Child Health Nursing - Disorders of Newborn | 12th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Child Health Nursing
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Child Health Nursing
Disorders of Newborn
DISORDERS OF NEWBORN
Neonatal disorders means
disturbance of normal state of body organs and abnormal function of a new born.
Minor Disorders of the Newborn
·
Molding: The head may appear asymmetric in the new born of a vertex
birth caused by the over riding of the cranial bones during labour and birth.
Diminishes within few days after birth.
·
Stuffy Nose: stuffy nose leads to mouth breathing and excessive air
swallowing which leads to abdominal distension and vomiting. Cleaning the
nostrils with cotton swabs socked with normal saline will reduce the problem.
·
Thrush: Thrush may be oral or in the napkin area including buttocks
and inner thighs. Treatment is 1% G.V paint or Nystatin suspension applied with
cotton swabs.
·
Phimosis: pinpoint prepuce which makes the baby cry during
micturition. It requires dilatation by mosquito forceps.
·
Mangolian Spots: Bluish black areas of pigmentation more
commonly noted on the back and buttocks. They fade gradually all over months or
years.
·
Nevi : Telengiectatic nevi are pink and easily planched. They may
appear on the upper eyelids, nose, upper lip and nap of the neck. They have no
clinical significance and fade my second year of life.
·
Physiological Jaundice: 40% of term neonates and 60% of preterm
neonates develop physiological jaundice. Jaundice becomes visible on second and
third day. Usually peaking between the second and fourth day and decreasing
between 5th and 7th days of life. It is believed to be the result of increased
bilirubin production from the break down of foetal RBCs. Treatment is not
necessary, but some children may need phototherapy.
·
h. Pseudo Menstruation:
Pseudo menstruation or vaginal bleeding is caused by
pregnancy hormones. It resolves when maternal hormones deplete from neonates
body. Reassure the parents.
·
Vomiting: Many newborns vomit, be alert indicate a bowel obstruction
which needs attention. Vomi of blood vomit, vomiting green - bile can ting can
be due to motion sickness or indigestion.
·
Dehydration: The water content in the body reduces resulting in
dehydration. When babies suffer from health problems like cold, cough or throat
infection, the intake reduces and resulting in dehydration.
·
Diarrhoea: The poop is normally much softer than an adult, if it
suddenly gets much looser or more watery and happens more often and in large
amounts it may be diarrhoea. An infection with a virus, bacteria or parasite.
Babies can get dehydrated very quickly within a day or two after diarrhoea
starts. Continue breast feeding or formula feeding. Small amounts of hydrating
solutions should be given frequently.
·
Cord infection : Infection of the umbilical cord stump is
called as omphalitis. It can be caused by skin bacteria. Application of an
antiseptic to umbilical cord is a best treatment.
Major New born Disorders
It can be divided into
congenital anomalies and acquired problems.
1. Congenital Anomalies
It can be defined as
structural or functional anomalies, for example metabolic disorders. That occur
during intra uterine life and can be identified in prenatal period or birth, or
some times may only be detected in infancy such as hearing defects.
Most Common Types
·
Congenital Heart Disease: An abnormality in the heart that
develops before birth ex. Ventricular septal defect.
·
Down Syndrome: A genetic chromosome 21 disorder causing
developmental symptoms.
·
Cleft Lip and Palate: Opening or splits in the roof of the mouth
and lip.
·
Spina Bifida: Failure in the development of spinal cord.
·
Club Foot: Foot is twisted out of shape or position.
·
Phenyl Ketonuria: A birth defect that causes amino acid called
phenylalanine to build up in the body.
·
Edward’s Syndrome : A condition that causes severe developmental
delays due to chromosome disorder. It also called as trisomy 18.
2. Acquired Disorders
These are not inherited
or present at birth, but developing after birth. Some of the disorders are
•
Low birth weight
•
Malnutrition
•
Infections and parasites
1. Low birth weight: A (LBW) low birth weight infant is an
infant with a birth weight of less than 2.5 kg regardless of gestational age.
a. Preterm babies: Babies born before 37 weeks of gestation.
If given good neonatal care these babies can catch up growth by 2-3 years of
age.
b. Small for date: (SFD) These babies may be born at term or
preterm. They weigh less than 10% of the gestational age. SFD have high
risk of dying not only during the neonatal period, but during their infancy
most of them become victims of protein energy malnutrition and infections.
Risk factors
·
Malnutrition
·
Infection
Treatment
·
Increase food intake
·
Control infections
·
Early detection and treatment of medical disorders.
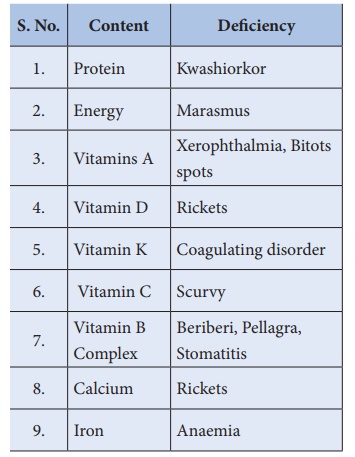
2. Malnutrition: Scarcity of suitable
food, lack of purchasing power of the family, traditional beliefs,
taboos, leads to an insufficient balanced diet resulting in malnutrition.
Common
deficiencies are
3. Infections and parasitic diseases
Young children fall an
easy prey to infectious diseases. They are diarrhoea, respiratory infections,
measles, pertussis, polio, neonatal tetanus, tuberculosis and diptheria. Intestinal
parasites such as ascariasis, hook worm, and giardiasis are common, because of
poor environmental sanitation and paucity of portable drinking water.
Related Topics