Definition, Example, Sample Questions Answers | Primary Auxiliary, Modals - Grammar: Auxiliary Verb | 9th English : UNIT 4 : Prose : Seventeen Oranges - by Bill Naughton
Chapter: 9th English : UNIT 4 : Prose : Seventeen Oranges - by Bill Naughton
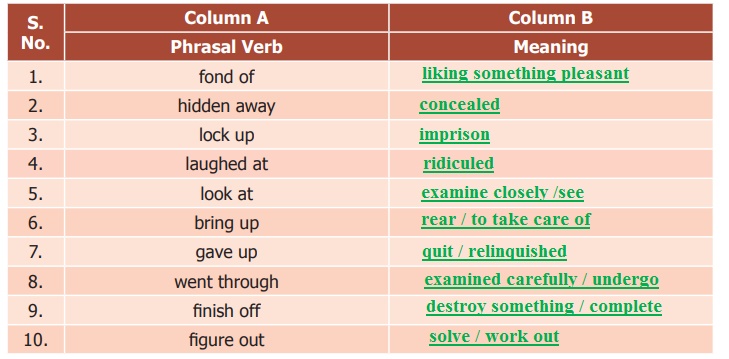
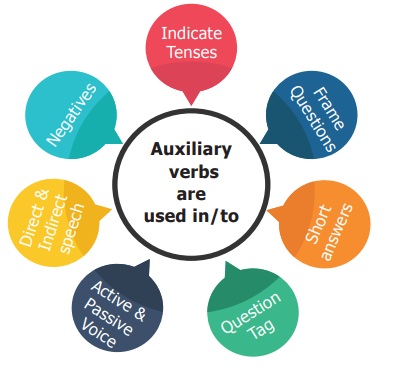
Grammar: Auxiliary Verb
Grammar
Phrasal verbs
A phrasal verb is a verb that has a main verb
together with an adverb or a preposition or both, to create a completely new
meaning.
A. Given below in Column A are some phrasal verbs taken
from the text. Find the meanings by using a dictionary and complete Column B.
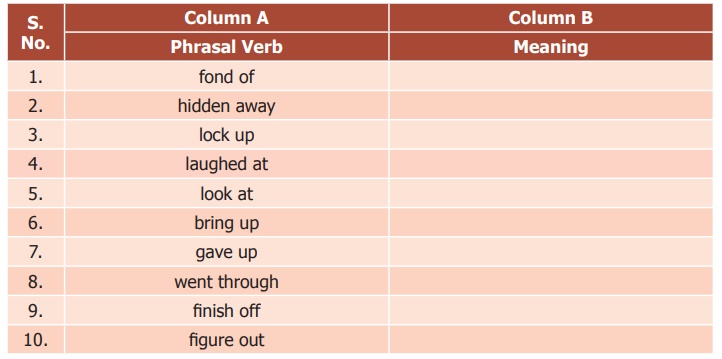
Answer:
Column A Column B
Phrasal Verb : Meaning
1. fond of: liking something pleasant
2. hidden away: concealed
3. lock up: imprison
4. laughed at: ridiculed
5. look at: examine closely /see
6. bring up: rear / to take care of
7. gave up: quit / relinquished
8. went through: examined carefully / undergo
9. finish off: destroy something / complete
10. figure out: solve / work out
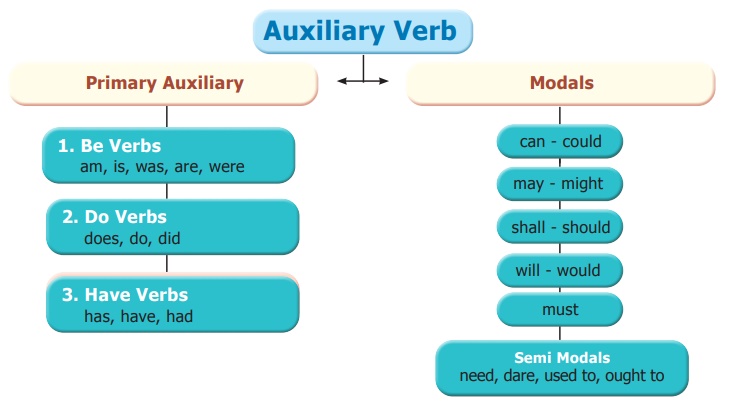
Modals
Must
Expressing
* strong obligation
* logical conclusion
* certainty
Example
* You must stop when the traffic lights turn red.
* He must be very tired. He's been working all day long.
Must not
Expressing
*prohibition

Example
* You must not smoke in the hospital.
Can
Expressing
*ability
* permission
* possibility

Example
* I can swim.
* Can I use your phone please?
* Smoking can cause cancer.
Could
Expressing
*ability in the past
*polite permission
*possibility

Example
When I was young I could run fast.
Excuse me, could I just say something?
It could rain tomorrow!
May
Expressing
* permission
* possibility / probability
Example
* May I come in?
* Where are my keys? They may be in the car.
Might
Expressing
* polite permission
* possibility / probability

Example
* Might I suggest an idea?
* I might go on holiday to Australia next year.
Need not
Expressing
*lack of necessity/ absence of obligation

Example
I need not buy tomatoes. There are plenty of tomatoes in the fridge.
Should/ought to
Expressing
*50 % obligation
*advice
* logical conclusion

