Child Health Nursing - Growth and Development | 12th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Child Health Nursing
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Child Health Nursing
Growth and Development
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
Growth is an increase in
the size of the whole body or any of its part. It can be measured in inches,
centimetres, pounds or kilograms. Development is functional maturation. It is a
progressive increase in skills and capacity of function. Each child has its own
rate of physical, social, emotional and spiritual growth and development. All
children grow through the normal sequence of development.
Factors influencing Growth and Development
·
Heredity: The characteristics are transmitted through genes that are
responsible for size, shape of the body and also the family illness.
·
Race: Similar physical characteristics are seen in people
belonging to the same race.
·
Sex: A male baby is larger than female
·
Intra uterine development: Maternal and nutritional
deficiencies, drugs and infections during pregnancy can have effect on the
growing foetus.![]()
·
Illness and injury: Illness may reduce the weight and
minimise the child’s process.
·
Nutrition: Quality and quantity of food consumed by the child have
effect on his/ her body building and resistance.
·
Environment: Sunshine, air, socio economic factors also affect
children’s development.
·
Ordinal position in the family: Younger children learn from older, which
may be lacked by the first child.
·
Emotions: Lack of love, security, and parent child attachment can
affect the personality. The disturbed children are always slow in development.
·
Intelligence: It influences motor development, Psycho social development
and learning ability.
·
Exercise: Stimulates physical and muscular activity.
·
Hormones: Plays an important role in growth and development. E.g.
deficiency of growth hormone causes dwarfism and over production leads to
gigantism.
Growth Periods
1. New born – From birth
to four weeks.
2. Infant – from birth to one year.
3. Toddler – from one year to three years.
Preschooler – from three
years to six years.
Schoolage – from
six to twelve years.
Adolescent – from
thirteen to nineteen years.
Physical Growth
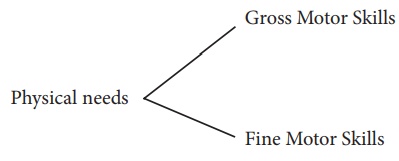
Gross Motor Skills:- Movement of the whole
body. (E.g. Holding a spoon)
Fine Motor Skills:- Takes more learning to
get the correct movement. (Eg. Head control)
Infant (1-12 months) :
The infancy period is one of the
rapid motor cognitive and social development period
Physical growth:- During infant period the
birth weight doubles at 6 months and triples at 1 year. Total height
increases by 50% at 1 year. Head and chest circumference are equal at 1 year.
Pulse rate is 130 –
140/mt.
Respiration is 36-40 /mt.
Blood pressure is 64/41
– 95/58 mmHg.
Dentition
Central incisors – 6-8
months.
Lateral incisors – 8-11
months
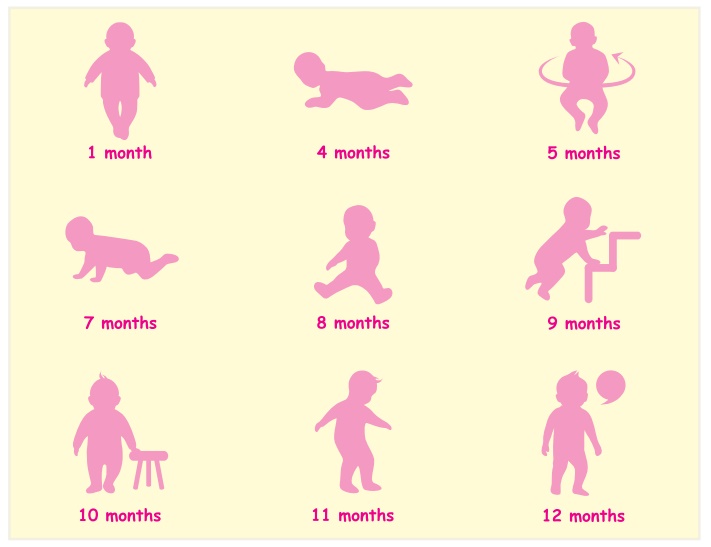
Mile stone development
1 month – Recognizes
mother’s voice
2 months – Social
smile
3 months – Head
control
4 months – Giggle
and laugh
5 months – Turn backs to abdomen
6 months – Sitting
with support
7 months – Sitting
without support
8 months – Crawling
9 months – Standing
with support
10 months – Stands
without support
11 months – Walking
with support
12 months – Walks
without support
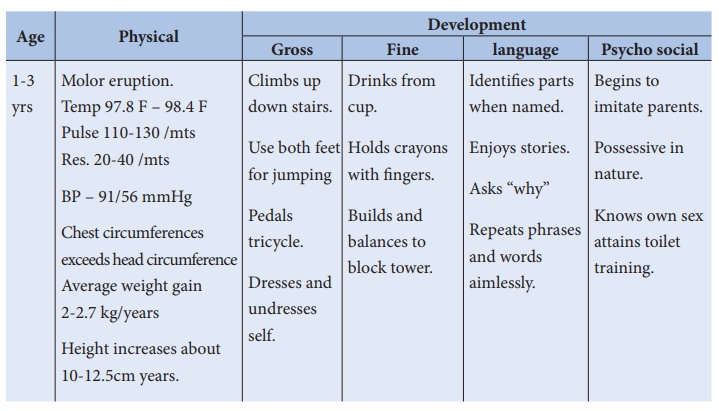
Toddler: (1-3 years)
Toddler period is
characterised by intense activity and discovery. It is a time of marked
physical and personality development.
