Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Geographic Information System
Geographic Information System
GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION SYSTEM
INTRODUCTION:
The expansion of GIS is Geographic Information System which
consists of three words, viz. Geographic, Information and System. Here the word
'Geographic'
deals with spatial objects or features which can be referenced or related
to a specific location on the earth surface. The object may be physical/natural
or may be cultural/manmade. Like wise the word 'Information'
deals with
the large volume of data about a particular object on the earth surface. The data includes a
Set of
qualitative and quantitative aspects which the real world objects acquire.
The term 'System'
is used to represent systems approach where the complex environment (consist
of a large number, of objects / features on the earth surface and their complex
characteristics) is broken down in to their component parts for easy understanding
and handling, but is considered to form an integrated whole form an aging and decision
making. Now-a-days this is possible in a very short span of time with the development
of sophisticated computer hardware and software. There fore, GIS is a computer based
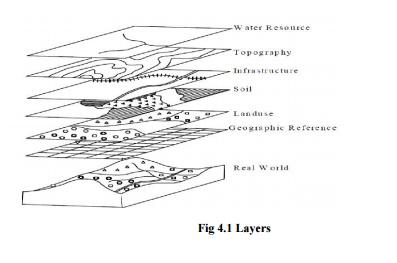
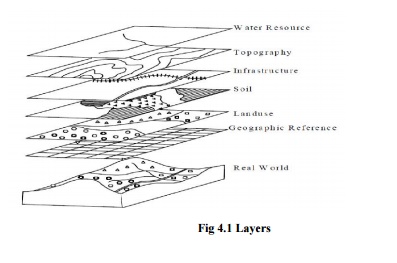
information system which attachesavariety of qualities and characteristics to
geographical location (Fig.5)and helps in planning and decision making. A Geographic
Information System(GIS) may bedefined in different manners. International
Training Centre (ITC), Holland defined Geographic Information System (GIS) as a
computerisedsystem that facilitatesthephases of dataentry, data analysis and data
presentation especially incases when we are dealing with geo referenced data.
Indian Society
of Geomatics (ISG) and Indian Space Application Centre (ISRO) defined GIS as a system
which provides a computerized mechanism for integrating various geo information
data sets and analysing them in order to generate information relevant to
planning needs in a context. According to Centre for Spatial Database
Management and Solutions (CSDMS), GIS is a
computerbasedtoolformappingandanalysingthingsthatexistandeventsthathappenone
earth.
Burrough (1986) defined GIS as a set of tools
for collecting, storing, retrieving atwill, transfor mingand displaying spatial
data from the real world for a particular set of purpose.
Arnoff (1989) defined GIS as ac omputer based system that provides
four sets of capabilities to handlegeoreferenced data, viz. data input, data management
(data storage and retrieval), manipulation analysis and data output.
From the above definitions, we can conclude that a GIS user expects
support from the system to enter geo referenced data to analyse it in various
ways and to produce output (maps and other) from the data. GIS draws on concepts
andideasfrommany different disciplines, such as cartography, cognitive science,
computer science, engineering, environmental sciences, geodesy, landscape
architecture, law, photogrammetry, public policy, remote sensing, statistics and
surveying. So, it involves not only the study of the fundamental issues arising
from the creation, handling, storage and use of geographic information, but it
also examines the impacts of GIS on individuals and society and the influences
of society on GIS.
1
DEVELOPMENT OF GIS
Keeping long tradition of map making as background, G.I.S. has
been developed during mid 20th century with the development of computer
science. The data analysis of geographic locations was being done by computers
in government organizations and universities in U.S.A. during 1950s and 1960s.
The first true operational G.I.S. was developed by Dr. Roger Tomlinson,
Department of Forestry and Rural Development , Canada. It was called as Canada Geographic
Information System (CGIS) and was used to store analyse and manipulateland
related data. Dr.Roger Tomlison was also known as the 'Father
of G.I.S'. In1964, alaboratory
Of Computer
Graphics and Spatial Analysis was established at the Harvard Graduate School of
Design by Howard T. Fisher. This organization developed a number of important the
oretical concepts of spatial data handling and in 1970 sit distributed seminal
software code and system such as 'SYMAP', 'GRID' and
'ODYSSEY'. This
inspired subsequent commercial development. By early 1980s, M&S Computing (later
Intergraph) and Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) emerged as commercial
vendors of G.I.S. software. ESRI released ARC/Info and ARC View software in 1981
and 1992 respectively. By the end of 20th Century, the development of
ARCView enabled viewing G.I.S. data through internet and eliminated many of the
hardware and licensing expenses of software packages. Since then a number of
organisations
anduniversitieshavebeendoingresearchinthefieldofG.I.S.anddeveloping user
friendly softwares . Now there is a growing number of free, open source G.I.S. packages
which run in a wide range of operating systems and perform specific tasks.
2
REQUIREMENT OF GIS
Primarily deals with geographic data to be analysed, manipulated
and managedinan organized manner through computers to solve real world
problems. So, GIS operation requires two things - computer
system and geographic data.
3
COMPUTER SYSTEM
Itincludes
both hardware and software. GIS runs through
computer system ranging from portable personal computers (PCs) to multi-user super
computers which are programmed by wide variety of software languages. In all ranges,
there area number things, that are essential for effective GIS operation. These
include: 1) a processor with sufficient power
to run the software, 2)sufficient memory for the storage of large
volumeofdata,3)a good quality, high resolution
colour graphic screen and 4)data input and output devices (for
example digitizers, scanners, keyboard, printers and plotters).
There are a wide range of software packages for GIS analysis,
each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Eventhoselists are too long to be
mentioned here, the important onesare different versions of ARC View, ARC Info,
Map Info., ARC GIS, Auto Cad Map etc.
Related Topics