Example
* I should / ought to see a doctor. I have a terrible headache.
* You should / ought to revise your lessons
* He should / ought to be very tired. He's been working all day long.
Uses of Auxiliary vebs
B. Can You do It?
*
Talking about the abilities of your class members is a great way to review the use of the
modal can.
* Work in pairs and discuss things a person might be able to do. Include things that some people can do and
others cannot do, and make a list on the board.
Can you?
Example: Can you play the guitar? Now you try:
Can you Play drums ?
Can you draw a picture?
Can you buy a car?
Can you ride a bicycle?
*
Once your list has 30-50 abilities, it’s time
to prepare for the game.
* Each of you will be given a blank paper and fill in the spaces with one of the
abilities you listed on the board.
* Then,
when the teacher says go, go around the classroom asking each other “Can you _________?” asking about
one of the activities listed on the board.
* If the person you ask can do that activity, you mark off the square with his/her name.
* If the person asked cannot do it, move on and ask another person about that ability or
another one on your paper.
* You can only ask each person about one ability before moving on to ask another
classmate, but you can come back to the same person as often as you like.
* When someone gets five spaces in a row, he calls “BINGO.”
Write it on the paper
Can you play Cricket?
Mugunthan
Can you sing songs?
Malar
Write down all the 'can do
activities' from the board and write down your classmates' names in the box
C. Do’s and Don’ts (Necessity, Obligation and Permission)
Choose
the correct option.
1. We use must (should/must/ought to) when
something is compulsory, obligatory and important.
2. We use should (should/must/ought to) when
something is the right thing to do.
3. We use ought to (should/must/ought to) when
something is suggested or recommended.
D. Complete the sentences with one of the modal verbs given below.
can, can’t, could, couldn’t, may, shouldn’t
1. Students may be quiet when they
write the examination.
2. You shouldn't wear a coat, it’s quite
warm.
3. could you open the window? It is very hot
in the room.
4. I couldn't go to the school yesterday
because I was ill.
5. When she was eighteen, she could run fast.
6. You shouldn't drive fast. It’s not safe.
7. Sachin is a famous cricketer. He Can bat well.
E. You are Aadhav. While you were away on a holiday, your house was burgled. Use appropriate modals and complete the letter to your friend telling him/ her about it.
No. 36, Gandhi Road
Chennai – 45
04 August 2018
Dear Ramesh,
How are you? I feel sad to inform you that my
house was burgled last week when I was on a holiday. Burglars might / would have known
from the accumulated newspaper pile that I had gone away. When I came back last
Sunday, I found the back-door lock broken. I could / might have forgotten to bolt the
back-door from inside and they should have entered through it. My room was
ransacked. They took my laptop and other valuables. I must / should have deposited the
jewellery in a bank locker to avoid this loss. I should have informed my
neighbours about my week-long trip. Well, I have registered an FIR with the
police. They are investigating the case. They have assured that I would / shall get my
jewels back. The burglars will be caught very soon. Convey my regards to all
at home.
Yours lovingly,
Aadhav
F. Match the Squares to form proper sentences.
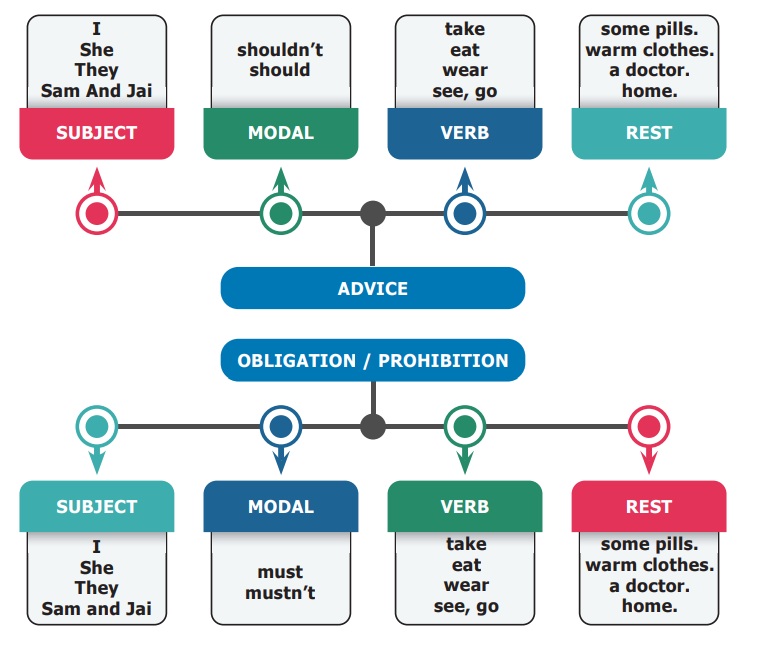
Answers:
1. I/She should
take some pills
2. She/They shouldn't
wear warm clothes.
3. She/They shouldn't go
home.
4. Sam and Jai should see
a doctor.
Obligation
/Prohibition
1. Obligation
(a) I/She/They must
take some pills
(b) She must
wear warm clothes.
(c) I/She/They/Sam and Jai must
see a doctor.
(d) I must go
home.
2. Prohibition
(a) She mustn't take
some pills.
(b) I mustn't wear
warm clothes.
(c) .Sam and Jai mustn't
go home.
(d) They mustn't
see a doctor.
Note: Rewrite the
sentences for other subjects.
G. Fill in the blanks with appropriate modals.
(will,
shall, would, should, can, could, may, might, ought to)
Milk is a nutritious food enriched with vitamins and proteins. We should take milk regularly so that we shall / will not develop deficiencies in our body. Aged persons, children and patients should take milk in sufficient quantities as it provides strength to their body. We could / should supplement it with fruits, vegetables and pulses for proper growth of the body. But we should consume milk of good quality. Otherwise it may cause harm to the body. We should / ought to be very careful while selecting our food items because there are chances that these might / may be adulterated. We should / must protect our health.
Related Topics