Chapter: 12th Office Management and Secretaryship : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Management
Functions of Management
Functions of Management
Different
experts have classified functions of management in different manner
According to George and Jerry,
“There are four fundamental
functions of management, (i.e.) Planning, Organising, Actuating and
Controlling”.
According to
Henry Fayol, “To manage is to forecast and plan, to organise, to
command and to control”.
Luther Gullick
has given a keyword, ‘POSDCORB” where

Most widely
accepted functions of management given by koontz and O Donnel (ie) Planning,
Organising, Staffing, Directing and Controlling.
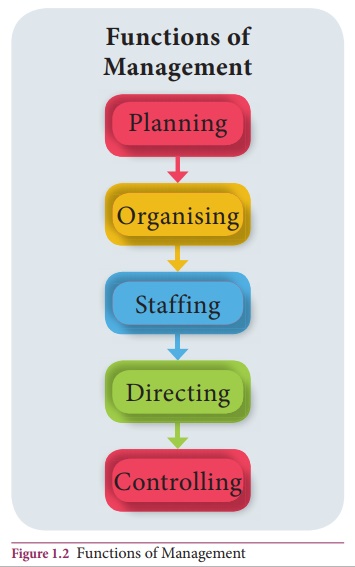
Functions of
management are overlapping in nature. Each function affects the performance of other.
1. Planning
It includes
determination of objectives, setting rules, procedure, policies, strategies,
budgeting etc., Planning may be short term or long term. Manager at all levels
want to prepare plans, so it is considered as a pervasive functions. Planning
looks into future without planning organization cannot achieve anything in
future. Planning is deciding in advance what has to done, and how and when it
has to be done. It bridges the gap between the present and the future.
Harold Koontz says that
planning has the following four
important objectives:
1. To offset
uncertainty and change,
2. To focus
attention of objectives,
3. To gain
economical operation, and
4. To facilitate
control.
Planning is
the basic function of management and all other functions of management are
greatly influenced by the planning process. Planning is an inevitable function
of management at levels of an organisation.

2. Organising
Organising
involves establishment of the formal structure of authority through which work
subdivisions are arranged, defined and coordinated to accomplish the defined
objective of the organization.
Designing and
maintaining these systems of roles is basically the managerial function of
organising.
Organising is:
a) Identification
and classification of required activities.
b) Grouping of
activities necessary to attain objectives
c) Assignment of
each grouping to a manager with the authority (delegation) necessary to
supervise it, and
d) Provision for
coordination horizontally (same organisation) and vertically (headquarters and
departments) in the organisation structure.
3. Staffing
Staffing
involves the process of filling positions in the organisation structure. The
staffing function relates to the recruitment, selection, training, promotion
and transfer of employees at all levels of management. The staffing function is
different from other functions because it deals only with people.

4. Directing
Direction is process by which the employees are guided to contribute towards organisational objectives. The term directing refers to that the managerial function which initiates organised action.
Formulating the policies and
plans which will be useful if it is converted into action. According to Earnest
Dale, “Direction is telling people what to do and seeing that they do it to
their abilities. It includes making assignments, corresponding procedures,
seeing that mistakes are corrected, providing on the job instructions and of
course, issuing orders”. It includes the following sub function. 1. Motivation
2. Leadership 3. Supervision 4. Communication and 5. Coordination.
5. Controlling
Controlling is
an important element in the management process. Controlling involves setting
standards measuring the performance comparing the actual with the standards and
find out the deviations and taking corrective actions. Hence business
enterprises can accomplish the goals only by establishing a proper control
system. Control activities generally relate to the measurement and achievement.
Each measures shows whether plans are working out or not.
Related Topics