Definition, Example, Sample Questions Answers - Grammar: Clauses, Phrases, Non-Finite Verbs, Infinitives and Gerunds | 9th English : UNIT 3 : Drama : Old Man River - by Dorothy Deming
Chapter: 9th English : UNIT 3 : Drama : Old Man River - by Dorothy Deming
Grammar: Clauses, Phrases, Non-Finite Verbs, Infinitives and Gerunds
Grammar
Clauses
A clause is a group of words that contains both a subject and a
predicate (or a verb). There are two types of clauses. They are independent
clause and dependent clause.
Examples:
* Kalpana wants to buy a phone, but she does not have enough money.
(Independent
Clause) (Independent Clause)
* If you don't study well, you won't pass the exam.
(Dependent
Clause) (Independent Clause)
* Kavin bought a car which was too expensive.
(Independent
Clause) (Dependent Clause)
* Sanjai is a talented player though he is out of form.
(Independent
Clause) (Dependent Clause)
Independent Clauses also known as main clauses are complete sentences. They can stand alone and express a complete thought.
Examples:
I need a book.
Mary prefers coffee.
Ram is a good volleyball player.
Dependent Clauses also known as subordinate clauses contain a subject and a predicate, but they do not express a complete thought.
Examples:
When it is raining
Because you were late
After you go to school
There are three main types of
Dependent clauses: Adjective, Adverb and Noun.
An Adjective Clause describes or gives more information about a noun—tells us which one, what kind, or how many.
Example: The book that I left on the
bus belongs to Mr. Baskar.
An Adverb Clause describes or gives more information about the verb—tells us when, where, how, to what extent, or
under what condition something is happening.
Example: She was happy because her
father gave her a watch.
A Noun Clause takes the place of a noun in the sentence.
Example: This is the best route that I
know.
Phrases
A Phrase is a group of words that forms
a meaningful unit, but it is not a complete sentence. In other words, it does not have a subject or a verb.
* the black hat
* blown away
* in the wind
Example:
The red umbrella was blown away in the wind.
There are several kinds of phrases
in the English language. Some of thecommon ones are described below.
Noun phrases
A Noun Phrase is a group of
words made up of a noun and its modifiers.
* the white car
* my English teacher
* the book shop
Example:
The pink house is for sale.
Verb Phrases
Verb phrase is a group of words
made up of a verb, helping verbs, and modifiers.
* ran quickly to catch
* filled with horror
* dedicated to
Example:
You have woken up everyone in the house
Prepositional Phrases
A Prepositional Phrase is a
group of words that begin with a preposition and help to explain the
relationship between two things.
* on the boat
* over the tree
* in the school
Example:
The present inside the big box is mine.
A. Identify the dependent clauses or phrases in the following sentences and underline them.
1. Texting on his phone, the man swerved into
a ditch.
2. It isn’t necessary to cram all night if
you have studied a little each day.
3. We climbed up the hill to enjoy the view.
4. I enjoy painting during my holidays.
5. Whether he attends the party or not, I
have decided to go.
6. I will stop playing the drums when you go
to sleep.
Answer:
1. Texting on his phone, the man swerved into a ditch.
2. It isn’t necessary to cram all night if
3. We climbed up the hill
4. I enjoy painting
5. Whether he attends the party or not, I have decided to go.
6. I will stop playing the drums when you go to sleep. (Dependent clause)
B. Complete the following sentences using appropriate prepositional phrases.
1. I would like to order coffee__________tea.
a) instead of
b) instead from
c) instead to
2. ____________ the rains, we went out.
a) In spite of
b) In
spite
c) In spite on
3. ______ fire, break the glass to escape.
a) In case of
b) In case
c) In case with
4. I am standing here_______ my friends.
a) in behalf of
b) on behalf of
c) on
behalf
5. We solved the problem _______ a new device
developed by our engineers.
a) by means of
b) by means
c) by means to
6. ______ we are impressed with their
performance.
a) In general
b) On general
c) In generally
Non-Finite Verbs
A non-finite verb (also known
as a verbal) is the term used to describe a verb that does not indicate tense.
The non-finite verbs are called gerunds, infinitives, and par-ticiples.
Finite verb
A verb that indicates tense and changes
according to the subject
Non-Finite verb
A verb that does not indicate tense and does
not change according to the subject
Finite verb:
Finite verbs change tense and
number according to the subject.
Arun invited Suresh to his daughter’s
birthday.
Her friends presented the girl with a toy.
His friend presented a watch.
Non-finite verbs have no
subject and do not change according to the tense or number.
Non-finite verbs are broadly
classified as follows:
i. Gerunds 1. Walking
is a healthy habit (Present participle used as a noun)
ii. Infinitive 2. I like to
walk early in the morning. (to infinitive)
iii. Present participle 3. These are my walking
shoes. (Present participle used as an adjective)
iv. Past participle 4. Having
walked a long distance I felt tired.
C. Look at the action words in bold. Identify whether they are either finite or non-finite verb.
They want to try a new approach. Answer: to try (Non-finite)
Trying is easy. Answer: Trying (Non-finite)
Having tried everything , he gave up. Answer: having tried (Non-finite)
All I can do is try. Answer: try (Non-finite)
If she tried, she would succeed. Answer: tried (Finite)
Infinitives and Gerunds
The infinitive is often called as ‘to verb’
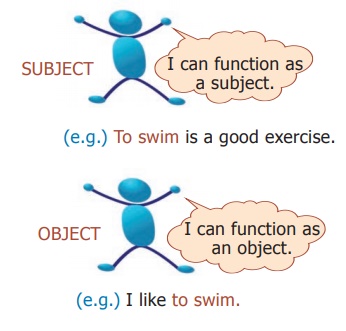
Infinitives may be used without to and we call such infinitives a plain infinitive or a bare infinitive.
(e.g.)She made me do my project.
We use plain/bare infinitives with these
modals.
shall, will, do, did, would, make,
need,
may, might, could, must, let, dare,
see
The infinitive may function as a subject,
direct object, subject complement, adjective, or adverb in a sentence. Although
an infinitive is easy to locate because of the to+verb form, deciding what function it has in a sentence depends on the
meaning.
(e.g.) To wait seemed foolish when decisive action was required.
(subject)
(e.g.) We intended to leave early. (direct object)
(e.g.) His ambition is to fly. (subject complement)
(e.g.) He lacked the strength to resist. (adjective)
(e.g.) We must study to learn. (adverb)
Gerunds
A gerund is an action word that
ends in –ing and functions as a noun
D. Read the following pairs of sentences
Identify the subject.
* Travelling might satisfy your
desire for new experiences.
* The study abroad program might
satisfy your desire for new experiences.
Answer: Travelling
Identify the direct object.
* They do not appreciate my
singing.
* They do not appreciate my
assistance.
Answer: Singing
Identify the subject complement.
* My cat’s favourite activity is
sleeping.
* My cat’s favourite food is
salmon.
Answer: Sleeping
Identify the object of the preposition.
* The police arrested him for
speeding.
* The police arrested him for
criminal activity.
Answer: Speeding
Points to remember:
A Gerund phrase consists of a
gerund plus modifier(s), object(s), and/or complement(s).
Dinesh and Divya have been
assigned homework on non-finites. They are not sure when to use a gerund and
when to use an infinitive.The decide to meet their teacher and get their doubts
cleared. The teacher introduces them to Mr. Gerund and Ms. Infinitive.\
Related Topics