Child Health Nursing - Artificial Feeding | 12th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Child Health Nursing
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Child Health Nursing
Artificial Feeding
FEEDING
The growth of the infants during the first 6 months of the life is greater and faster than any other period of life. Feeding plays an important role in it.
Principles
· To provide sufficient fluid
· To get adequate food
· To provide balanced composition
· To provide easily digestible food
Types of Feeding

ARTIFICIAL FEEDING
When the infant is feed
by any preparation other than breast milk is called artificial feeding.
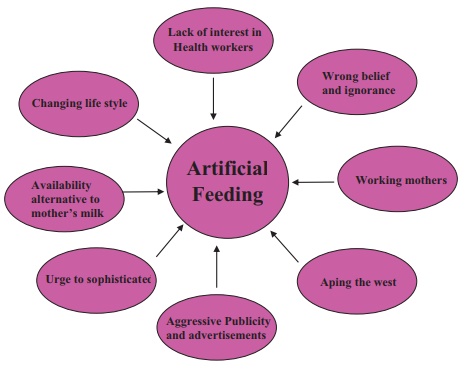
Factors contributing to rising incidence of artificial feeding in India
Indication
·
Contraindication of breast feeding either temporary or permanent
reason.
·
Mother reluctant in breast feeding.
·
Inadequate of breast milk as evidenced by first feeding.
·
Changing life style of women or pressurized under socio economic
condition.
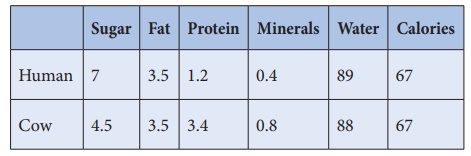
Foods used
There is no perfect
substitute for breast milk. In general boiled liquid cow’s milk various dried
milk preparation and to a lessen event unsweetened or sweetened condensed milk
are commonly used as artificial feeds. In some countries goat’s milk or buffalo
milk are used.
Composition
Cup feeding
Various types of
utensils are used for artificial feeding of infant. In some communities metal
cups or container with a spout are used for this purpose. But cup feeding is
more advisable for newborn than bottle feeding.

Advantages of Cup
Feeding
Promotes tongue action Heat confusion
Encourages the initial
digestion of the milk in the mouth
Easy to sterilize than bottle
and heat
Disadvantages
Addiction to the cup
feed
Aspiration may occur
with an incorrect technique
The length of the feed
is longer
Indication
As an interim measure
for full term babies when breast feeding is not yet established e.g. maternal
infant separation.
For the preterm infant
without sufficient suck / swallow coordination.
Procedure
•
Ensure the baby is alert and interested.
Gather equipment.
Expressed breast milk.
Sterilized cup (small,
open, slightly shaped and made from polyethylene or similar)
Bib / napkin
Baby’s records
·
Wash and dry hands
·
Sit comfortably with the baby in an upright sitting position.
Cuddled close to the parent’s body. Consider swaddling the top half of the baby
(to prevent hands knocking the cup) and using a suitably placed bib. Choose to
feed in skin-to-skin contact.
·
Place the cup (about half full, if possible) lightly on the baby’s
bottom lip, reaching the corners of his mouth, with the level of milk touching
his lips. Begin slowly.
·
Retain the cup in this position (throughout any pauses) allowing
the baby to lap with tongue forwards. Avoid the temptation to pour the milk in.
·
The baby will determine the pace and cease feeding when no longer
hungry.
·
Ensure that the feed time has been relaxed and pleasurable with
lots of comfort and social interaction for the baby. Return the baby to a safe
environment once finished.
·
Wash and sterilize the cup, wash and dry hands.
·
Complete documentation, note the volume of liquid ingested, the
time taken and the effect for the baby.
When a baby is not being
breast fed the midwife has an important role in facilitating safe and effective
infant nutrition using formula milk.
Powdered infant formula
milk is suitable for newborn babies are modified cow’s milk and are either whey
or casein dominant whichever milk is chosen, it must be an age suitable
formula. Equally where the manufacturers suggest preparation at a lower water
temperature; this advice should be disregarded.
Storage of prepared Feeds
•
Preparing a powdered feed and then storing it is strongly
discouraged.
·
It should be prepared as near to the time to leave as possible.
·
If the feed is not used within 2 hours it should be discarded.
·
If reheating a feed, warm water can be used for upto 15 minute
either by placing the bottle in the water or by holding it under a running tap.
·
Microwaves should not be used due to the inconsistent action of
reheating.
Complementary Feeding
It’s a gradual addition
of solid foods to the infant’s diet according to individual infant’s capacity
and gradual withdrawal of breast / artificial feeding in frequency and quality.
Principles
·
Start weaning when child is free from any Gastrointestinal
trouble.
·
One food item is introduced at interval of 4-7 days to allow for
identification of food allergies and to allow the child to get used to it.
·
New foods are fed in small amounts from one teaspoon to few
tablespoons.
·
Food should not be mixed in bottle and feed through nipple.
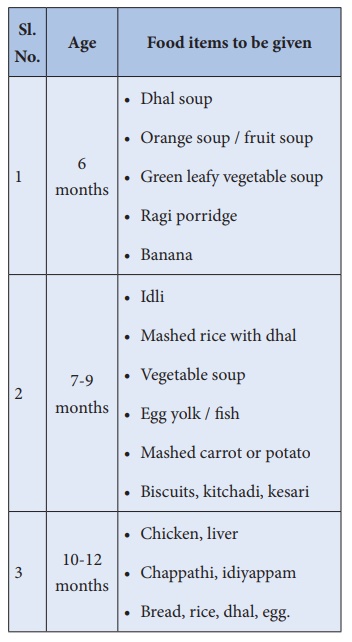
Methods of Complementary Feeding
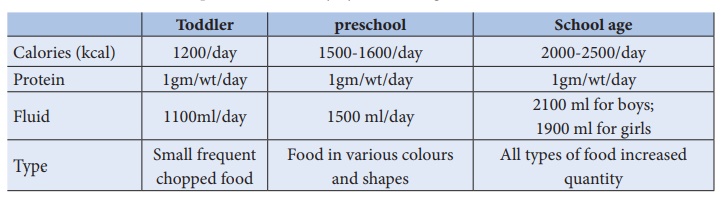
Dietary need
Growth requirements
combined with physical activity play a role in determining a child’s
nutritional needs. Nutritional needs change with different life stages. It is
important to take into account the extra demands placed on the body by these
changes.
Food pyramid
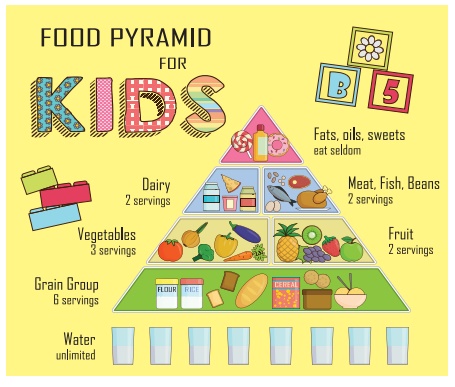
Foods to be avoided for children
·
Fast food and junk food like chips, popcorn etc
·
Processed meats
·
Canned fruits and drinks
·
Honey
·
Dipping sauces
·
Raw milk and eggs
Related Topics