Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Patients With Hypertension
Hypertension Defined
Hypertension Defined
Hypertension
is a systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mm Hg and a diastolic pressure
greater than 90 mm Hg over a sus-tained period, based on the average of two or
more blood pres-sure measurements taken in two or more contacts with the health
care provider after an initial screening (Sixth Report of the Joint National
Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood
Pressure [JNC VI], 1997). Table 32-1
shows the categories of blood pressure established in 1997 by the JNC VI . The
classification shows the direct relation between the risk of morbidity and
mortality from hypertension and the level of systolic and diastolic blood
pressures. The higher the systolic or diastolic pressure, the greater the risk.
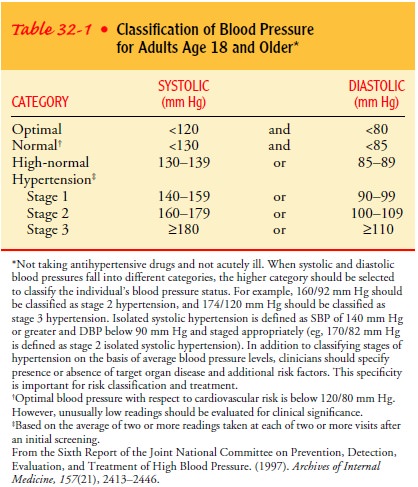
Three
stages (1, 2, and 3) of hypertension are defined by the JNC VI, which used
these terms, similar to those used to de-scribe cancer progression, so that the
public and health care pro-fessionals would be aware that sustained elevations
in blood pressure are associated with increased risks to health. Even within
the normotensive range, three levels of blood pressure— optimal, normal, and
high-normal—were specified to empha-size that the lower the blood pressure, the
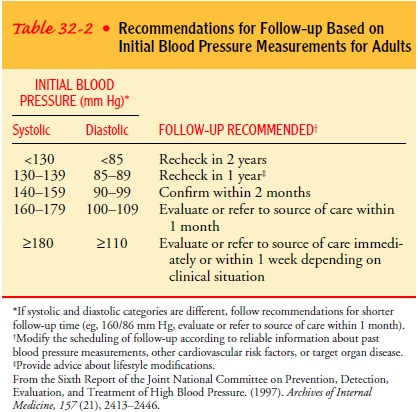
lower the risk. The JNC VI also developed recommendations for follow-up
moni-toring according to initial blood pressure readings at the time of
diagnosis (Table 32-2).
Related Topics