Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Geographic Information System
DBMS (Data Base Management Systems)
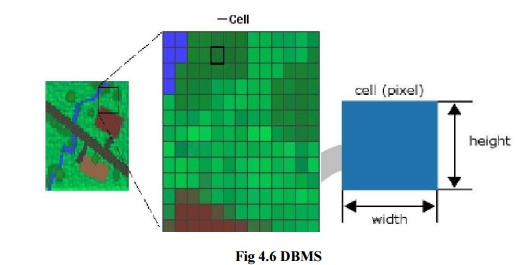
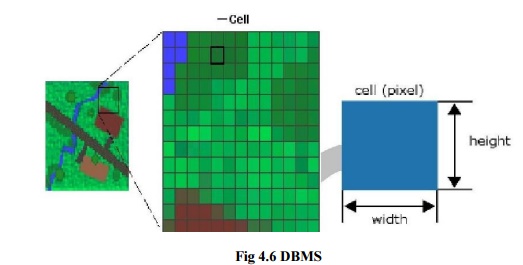
GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION SYSTEM
DBMS
(DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS)
The data
bases used in GIS are most commonly relational. Nevertheless, Object Oriented
data bases are progressively incorporated.
1
Hierarchical database
A hierarchical database is a kind of database management
system that links records together in a tree data structure such that each
record type has only one owner, e.g. an order is owned by only one customer.
Hierarchical structures were widely used in the first mainframe database
management systems. However, due to their restrictions, they often cannot be
used to relate structures that exist in the real world. Hierarchical
relationships between different types of data can make it very easy to answer
some questions, but very difficult to answer others. If one-to-many
relationship is violated (e.g., a patient can have more than one physician)
then the hierarchy becomes a network.
Field -
smallest unit of data
Segment -
groups of fields; nodes of the tree structure
Data base record - a collection of related segments; a
particular tree structure Data base - composed of database records
Data base description - how data base records are defined; set
of assembly-language macro instructions
Root -
first segment
Sequence
field - one field in each segment used to order the occurrences of a given type
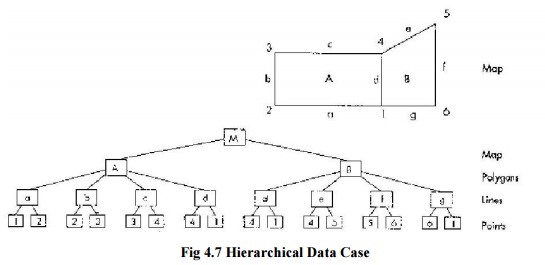
Fig 4.7
Hierarchical Data Case
2 NETWORK
MODEL
A network model database management system has a more
flexible structure than the hierarchical model or relational model, but pays
for it in processing time and specialization of types. Some object-oriented
database systems use a general network model, but most have some hierarchical
limitations.
The
neural network is an important modern example of a network database - a large
number of similar simple processing units, analogous to neurons in the human
brain, 'learn' the differences and similarities between a number of inputs.
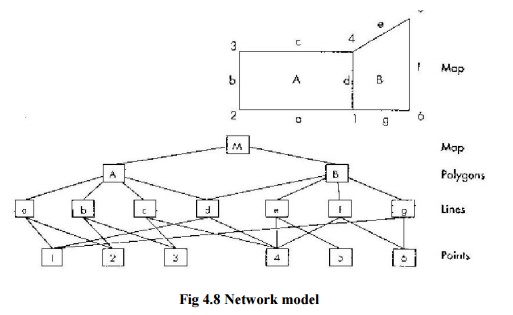
Fig 4.8
Network model
3
Relational data bases
In a relational data base, data is stored in tables where rows
represent the objects or entities and columns the attributes or variables. A
data base is usually composed of several tables and the relations between them
is possible through a common identifier that is unique for each entity. Most of
the relational data bases in GIS present two variables with identifiers; one
ofthem is unique and correlative, it could be numeric or alphabetic, and the
second one might be repeated and helps to organize the attribute table.
The
advantages of using this kind of data base are:
The design is based in a methodology with heavy theoretical
basis, which offers confidence in its capacity to evolve.
It is very easy to implement it, specially in comparison with
other models such as hierarchical, network, and object oriented
It is
very flexible. New tables can be appended easily.
Finally, many powerful DBMS using this approach contains query
languages (like SQL) which makes easy to include this tool in a GIS. Thus, some
commercialised GIS packages include a DBMS pre- existent.
4 OBJECT
ORIENTED DATA BASES
Based on
objects, it can be defined as an entity with a localisation represented by
values and by a group of operations. Thus, the advantage in comparison with relational
data bases is based on the inclusion, in the definition of an objet, not only
its attributes but also the methods or operations that act on this object. In
addition, the objects belong to classes that can have their own variables and
these classes can belong to super-classes.

Fig 4.9
Object oriented Data Base
A simple,
unstructured, unordered list of data records.
Easy to
construct, but inefficient to access and retrieve.
For a simple flat file with n records, (n+1)/2
search operations are required to find a record.
2).
Ordered Sequential Files
Records are organized as a sequential list according to
alphabetic order or other criteria.
Only LOG2(n+1) searching operations are required to
find a record from the file if divide-and-conquer searching method is used.
3).
Indexed files
Easy to
find a specific record with associated, cross-referenced attributes.
The index is used to quickly find a particular type of
information in a larger file by selecting key features that can be searched for
Direct
index file
Inverted
index files
Related Topics