Chapter: Transmission and Distribution : Modelling and Performance of Transmission Lines
Ferranti Effect
FERRANTI EFFECT
A long
transmission line draws a substantial quantity of charging current. If such a
line is open circuited or very lightly loaded at the receiving end, the voltage
at receiving end may become greater than voltage at sending end. This is known
as Ferranti Effect and is due to the
voltage drop across the line inductance (due to charging current) being in
phase with the sending end voltages. Therefore both capacitance and inductance
is responsible to produce this phenomenon The capacitance (and charging
current) is negligible in short line but significant in medium line and
appreciable in long line. Therefore this phenomenon occurs in medium and long
lines.
Represent
line by equivalent π model.
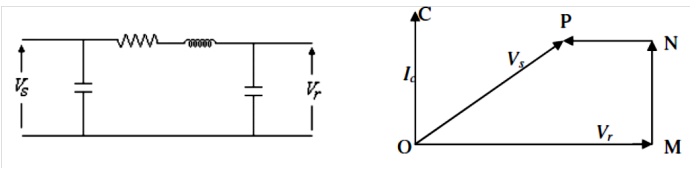
Line capacitance is assumed to be concentrated at the receiving end. OM
= receiving end voltage Vr
OC = Current drawn by capacitance = Ic
MN = Resistance drop
NP =
Inductive reactance drop Therefore;
OP =
Sending end voltage at no load and is less than receiving end voltage (Vr)
Since,
resistance is small compared to reactance; resistance can be neglected in
calculating Ferranti effect.
From π
model,
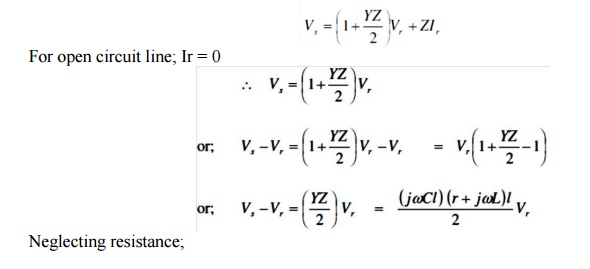
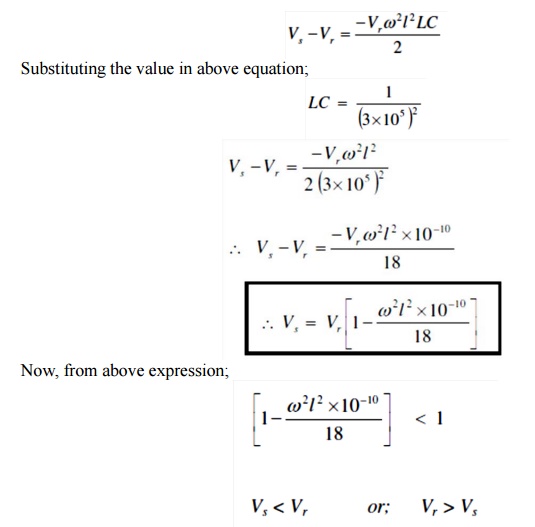
i.e.
receiving end voltage is greater than sending end voltage and this effect is
called Ferranti Effect. It is valid for open circuit condition of long line.
Related Topics