Chapter: 12th Botany : Competitive Examination Questions
Biotechnology - Competitive Examination Questions
UNIT
VIII – Biotechnology
1. What is the criterion for DNA
fragments movement on agarose gel during gel electrophoresis?
a)
The smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
b) Positively charged fragments move to
farther end.
c) Negatively charged fragments do not
move.
d) The larger the fragment size, the
farther it moves.
2. Stirred-tank bioreactors have been
designed for
a) Purification of product.
b) Addition of preservatives to the
product
c)
Availability of oxygen throughout the process
d) Ensuring anaerobic conditions in the
culture vessel.
3. Which of the following is not a
component of downstream processing?
a) Separation
b) Purification
c) Preservation
d)
Expression
4. Which of the following is not a
feature of the plasmids?
a) Transferable
b)
Single-stranded
c) Independent replication
d) Circular structure
5. Which of the following is not
required for nay of the techniques of DNA fingerprinting available at present?
a) Restriction enzymes
b) DNA-DNA hybridization
c) Polymerase chain reaction
d)
Zinc finger analysis
6. Which vector can clone only a small fragment
of DNA?
a) Bacterial artificial chromosome
b) Yeast artificial chromosome
c)
Plasmid
d) Cosmid
7. The colonies of recombinant bacteria
appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non-recombinant bacteria because
of
a) Insertional inactivation of alpha
galactosidase in recombinant bacteria.
b) nactivation of glycosidase enzyme in
recombinant bacteria.
c)
Non-recombinant bacteria containing beta galactosidase.
d) Insertional inactivation of alpha
galactosidase in non-recombinant bacteria.
8. During the process of isolation of
DNA, chilled ethanol is added to
a)
Precipitate DNA
b) Break open the cell to release DNA
c) Facilitate action of restriction
enzymes
d) Remove proteins such as histones.
9. For transformation, micro-particles
coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of
a) Silver or platinum
b) Platinum or zinc
c) Silicon or platinum
d)
Gold or tungsten.
10. Biolistics (gene-gun) is suitable
for
a) disarming pathogen vectors
b)
transformation of plant cells
c) constructing recombinant DNA by
joining with vectors
d) DNA fingerprinting.
11. Genetic engineering is possible
because
a) phenomenon of transduction in
bacteria understood
b) we can see DNA by electron microscope
c) we can cut DNA at specific sites by
endonuclease like DNAase I
d)
restriction endonuclease purified from bacteria can be used invitro
12. Genetic Engineering is
a) Making artificial genes
b)
Hybridisation of DNA of one organism to that of the others
c) Production of alcohol by using
microorganisms
d) Making artificial limbs, diagnostic
instruments such as ECG, EFG, etc.
13. Ligase is used for
a)
Joining of two DNA fragments
b) Separating DNA
c) DNA polymerase reaction
d) All of these
14. In genetic engineering, gene of
interest is transferred to the host cell through a vector. Consider the
following four agents (1-4) in this regard and select the correct option about
which one or more of these can be used as vectors
1. A bacterium 2. Plasmid 3. Plasmodium
4. Bacteriophage
a) 1 and 4 only
b)
2 and 4 only
c) 1 only
d) 1 and 3 only
15. Given below is a sample of a portion
of DNA strand giving the base sequence on the opposite strands. What is so
special shown in it?
5’---GAATTC---3’ 3’---CTTAAG---5’
a)
Palindromic sequence of base pairs
b) Replication completed
c) Deletion mutation
d) Start codon at the 5’end
16. There is a restriction endonuclease
called EcoRI. What does “co” part in it stand for ?
a) Coelom
b) Colon
c)
Coli
d) Coenzyme
17. The figure below is the diagrammatic
representation of the vector pBR322. Which one of the given options correctly
identifies its certain components?
