Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 7 : Cell Cycle
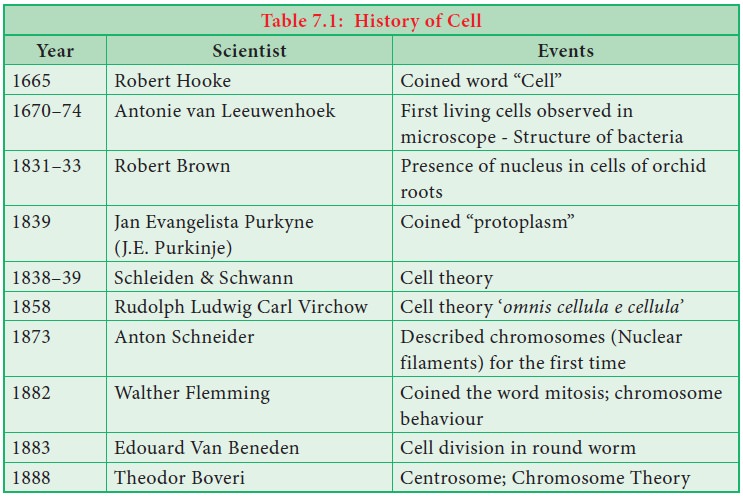
History of a Cell
Cell Cycle
One of the most important features of the living
cells is their power to grow and divide. New cells are formed by the division
of pre -existing cells. Cells increase in number by cell division. The parent
cell divides and passes on genetic material to the daughter cells.
Neurons can be replaced! Stem cells in the human brain : - most neurons are in G0 and do not divide. As neurons and neuroglia die or injured they are replaced
by neural stem cells
Edouard Van
Beneden, a Belgian cytologist,
embryologist and marine biologist. He was Professor of Zoology at the
University of Liège. He contributed to cytogenetics by his works on the
roundworm Ascaris. In his work he
discovered how chromosomes organized meiosis (the production of gametes).
History of a Cell
1. The Role of the Nucleus
As studied earlier, the nucleus is the organising
centre of the cell. The information in the nucleus is contained within
structures called chromosomes. These
uniquely:
·
Control activities of the cell.
·
Genetic information copied from cell to cell while
the cell divides.
·
Hereditary characters are passed on to new
individuals when gametic cells fuse together in sexual reproduction.
2. Chromosomes
At the time when a nucleus divides, the chromosomes
become compact and multicoiled structure. Only in this condensed state do the
chromosomes become clearly visible in cells. All other times, the chromosomes
are very long, thin, uncoiled threads. In this condition they give the stained
nucleus the granular appearance. The granules are called chromatin.
The four important features of the chromosome are:
·
The shape
of the chromosome is specific: The long, thin, lengthy
structured chromosome contains a short, constricted region called centromere. A centromere may occur anywhere along the chromosome, but it
is always in the same position on any given chromosome.
·
The
number of chromosomes per species is fixed: for example the mouse has 40 chromosomes, the onion has 16
and humans have 46.
· Chromosomes
occur in pairs: The chromosomes
of a cell occur in pairs, called homologous
pairs. One of each pair come originally from each parent. Example, human
has 46 chromosomes, 23 coming originally from each parent in the process of
sexual reproduction.
·
Chromosomes
are copied: Between nuclear
divisions, whilst the chromosomes are uncoiled and cannot be seen, each
chromosome is copied. The two identical structures formed are called chromatids.
3. Nuclear Divisions
There are two types of nuclear division, as mitosis and meiosis. In mitosis, the daughter cells formed will have the same
number of chromosomes as the parent cell, typically diploid (2n) state. Mitosis
is the nuclear division that occurs when cells grow or when cells need to be
replaced and when organism reproduces asexually.
In meiosis, the daughter cells contain half the
number of chromosomes of the parent cell and is known as haploid state (n).
Whichever division takes place, it is normally
followed by division of the cytoplasm to form separate cells, called as cytokinesis.
Related Topics