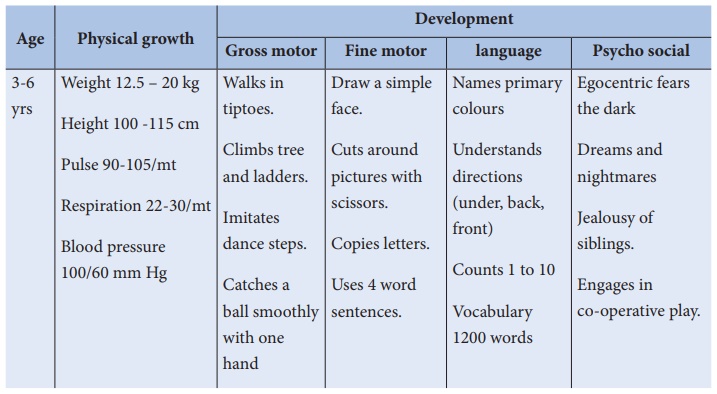
Preschooler: (3–6 years)
The children between 3
and 6 years of age are known as preschooler. Children in the preschool years
grow relatively slow. They become taller and thinner without gaining much
weight. They look more like an adult because of skeletal maturation.
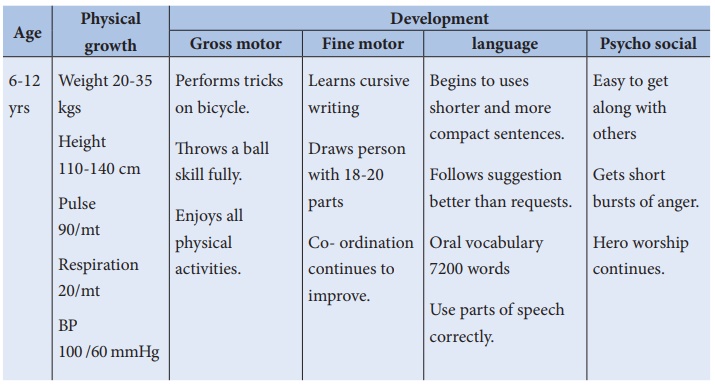
School aged child (6-12 years)
This is the time of gradual
growth and development with more event progress in both physical and emotional
aspects.
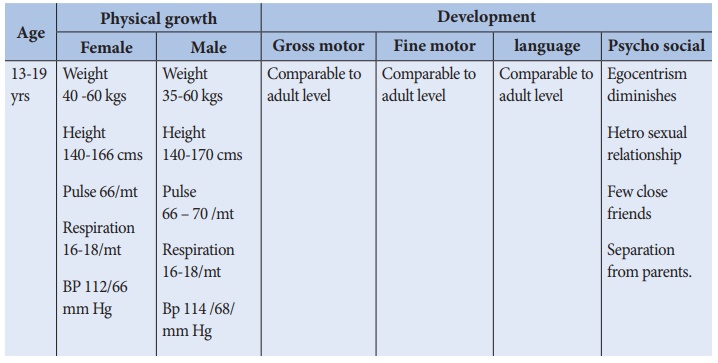
Adolescent: (13-19 years)
Adolescent is a period
of transition from child hood to adulthood. It is time of rapid physical,
cognitive, social and emotional maturing. This period is viewed as beginning
with the gradual appearance of secondary sex characteristics (11-12 yrs) and
ending with cessation of body growth at 18 – 20yrs.
For girls
·
Beginning of puberty 8-13 years
·
First pubertal change – breast development.
·
Pubic hair development.
·
Under arm hair development.
·
Menstrual period 10 -16.5 years of age.
For boys
·
Enlargement of scrotum and testes.
·
Pubic hair development.
·
Under arm hair development.
·
Crack and breaky voice.
Related Topics