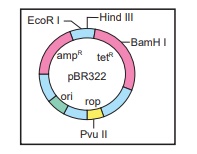
a) Ori-original restriction enzyme
b) rop-reduced osmotic pressure
c) Hind III, EcoRI – selectable markers
d)
ampR, tetR – antibiotic resistance genes
18. A mixture containing DNA fragments
a,b,c,d with molecular weights of a+b=c, a>b and d>c, was subjected to
agarose gel electrophoresis. The position of these fragmets from cathode to
anode sides of the gel would be
a)
b,a,c,d
b) a,b,c,d
c) c,b,a,d
d) b,a,d,c
19. An analysis of chromosomal DNA using
the southern hybridisation technique does not use
a) Electrophoresis
b) Blotting
c) Autoradiography
d)
PCR
20. The colonies of recombinant bacteria
appear white in contrast to blue colonies of non- recombinant bacteria because
of
a) Non-recombinant bacteria containing
beta galactosidase
b) Insertionalinactivationofa-galactosidase
in non-recombinant bacteria
c)
Insertional inactivation of b-galactosidase in recombinant bacteria
d) Inactivation of glycosidase enzyme in
recombinant bacteria
21. Which one of the following
palindromic base sequence in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some
particular restriction enzyme?
a) 5’CGTTCG3’ 3’ATCGTA 5’
b) 5’ GATATG 3’ 3’ CTACTA 5’
c)
5’ GAATTC 3’ 3’ CTTAAG 5’
d) 5’ CACGTA 3’ 3’ CTCAGT 5’
22. Silencing of mRNA has been used in
producing transgenic plants resistant to
a) Boll worms
b)
Nematodes
c) White rusts
d) Bacterial blights
23. Some of the characteristics of Bt
cotton are
a) Long fibre and resistant to aphids
b) Medium yield, long fibre and
resistant to beetle pests
c) High yield and production of toxic
protein crystals which kill dipteran pests
d)
High yield and resistant to boll worms
24. An improved variety of transgenic
basmati rice
a) Does not require chemical fertilisers
and growth hormones
b)
Gives high yield and is rich in vitamin A
c) Is completely resistant to all insect
pests and diseases of paddy
d) Gives high yield but no
characteristic aroma
25. Consumption of which one of the
following foods prevent the kind of blindness associated with vitamin A
deficiency?
a) Flavr Savr
b) Canola
c)
Golden rice
d) Bt brinjal
26. A protoplast is a cell
a) undergoing division
b)
without cell wall
c) without plasma membrane
d) without nucleus.
27. A technique of micropropagation is
a) Protoplast fusion
b) embryo rescue
c) somatic hybridization
d)
somatic embryogenesis
28. To obtain virus-free healthy plants
from a diseased one by tissue culture technique, which part/parts of the
diseased plant will be taken?
a) Apical meristem only
b) Palisade parenchyma
c)
Both apical and axillary meristems
d) Epidermis only.
29. Cellular totipotency was
demonstrated by
a) Theodore Schwann
b) A.V. Leeuwenhoek
c)
F.C. Steward
d) Robert Hooke
30. Tissue culture technique can produce
infinite number of new plants from a small parental tissue. The economic
importance of the technique is raising.
a)
genetically uniform population identical to the original parent.
b) homozygous diploid plants
c) new species
d) variants through picking up
somaclonal variations
31. Which of the following statements is
not true about somatic embryogenesis?
a) The pattern of development of a
somatic embryo is comparable to that of a zygotic embryo.
b)
Somatic embryos can develop from microspores.
c) Somatic embryo is induced usually by
an auxin such as 2, 4-D.
d) A somatic embryo develops from a
somatic cell.
32. Which one of the following is a case
of wrong matching?
a) Somatic - Fusion of two diverse
hybridization cells
b)
Vector DNA - Site for tRNA synthesis - in vitro
c) Micropropagation production of plants in large numbers
d) Callus - Unorganised mass of cells
produced in tissue culture.
33. Polyethylene glycol method is used
for
a) biodiesel production
b) seedless fruit production
c) energy production from sewage
d)
gene transfer without a vector.
34. Somaclones are obtained by
a) Plant breeding
b) Irradiation
c) genetic engineering
d)
tissue culture.
35. The technique of obtaining large
number of plantlets by tissue culture method is called
a) Plantlet culture
b) Organ culture
c)
Micropropagation
d) Macropropagation
36. Coconut milk is used in tissue
culture in which present
a)
cytokinin
b) auxin
c) gibberellins
d) ethylene.
37. Haploid plants can be obtained by culturing.
a)
pollen grains
b) root tips
c) young leaves
d) endosperm.
Related Topics