Development Experiences in India - Fiscal Reforms | 11th Economics : Chapter 9 : Development Experiences in India
Chapter: 11th Economics : Chapter 9 : Development Experiences in India
Fiscal Reforms
Fiscal
Reforms
A key
element in the stabilization effort was to restore fiscal discipline. It means
reduction of fiscal deficit to the extent of just 3% of GDP, as suggested by
Fund Bank Policies. In this way, the budget aimed at containing government
expenditure and augmenting revenues; reversing the downtrend in the share of
direct taxes to total tax revenues and curbing conspicuous consumption. Some of
the important policy initiatives introduced for correcting the fiscal imbalance
were: reduction in fertilizer subsidy, abolition of subsidy on sugar and
disinvestment of a part of the government’s equity holdings in select public
sector undertakings. Gradually expenditures on welfare measures were reduced;
takes on corporate sectors were reduced; and takes on poor people were
increased.
Goods and Services Tax
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is defined as the tax levied when a consumer buys a good or service. It is proposed to be a comprehensive indirect tax levied on manufacture, sale and consumption of goods as well as services. GST aims to replace all indirect taxes levied on goods and services by the Indian Central and State governments. GST would eliminatie the cascading effect of taxes on the production and distribution of goods and services. It is also a “one-point tax” Unlike VAT which was a multipoint tax.
The Goods
and Service Tax Act was passed in the Parliament on 29th March 2017. The Act
came into effect on 1st July 2017.The
motto is one nation, one market, one tax.
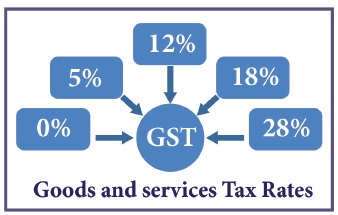
Current GST Rates in India
Advantages of GST
·
Removing cascading tax effect
·
Single point tax
·
Higher threshold for registration
·
Composition scheme for small business
·
Online simpler procedure under GST
·
Defined treatment for e-ecommerce
·
Increased efficiency in logistics
·
Regulating the unorganized sector
Related Topics