Chapter: 12th Botany : Competitive Examination Questions
Genetics - Competitive Examination Questions
UNIT
VII – Genetics
1. Genes for cytoplasmic male sterility
in plants are generally located in
a)
Mitrochondrial genome
b) Cytosol
c) Chloroplast genome
d) Nuclear genome
2. In which mode of inheritance do you
expect more maternal influence among the off spring
a) Autosomal
b)
Cytoplasmic
c) Y-linked
d) X-linked
3. Which one of the following cannot be
explained on the basis of Mendel’s Law of Dominance?
a) Factors occur in pairs
b) The discrete unit controlling a
particular character is called a factor
c) Out of one pair of factors one is
dominant and the other is recessive
d)
Alleles does not show any blending and both the characters recover as such in F2
generation
4. F2 generation in a
Mendelian cross shows that both genotypic and phenotypic ratios are same as
1:2:1. It represents a case of
a)
Monohybrid crosses with incomplete dominance
b) Co-dominance
c) Dihybrid cross
d)
Monohybrid cross with complete dominance
5. A Pleiotropic gene
a)
Controls multiple traits in an individual
b) Is expressed only in primitive plants
c) Is a gene evolved during Pliocene
d) Controls a trait only in combination with
another L gene
6. A true breeding plant is
a)
Near homozygous and produces offspring of its own kind
b) Always homozygous recessive in its
genetic construction
c) One that is able to breed on its own
d) Produced due to cross pollination
among unrelated plants
7. Mendel obtained wrinkled seeds in pea
due to the deposition of sugars instead of starch. It was due to which enzyme?
a) Amylase
b) Invertase
c) Diastase
d)
Absence of starch branching enzyme
8. Ratio of complementary gene is
a) 9:3:4
b) 12:3:1
c) 9:3:3:4
d)
9:7
9. If there are 999 bases in an RNA that
codes for a protein with 333 amino acid and the base at position 901 is deleted
such that the length of the RNA becomes 998 bases, how many codons will be
altered?
a) 1
b) 11
c) 33
d)
333
10. If a homozygous red flowered plant
is crossed with a homozygous white flowered plant, then the off-springs will be
a) Half-white flowered
b) Half-red flowered
c) All white flowered
d)
All red flowered
11. The ratio in a dihyrbid test cross
between two individuals is given by
a) 2:1
b) 1:2:1
c) 3:1
d)
1:1:1:1
12. Pure line breed refers to
a) Heterozygosity only
b) Heterozygosity and linkage
c)
Homozygosity only
d) Homozygosity and self assortment
13. How many different types of gametes
can be formed by F1 progeny, resulting from the following cross
AABBCC x aabbcc
a) 3
b)
8
c) 27
d) 64
14. Which of the following conditions
represents a case of co-dominant genes?
a) A gene expresses itself, suppressing
the phenotypic effect of its alleles
b) Genes that are similar in phenotypic
effect when present separately, but when together interact to produce a
different trait
c) Alleles both of which interact to
produce a trait which may or may not resemble either of the parental type
d)
Alleles, each of which produces an independent effect in a heterozygous
condition.
15. If ‘A’ represents the dominant gene
and ‘a’ represents its recessive allele, which of the following would be most
likely result in the first generation off spring when Aa is crossed with aa?
a) All will exhibit dominant phenotype
b) All will exhibit recessive phenotype
c)
Dominant and recessive phenotypes will be 50% each
d) Dominant phenotype will be 75%
16. In Pisum Sativum, there are 14 chromosomes.
How many types of homologous pairs can be prepared?
a) 14
b)
7
c) 214
d) 210
17. The year 1900 AD is highly
significant for geneticists due to
a) Discovery of genes
b) Principle of linkage
c) Chromosomal theory of heredity
d)
Rediscovery of Mendelism
18. The phenotypic ratio of trihybrid
cross in F2 generation is
a)
27:9:9:9:3:3:3:1
b) 9:3:3:1
c) 1:4:6:4:1
d) 27:9:3:3:9:1:2:1
19. In a mutational event when adenine
is replaced by guanine, it is the case of
a) Frameshift mutatin
b) Transcription
c)
Transition
d) Transversion
20. Mutations can be induced with
a)
Gamma radiations
b) Infrared radiations
c) IAA
d) Ethylene
21. The mechanism that causes a gene to
move from one linkage group to another is called
a)
Translocation
b) Crossing over
c) Inversion
d) Duplication
22. A point mutation comprising the
substitution of a purine by pyrimidine is called
a) Transition
b) Translocation
c) Deletion
d)
Transversion
23. Frameshift mutation occurs when
a) Base is substituted
b)
base is deleted or added
c) Anticodons are absent
d) None of these
24. The distance between two genes in a
chromosome is measured in cross-over units which represent
a) Ratio of crossing over between them
b)
Percentage of crossing over between them
c) Number of crossing over between them
d) None of these
25. When a cluster of genes show linkage
behaviour they
a) do not show a chromosome map
b) show recombination during meiosis
c)
do not show independent assortment
d) induce cell division
26. Genetic map is one that
a)
Establish sites of the genes on a chromosome
b) Establishes the various stages in
gene evolution
c) Shows the stages during the cell
division
d) Shows the distribution of various
species in a region
27. After a mutation at a genetic locus
of the character of an organism changes due to the change in
a) DNA replication
b) Protein synthesis pattern
c) RNA transcription pattern
d)
Protein structure
28. In a hexaploidy wheat, the haploid
(n) and basic (x) numbers of chromosomes are
a)
n =21 and x =7
b) n =7 and x =21
c) n =21 and x =21
d) n =21 and x =14
29. Point mutation involves
a) Deletion
b) Insertion
c)
Change in single base pair
d) duplication
30. Which one of the following is a
wrong statement regarding mutations?
