Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Ill Effects of Obesity and Underweight
ILL EFFECTS OF OBESITY
The impact of obesity on health are
Physical disability: Since the feet have to carry extra load complications like flat feet, osteoarthritis of knee, hip and
lumbar spine are common, Adipose tissues around chest and diaphragm interferes
with respiration and predisposes to bronchitis.
Metabolic disorders:
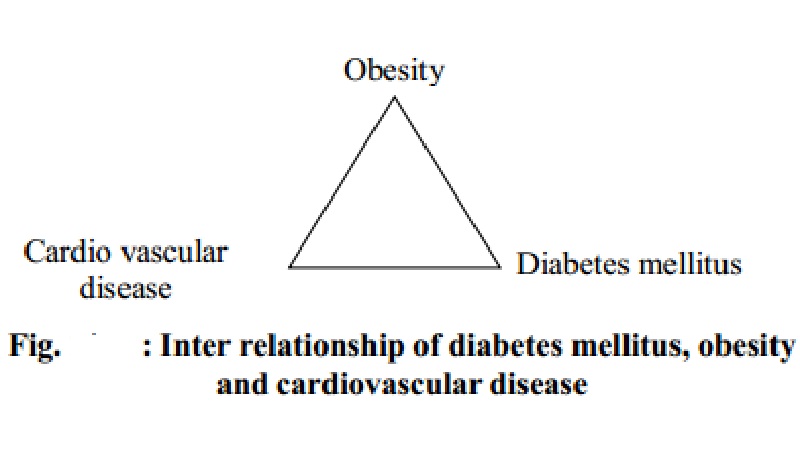
There is a close association between obesity, diabetes mellitus and
cardiovascular disease (fig. 11b). There is insulin resistance especially in
muscle.
Plasma cholesterol level is high and hence obese individuals are more
prone to develop gall stones.
Excess
cholesterol and triglycerides with low levels of HDL in plasma leads to
atherosclerosis
Obese people develop high blood pressure and there is an increased
incidence of varicose veins.
Obsterical risk: Obese women when pregnant have greater obsterical risks because of hypertension, diabetes mellitus and
post partum infection.
Cancer: Certain cancers (colon, rectum and prostrate in men, uterus, breast and ovary in women) are more prevalent in the
obese.
Psychological
Disturbances: Obese adolescents have personality characteristics of self blame, withdrawal and feeling
of inferiority.
UNDERWEIGHT
People
with BMI less than 18.5 are considered as under weight
Aetiology: Some
of the causes of underweight are
Starvation due to famine
Diet inadequate in proteins
Debilitating diseases like tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus
Malabsorption syndrome or cancer
Psychological factors as in anorexia nervosa seen in girls in the age
group 15 to 25 years
Pathological conditions such as fevers, gastro-intestinal disturbances
where the digestion and absorption capacities are decreased.
Dietary Modification
A high energy, high protein, high fat diet with liberal vitamin intake
is recommended. Before consuming such a diet the first step should be to
determine and eliminate the cause for under eating.
Energy: The calorie requirements vary depending upon the activity. An additional 500 kcals per day to the recommended
dietary allowances is recommended. The increase should be gradual over one or
two weeks to prevent digestive disturbances.
Proteins: Instead of 1g of protein, over 1.2 g per kg body weight is recommended for tissue building. Good quality protein
which is completely utilized by the body should be given.
Fats: Easily digestible fats are to be included. Excessive consumption of fried and fatty foods are not recommended as they
may cause diarrhoea. Further, fatty foods taken at the beginning of a meal also
reduces appetite. High calorie foods such as cream, butter, and oils increase
weight and can be included.
Carbohydrates: High carbohydrate sources must form the basis of the diet. Dried fruits, sweets, nuts, jams, desserts,
cereal and cereal products, potato chips and non vegetarian foods are a rich
source of energy and should be included in the diet. Apart from the three
meals, two feeds incorporating soups, juices or sweets in between main meals
improve the nutritive value of the diet.
Vitamins and minerals: There is no need for extra vitamin and mineral supplements when the dietary intake is liberal.
Fluids: Fluids
should not be taken before or with a meal, but only after a meal so that the food intake is not reduced.
Exercise: Regular outdoor exercise (light/moderate activity) should be performed as it helps to stimulate
appetite and thereby increases foodintake.
Related Topics