Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Function of Kidney
FUNCTIONS OF KIDNEY
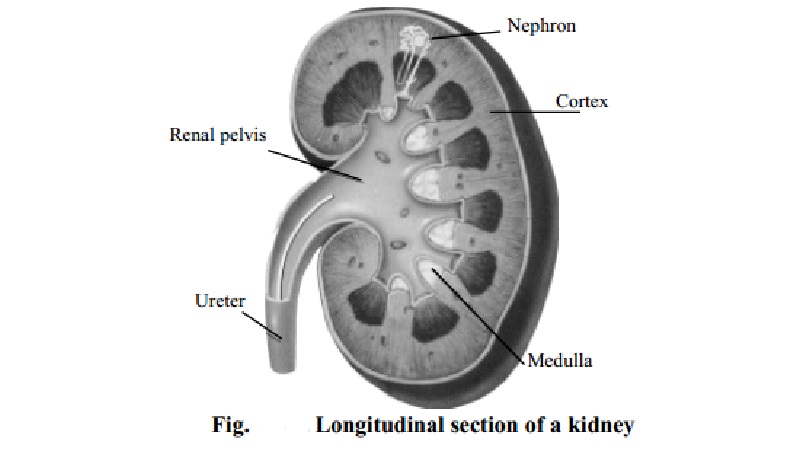
The basic anatomic and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron.
Each kidney contains 1 million nephrons. As the body fluid flows through these
finely structured units, the nephrons perform four significant functions to
support life.
1.
Filtering : The nephrons filter most
constituents to prevent them from entering the blood, except red cells and
proteins.
2.
Resorbing : Needed substances are resorbed as
the filtrate continues along the winding tubules.
3.
Secreting : Additional ions are secreted to
maintain acid base balance.
4.
Excreting : Unneeded materials are excreted in a
concentrated urine.
The primary function of the kidney is to maintain the constant
composition and volume of the blood. This includes the regulation of
1.
The osmotic pressure
2.
The electrolyte and water balance and
3.
The acid-base balance. The production of urine
permits the elimination of excess water and solutes such as sodium, chloride
and byproducts of metabolism such as urea, and ingested substances that may be
toxic
4.
Kidneys are the exclusive site for the
production of 1,25 dihydroxy cholecalciferol the active form of vitamin D.
Improper function can lead to bone disease
5.
Kidneys produce erythropoietin - which is essential
for the formation of RBC
6.
Renin is released from the kidney in response to
low blood pressure directly and stimulates the production of aldosterone.
7.
Parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, insulin and
gastrin are degraded by the kidneys.
Related Topics