Cell Cycle | Botany - Answer the following questions | 11th Botany : Chapter 7 : Cell Cycle
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 7 : Cell Cycle
Answer the following questions
Cell Cycle
11. Write any three significance of mitosis
(1) Genetic stability -
daughter cells are genetically identical to parent cells
(2) Growth - as
multicellular organisms grow the number of cells making up their tissues
increases - the new cells must be identical to the parent Eg. Yeast and Amoeba
(3) Repair of tissues -
damages cells must be replaced by identical new cells by mitosis
12. Differentiate between mitosis and meiosis
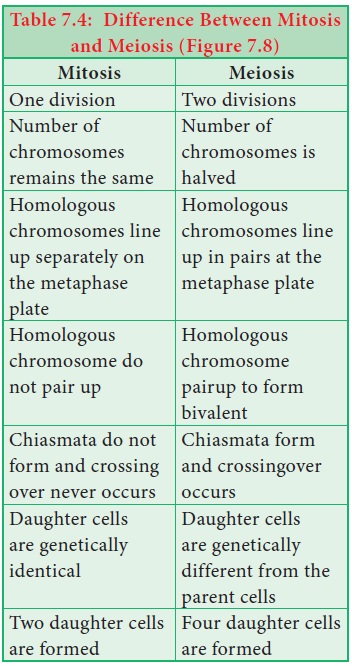
Mitosis
•
One division
•
Number of chromosomes remains the same
•
Homologous chromosomes line up separately on the metaphase plate
•
Homologous chromosome do not pair up
•
Chiasmata do not form and crossing over never occurs
•
Daughter cells are genetically identical
•
Two daughter cells are formed
Meiosis
•
Two division
•
Number of chromosomes is halved
•
Homologous chromosomes line up in pairs at the metaphase plate
•
Homologous chromosome pairup to form bivalent
•
Chiasmata form and crossingover occurs
•
Daughter cells are genetically different from the parent cells
•
Four daughter cells are formed
13. Given an account of G0 phase
Sometime
some cells exit G1 and enters a quiescent stage called GO.
•
Cells are metabolically active
•
No proliferation & no growth
•
reduced rate of RNA and protein synthesis
•
can remain in this stage for long period
•
But this GO is not permanent
Exception - Mature neuron &
Skeletal muscles
•
This GO stage (quiescent stage) will get activated (because GO
cells are not dormant after getting appropriate growth factors or other
extracellular signals.
•
This idea is exploited in cloning experiments
Eg -
Development of Dolly
14. Differentiate cytokinesis in plant cells and animal cells
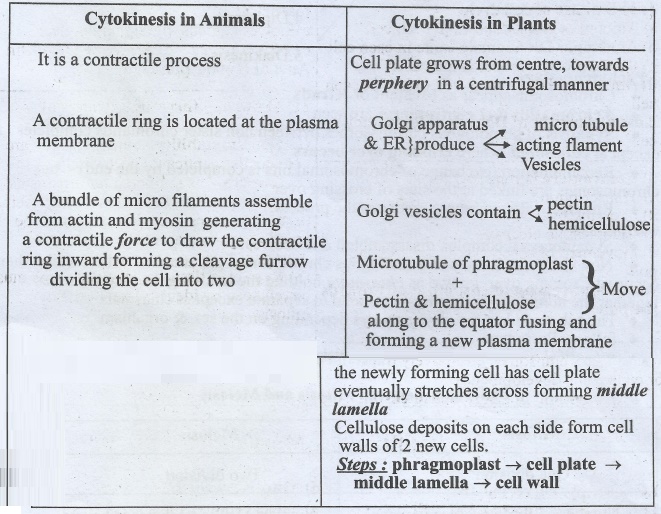
Cytokinesis in Animals
•
It is a contractile process
•
A contractile ring is located at the plasma membrane
•
A bundle of micro filaments assemble from actin and myosin generating a
contractile force to draw the
contractile ring inward forming a cleavage furrow dividing the cell into two
Cytokinesis in Plants
•
Cell plate grows from centre, towards perphery in a centrifugal manner
•
Golgi apparatus & ER produce
|→ micro tubule
|→ acting flament
|→ Vesicles
•
Golgi vesicles contain
|→ Pectin
|→ hemicellulose
•
Microtubule of phragmoplast + Pectin & hemicellulose - Move
along
to the equator fusing and forming a new plasma membrane the newly forming cell
has cell plate eventually stretches across forming middle lamella
Cellulose
deposits on each side form cell walls of 2 new cells.
Steps: phragmoplast → cell plate → middle lamella →
cell wall
15. Write about Pachytene and Diplotene of Prophase I
Prophase I – longer 5 subtages
1. Leptalene
2. Zygolene
3. Pachytene
4. Diplotene
5. Diakinesis
3. Pachytene stage
•
Chromosome appear as bivalent or tetrads
•
4 chromatids & 2 centromeres are
seen
•
Synapsis of homologous chromasomes
between non sister chromatids completes except at chiasmata where crossing over occurs
•
Recombination (exchange of chromosomal bits is completed by the end) - but
chromosomes are linked at the sites of crossing over
•
Enzyme - Recombinase mediates the
process.
4. Diplotene
•
Synaptonemal complex disassembled & dissolves
•
Non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes get attached where x like shape
occur at Crossing over known as chiasmata holding the homologous
chromosomes together the homologous chromosomes tend to separate except at
chiasmata
•
The sub stage last for days or years depending on the sex & organism
•
follows Pachytene
•
synaptical complex disassembled & dissolves
•
The chromosomes are actively transcribed in females as the eggs stores
upmaterials for embryonic development
• Exception In Lamp brush chromosome prominent loops occur.
Related Topics