Chapter: Human Neuroanatomy(Fundamental and Clinical): Cranial Nerve Nuclei
General Visceral Efferent Nuclei - Cranial Nerve Nuclei
General Visceral Efferent Nuclei
The nuclei of this column give origin to preganglionic fibres that constitute the cranial parasympathetic outflow. These fibres end in peripheral ganglia. Postganglionic fibres arising in these ganglia supply smooth muscle or glands. The nuclei are as follows.
1. TheEdinger-Westphal nucleus(oraccessory oculomotor nucleus) lies in the midbrain(Figs. 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3F). It is closely related to the oculomotor complex. Fibres arising in this nucleus pass through the oculomotor nerve. They relay in the ciliary ganglion to supply the sphincter pupillae and the ciliaris muscle.
2. Thesalivary(orsalivatory)nuclei(superior and inferior) lie in the dorsal part of the pons,just above its junction with the medulla (Figs. 10.1, 10.2). They are located just above the upper end of the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve . The superior nucleus sends fibres into the facial nerve. These relay in the submandibular ganglion to supply the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. The inferior nucleus sends fibres into the glossopharyngeal nerve. These fibres relay in the otic ganglion to supply the parotid gland. (The parotid gland may also receive some fibres from the superior salivatory nucleus, through the submandibular ganglion).Other neurons probably located near the salivary nuclei send out fibres that supply the lacrimal gland, after relaying in the pterygopalatine ganglion. These fibres travel through the facial nerve.
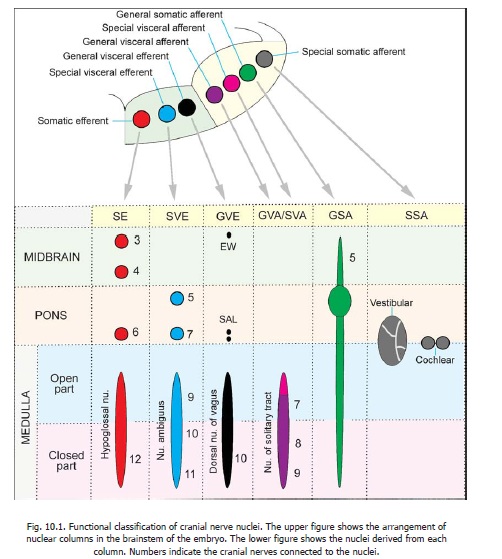
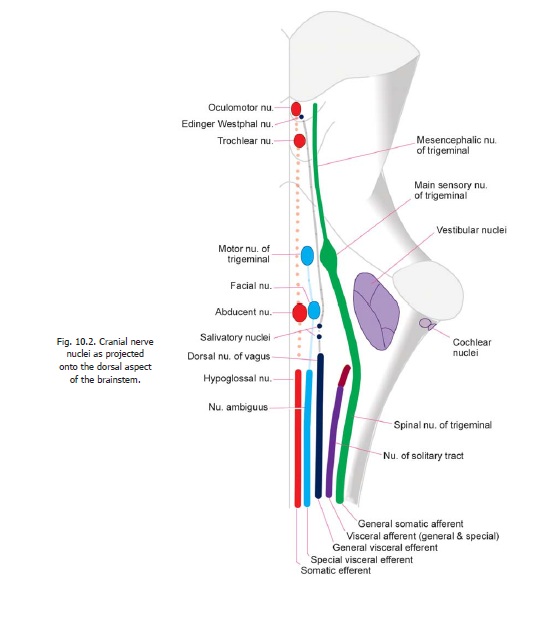
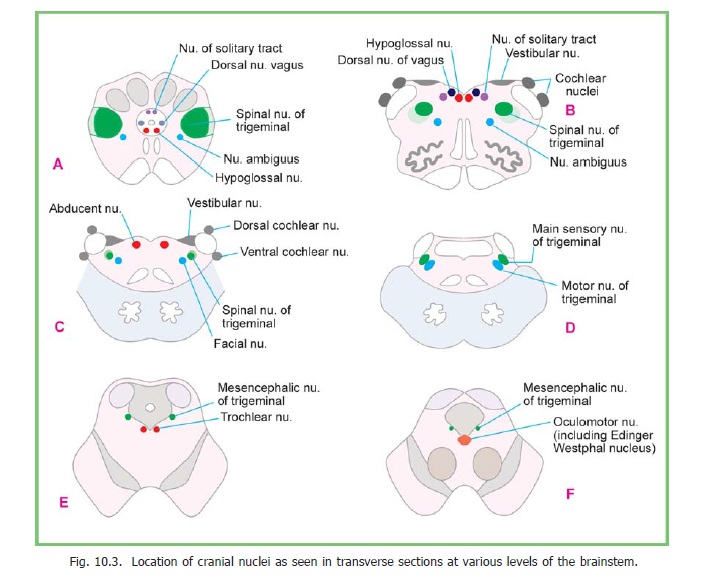
3. Thedorsal (motor) nucleus of the vagus(ordorsal vagal nucleus) lies in the medulla. Itis a long nucleus lying vertically. Its upper end lies deep to the vagal triangle in the floor of the fourth ventricle. When traced downwards it extends into the closed part of the medulla where it lies in the lateral part of the central grey matter (Figs. 10.1, 10.2 and 10.3 A,B). Fibres arising in this nucleus supply the heart, lungs, bronchi, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine up to the right two-thirds of the transverse colon. They end in ganglia (or nerve plexuses) closely related to these organs. Postganglionic fibres arise in these ganglia, and run a short course to supply smooth muscle and glands in these organs.
Subdivisions of the nucleus (supplying different regions) have been described.
Some general visceral efferent fibres arise from the retrofacial nucleus which is a small collection of neurons located near the upper end of the nucleus ambiguus.
Related Topics