Economics - Features, Merits, Demerits of Mixed Economy (Mixedism) | 12th Economics : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Macro Economics
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Macro Economics
Features, Merits, Demerits of Mixed Economy (Mixedism)
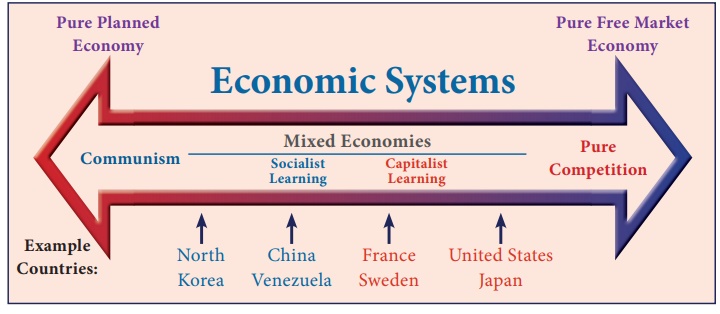
Mixed Economy (Mixedism)
In a mixed economy system both private and public sectors co-exist
and work together towards economic development.
It is a combination of both capitalism and socialism. It tends to
eliminate the evils of both capitalism and socialism.
In these economies, resources are owned by individuals and the
government. India, England, France and Brazil are the examples of mixed
economy.

Features of Mixed Economy
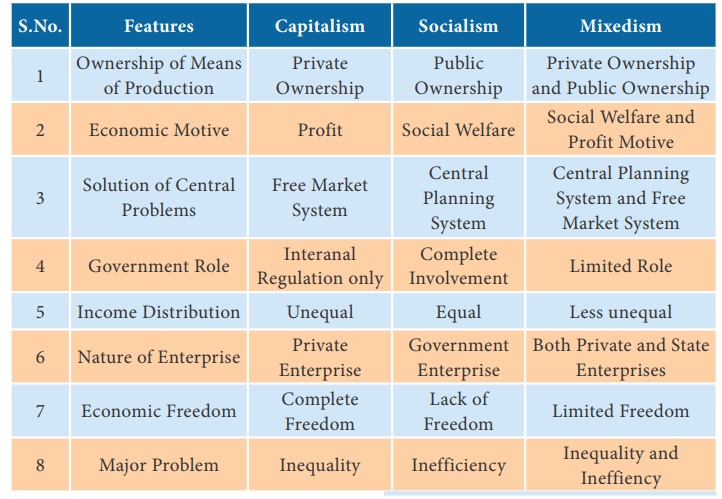
1. Ownership of Property and Means of Production: The means of production
and properties are owned by both private and public. Public and Private
have the right to purchase, use or transfer their resources.
2. Coexistence of Public and Private Sectors: In mixed economies, both
private and public sectors coexist. Private industries undertake activities
primarily for profit. Public sector firms are owned by the government with a
view to maximize social welfare.
3. Economic Planning: The central planning authority prepares
the economic plans. National plans are drawn up by the Government and both
private and public sectors abide. In general, all sectors of the economy
function according to the objectives, priorities and targets laid down in the
plan.
4. Solution to Economic Problems: The basic
problems of what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce and how to
distribute are solved through the price mechanism as well as state
intervention.
6. Freedom and Control: Though private has freedom to own
resources, produce goods and services and distribute the same, the overall
control on the economic activities rests with the government.
Merits of Mixed Economy
1. Rapid Economic Growth: The best advantage of mixed economy is
that it promotes rapid economic growth. Thus, both public requirements and
private needs are taken care of.
2. Balanced Economic Growth: Mixedism promotes balanced growth of the
economy. It promotes balanced growth between agriculture and industry, consumer
goods and capital goods, rural and urban etc.
3. Proper Utilization of Resources: In a mixed
economy, the government can ensure proper utilization of resources. The
government controls most of the important activities directly and the private
sector indirectly.
4. Economic Equality: The government uses progressive rates of
taxation for levying income tax to bring about economic equality.
5. Special Advantages to the Society: The government
safeguards the interest of the workers and weaker sections by legislating on
minimum wages, and rationing, establishing fair price shops and formulating
social welfare measures.
Demerits of Mixed Economy
1. Lack of Coordination: The greatest drawback of mixedism is lack
of coordination between public sector and private sector. As both work with
divergent motives, it creates many coordination related problems.
2. Competitive Attitude: It is expected that both government and private
should work with a complementary spirit towards the welfare of the society, but
in reality they are competitive in their activities.
3. Inefficiency: Most of the public sector enterprises
remain inefficient due to lethargic bureaucracy, red tapism and lack of
motivation.
4. Fear of Nationalization: In a mixed economy, the fear of nationalization
discourages the private entrepreneurs in their business operations and
innovative initiatives.
5. Widening Inequality: Ownership of resources, laws of
inheritance and profit motive of people widens the gap between rich and poor.
Ultimately the inequality of capitalism and inefficiency of
socialism are found in mixed economies.
Related Topics