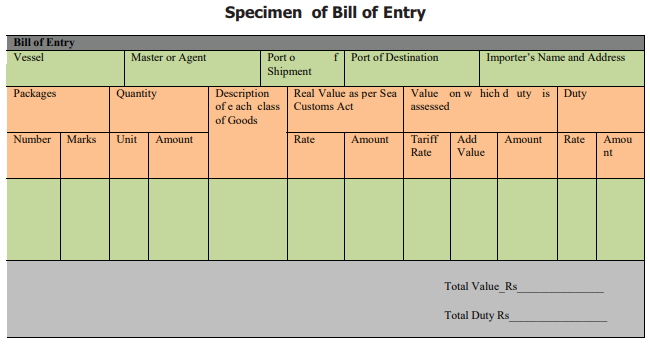
He would provide as much as details
possible about the goods imported to the extent of his memory and with specific
remark that he cannot give complete information about the goods imported. In
such a case , customs authorities will complete the statement and import duty
only after assessing the arrival of goods at the port of delivery.
iv.
Payment of Import Duty
The clearing agent / importer submits
the bill of entry and other required documents to the customs authorities. He
pays import duty in the case of dutiable goods to the customs authorities.
v.
Release Order From Dock
After payment of customs
duty, the bill of entry has to be marked by the dock.
Superintendent and an examiner are instructed to physically examine the goods.
He gives his report on the bill of entry. Then the bill is passed over to the
port authority. He would issue release order.
vi.
Getting Delivery From The Dock.
The clearing agent takes delivery of
goods from the dock after submitting the documents like, Port Trust Dues
Receipt, Bill of Entry and Bill of Lading. If the goods are imported for
re-export, the agent / importer will deposit them in a bonded warehouse and
receives Dock Warrant.
vii.
Dispatching Goods to the Importer
The agent despatches the goods to the
importer by the rail/ road. He gets Railway Receipt (R/R) or Lorry Receipt
(L/R) from the transporter.
viii.
Sending Advice to the Importer
Clearing agent informs the despatch of
goods to the importer and sends Railway Receipt / Lorry Receipt with the
statements of expenses incurred by him and the commission payable to him for
his service.
9. Taking Delivery of Goods
Importer takes delivery of goods
from the Railway /Carrier after
producing the Railway Receipt or Lorry Receipt.
10. Settlement of Import Bill
The importer settles the import bill in
the following ways.
a.
Importer collects shipping document
after payment
b.
Importer gets shipping documents after
payment of bills of exchange in the case of Documents against payments (D/P)
c.
Importer gets shipping documents after
giving acceptance on bills of exchange in the case of Documents against
Acceptance(D/A)
Documents
used in import trade
1.Import License (IEC)
2.Indent
3. Letter of Credit
Import
Documents
·
Import License
·
Indent
·
Letter of Credit
·
Bill of Entry
·
Bill of sight
·
Port Trust Dues Receipt
·
Bill Of Lading
·
Bill of Exchange
·
Advice Note
Intermediaries in Import Trade
1. Indent Houses/ Import Agent
This intermediary is specialized in a
particular trade. He charges fees for his service. Importer has to enter into
contract with indent house to avail himself of his service
Services
rendered by Indent Houses/ Import Agent
The services rendered include the
following
·
Helping the importer get orders from
foreign countries
·
Providing information about the
availability of goods of various types and arranging credit facilities to
importer
·
Maintaining regular contact with the
exporter and obtaining sample and transmitting it to the importer
2. Clearing Agent
Clearing Agent is specialised in
clearing the goods from the port of discharge destination and transport it over
to the importer. They fulfill the various custom formalities on behalf of the
importer and get the goods cleared from the port. They charge commission for
their service.
Related Topics