Indian Economy - Green Revolution | 11th Economics : Chapter 8 : Indian Economy Before and After Independence
Chapter: 11th Economics : Chapter 8 : Indian Economy Before and After Independence
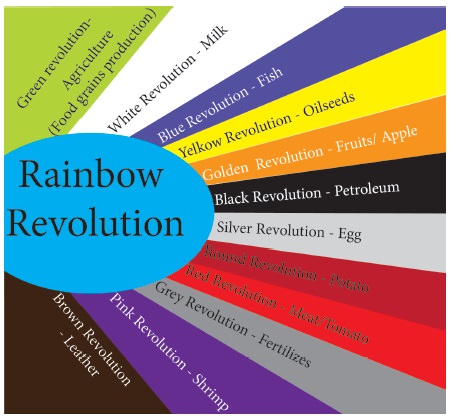
Green Revolution
Green
Revolution
The term
Green Revolution refers to the technological breakthrough in of agricultural
practices. During 1960’s the traditional agricultural practices were
Initially
the new technology was tried in 1960-61 as a pilot project in seven districts.
It was called as the High Yielding Varieties Programme (HYVP).

Achievement of Green Revolution
i.
The major achievement of the new strategy was to
boost the production of major cereals viz., wheat and rice. India was depending
on the US for the food grain. The US by using Public Law 480 (PL480) exported
wheat to India. Indians were waiting for the ships to sip their food. On the
other hand, India lost lots of minerals. The US could strategically exploit
Indian mineral resources at cheapest price for manufacturing missiles and
weapons, which gave job opportunity for larger US youth and largely contributed
to US GDP. But now India is food surplus, exporting food grains to the European
countries.
ii.
The Green revolution was confined only to High
Yielding Varieties (HYV) cereals, mainly rice, wheat, maize and jowar.
iii.
This Strategy was mainly directed to increase the
production of commercial crops or cash crops such as sugarcane, cotton, jute,
oilseeds and potatoes.
iv.
Per hectare productivity of all crops had increased
due to better seeds.
v.
Green Revolution had positive effect on development
of industries, which manufactured agricultural tools like tractors, engines,
threshers and pumping sets.
vi.
Green Revolution had brought prosperity to rural
people. Increased production had generated employment opportunities for rural
masses. Due to this, their standard of living had increased.
vii.
Due to multiple cropping and more use of chemical
fertilizers, the demand for labour increased.
viii.
Financial resources were provided by banks and
co-operative societies. These banks provided loans to farmer on easy terms.
The New Agricultural strategy was also called by various names.
Modern agricultural technology, seed – fertilizer – water technology, or simply
green revolution.
Weaknesses of Green Revolution
i.
Indian Agriculture was still a gamble of the
monsoons.
ii.
This strategy needed heavy investment in seeds,
fertilizers, pesticides and water.
iii.
The income gap between large, marginal and small
farmers had increased. Gap between irrigated and rain fed areas had widened.
iv. Except in Punjab, and to some extent in Haryana, farm mechanization had created widespread unemployment among agricultural labourers in the rural areas.
v.
Larger chemical use and inorganic materials reduced
the soil fertility and spoiled human health. Now organic farming is encouraged.
Second Green Revolution
The
Government of India had implemented ‘Second Green revolution’ to achieve higher
agricultural growth. The target of Second Green Revolution was to increase 400
million tons of food grain production as against about 214 million tons in 2006-07.
This is to be achieved by 2020. In agricultural sector, the growth rate of 5%
to 6% has to be maintained over next 15 years. There may be changes in these
statistics.
Requirements
of Second Green revolution:
·
Introduction of Genetically Modified (GM) seeds
which double the per acreage production.
·
Contribution of private sector to market the usage
of GM foods.
·
Government can play a key role in expediting
irrigation schemes and managing water resources.
·
Linking of rivers to transfer surplus water to
deficient areas.
Related Topics