Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Geographic Information System
Geographic Information System: Map Analysis
GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION SYSTEM
MAP
ANALYSIS
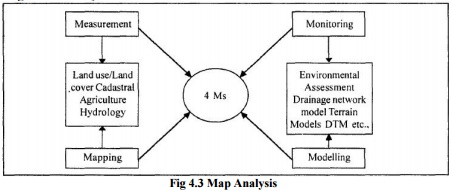
There are
mainly four key activities that any urban planners or scientists orresource
managers and others use geographic information for. They observe and measure
environmental parameters and develop maps which portray characteristics of the
earth. They monitor changes in our surroundings in space and time. In addition,
they model alternatives of actions and process operation in the environment.
These, four activities are Measurement, Mapping, Monitoring and Modelling
termed as key activities which can be enhanced by the using information
systems.
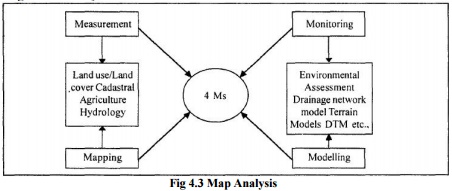
Fig 4.3
Map Analysis
GIS technology is more different from traditional mapping and
map analysis.GIS is based on a mathematical framework of primitive map analysis
operations analogous to those of traditional statistics and algebra. From this
perspective, GIS forms a toolbox for processing maps and fundamental concepts
for spatial measurement. It provides a foundation for advanced analytic
operations involving spatial analysis and measurement. Most of GISs contain
analytic capabilities for reclassifying and overlaying maps. Any GIS system for
the measurement of areas, distances, angles and so on requires two components,
namely, a standard measurement unit and a measurement procedure. Another major
function of GIS capability is the study of environmental surroundings and the
monitoring of environmental parameters (Burrough et ai, 1988). Although
analytical models have been linked to GIS for spatial measurement and resource
assessment, the cross fertilisation between the modules of modelling,
measurement and automated mapping allows the GIS user to monitor the
environment∑ and the earth system. In principle, it is possible to make a clear
distinction between GIS and digital cartography. Mapping technology or digital
cartography deals with map features and with associated attributes of colour,
symbology, name of annotation, legends, neatlinesand north arrows. GIS includes
the capabilities for storing, editing, and handling the relationships of attributes
with their spatial entities along with the capabilities of digital cartography.
A map, an ultimate product of digital cartography or GIS, is a very persuasive
form of data display and a computer drawn map carries the authority of a
powerful technology. GIS applications now span a wide range, from sophisticated
analysis and modelling of spatial data to simple inventory and management. They
also dictate the development directions of much of the industry. However,
several vendors have chosen to concentrate on the niche market for
environmental applications and to emphasise support for environmental
modelling. GRASS is a Significant public domain GIS software developed by USA
with substantial capabilities for modelling.
Related Topics