Chapter: Human Neuroanatomy(Fundamental and Clinical): Basic Neuronal Arrangements
General Visceral Efferent Neurons
General Visceral Efferent Neurons
These are the neurons that constitute the autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic). They supply smooth muscle or glands. The nerves to glands are called secretomotor nerves. The pathway for the supply of smooth muscle or gland always consists of two neurons that synapse in a ganglion (Fig. 3.2). The first neuron carries the impulse from the CNS to the ganglion and is, therefore, called the preganglionic neuron. The second neuron carries the impulse from the ganglion to smooth muscle or gland and is called the postganglionic neuron.
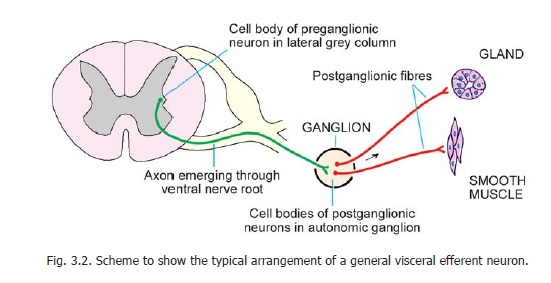
The cell bodies of preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system are located in the lateral grey column of the spinal cord in the thoracic and upper two lumbar segments (Fig. 19.3). Their cell bodies are multipolar, but are smaller than those of somatic efferent neurons. The Nissl substance in them is also less prominent. The axons leave the spinal cord through the anterior nerve
roots of spinal nerves and terminate in a sympathetic ganglion. The cell bodies of postganglionic neurons are located in sympathetic ganglia, and in some cases in peripherally situated ganglia and plexuses. The axons of these postganglionic neurons terminate in relation to smooth muscle in the walls of blood vessels and in viscera. They also supply the arrectores pilorum muscles of the skin, and give a secretomotor supply to sweat glands.
The cell bodies of preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system are located in two different situations (Fig. 19.3).
a. One group is located in the lateral grey column of the spinal cord in the second, third and fourth sacral segments. Their axons end in peripheral ganglia (or plexuses) situated in intimate relationship to pelvic viscera. These ganglia contain the cell bodies of postganglionic neurons. The axons of these neurons are short and end by supplying smooth muscle or glands of the viscera concerned.
b. The other group of parasympathetic preganglionic neurons is located in the general visceral efferent nuclei of cranial nerves. The axons of these neurons terminate in autonomic ganglia associated with the third, seventh, ninth and tenth cranial nerves. The postganglionic neurons are situated in these ganglia. They supply smooth muscle or glands.
Related Topics