a) UV and Gamma rays are mutagens
b)
Change in a single base pair of DNA does not cause mutation
c) Deletion and insertion of base pairs
cause frame shift mutations.
d) Cancer cells commonly show
chromosomal aberrations.
31. Which of the following statement is
not true of two genes that show 50% recombination frequency?
a) The genes may be on different
chromosomes
b)
The genes are tightly linked
c) The genes show independent assortment
d) If the genes are present on the same
chromosome, they undergo more than one crossover in every meiosis.
32. Haploids are more suitable for
mutation studies than the diploids. This is because
a)
All mutations, whether dominant or recessive are expressed in haploids
b) Haploids are reproductively more
stable than diploids
c) Mutagens penetrate in haploids more
effectively than diploids
d) Haploids are more abundant in nature
than diploids
33. Crossing over that results in
genetic recombination in higher organisms occurs between
a)
Non-sister chromatids of a bivalent
b) Two daughter nuclei
c) Two different bivalents
d) Sister chromatids of bivalents
34. Removal of introns and joining the
exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called
a) Tailing
b) Transformation
c) Capping
d)
Splicing
35. Selection the correct option
Direction of RNA synthesis : Direction
of reading of the template DNA strand
a) 5’ – 3’ : 3’ – 5’
b) 3’ – 5’ : 5’ – 3’
c) 5’ – 3’ : 5’ – 3’
d) 3’ – 5’ : 3 ‘ – 5’
36. Peptide synthesis inside a cell
takes place in
a)
Ribosomes
b) Chloroplast
c) Mitrochondria
d) Chloroplast
37. During protein synthesis in a
organism at one point the process comes to a halt. Select the group of the
three codons from the following from which any one of the three could bring
about this halt.
a) UUU, UCC, UAU
b) UUUC, UUA, UAC
c) UAG, UGA, UAA
d) UUG, UCA, UCG
38. The binding site of tRNA with mRNA
and amino acids respectively are
a) mRNA with DHU loop and amino acid
with CCA end
b) mRNA with CCA end and amino acid with
anticodon loop
c) mRNA with anticodon loop and amino
acid with DHU loop
d)
mRNA with anticodon loop and amino acid with CCA end
39. Which of the following is correct
regarding genetic code?
a) UUU is the initiation codon which
also codes for phenylalanine
b)
There are 64 triplet codons and only 20 amino acids
c) Three random nitrogen bases specify
the placement of one amino acid
d) UAA is the nonsense codon which also
codes for methionine
40. Which of the following set of
options is used in translation?
a) hnRNA, tRNA, rRNA
b)
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
c) mRNA, tRNA, hnRNA
d) hnRNA, rRNA, lRNA
41. Sequence of DNA (non-coding) is
known as
a) exon
b)
intron
b) cistron
d) none of these
42. During transcription holoenzyme RNA
polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle like structure
at that point. What is that sequence called
a) CAAT box
b) GGTT box
c) AAAT box
d)
TATA box
43. The successive nucleotides of RNA
are covalently linked through
a) Hydrogen bonds
b)
Phosphodiester bonds
c) Glycosidic bonds
d) None of these
44. The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain
growth
a) Polymerize in the 3’ - to 5’
direction and forms replication fork
b) Prove semi conservative nature of DNA
replication
c)
Polymerize in the 5’ to 3’ direction and explains 3’ – to – 5’ DNA replication
d) Result in transcription
45. Taylor conducted the experiment to
prove semiconservative mode of chromosome replication on
a) Drosophila melanogaster
b) e-coli
c) Vinca rosea
d)
vicia faba
46. The new strand synthesized in small
pieces and then joined together during DNA replication is called
a) Dead strand
b)
Lagging strand
c) Leading strand
d) All of these
47. What is incorrect about the
following figure representing DNA replication
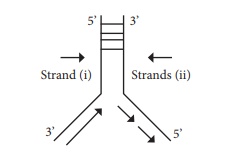
a) The direction of DNA replication in
strand (i)
b) The direction of DNA replication in
strand (ii)
c)
Discontinuous replication of strand (i)
d) Discontinuous replication of strand
(ii)
48. DNA multiplication is called
a) Translation
b)
Replication
c) Transduction
d) Transcription
49. The complete set of chromosome
inherited as a single unit from one parent is known as
a)
Genome
b) Linkage
c) Gene pool
d) Genotype
50. The mobile genetic element is
a)
Transposon
b) Mutation
c) Endonuclease
d) Variation
Related Topics