Chapter: Mechanical : Automobile Engineering : Steering, Brakesa and Suspension Systems
Hydraulic braking system
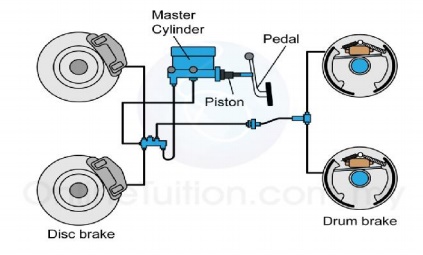
Hydraulic braking system
The disc brake or disk brake is a device for slowing or
stopping the rotation of a wheel while it is in motion. A brake disc (or rotor
in U.S. English) is usually made of cast iron, but may in some cases be made of
composites such as reinforced carbon-carbon or ceramic-matrix composites.
This is connected to the wheel and/or the axle. To stop the
wheel, friction material in the form of brake pads (mounted on a device called
a brake caliper) is forced mechanically, hydraulically, pneumatically or
electromagnetically against both sides of the disc. Friction causes the disc
and attached wheel to slow or stop. Brakes (both disc and drum) convert motion
to heat, but if the brakes get too hot, they will become less effective because
they cannot dissipate enough heat. This condition of failure is known as brake
fade.
Construction of Braking system;
The most common arrangement of hydraulic brakes for passenger
vehicles, motorcycles, scooters, and mopeds, consists of the following:
·
Brake pedal or lever
·
A pushrod (also called an actuating rod)
·
A master cylinder assembly containing a piston
assembly
·
Reinforced hydraulic lines
Brake caliper assembly usually consisting of one or two hollow
aluminum or chrome-plated steel pistons (called caliper pistons), a set of
thermally conductive brake pads and a rotor (also called a brake disc) or drum
attached to an axle.The system is usually filled with a glycol-ether based
brake fluid (other fluids may also be used).
At one time, passenger vehicles commonly employed drum brakes
on all four wheels. Later, disc brakes were used for the front and drum brakes
for the rear. However disc brakes have shown better heat dissipation and
greater resistance to 'fading' and are therefore generally safer than drum
brakes. So four-wheel disc brakes have become increasingly popular, replacing
drums on all but the most basic vehicles. Many two-wheel vehicle designs,
however, continue to employ a drum brake for the rear wheel.The following
description uses the terminology for and configuration of a simple
In a hydraulic brake system, when the brake pedal is pressed,
a pushrod exerts force on the piston(s) in the master cylinder, causing fluid
from the brake fluid reservoir to flow into a pressure chamber through a
compensating port. This results in an increase in the pressure of the entire
hydraulic system, forcing fluid through the hydraulic lines toward one or more
calipers where it acts upon one or two caliper pistons sealed by one or more
seated O-rings (which prevent leakage of the fluid).
The brake caliper pistons then apply force to the brake pads,
pushing them against the spinning rotor, and the friction between the pads and
the rotor causes a brakingtorque to be generated, slowing the vehicle. Heat
generated by this friction is either dissipated through vents and channels in
the rotor or is conducted through the pads, which are made of specialized
heat-tolerant materials such as kevlar orsintered glass.
Subsequent release of the brake pedal/lever allows the
spring(s) in my master cylinder assembly to return the master piston(s) back
into position. This action first relieves the hydraulic pressure on the
caliper, then applies suction to the brake piston in the caliper assembly,
moving it back into its housing and allowing the brake pads to release the
rotor.
The hydraulic braking system is designed as a closed system:
unless there is a leak in the system, none of the brake fluid enters or leaves
it, nor does the fluid get consumed through use.
Related Topics