Economics - Features, Merits, Demerits of Capitalistic Economy (Capitalism) | 12th Economics : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Macro Economics
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 1 : Introduction to Macro Economics
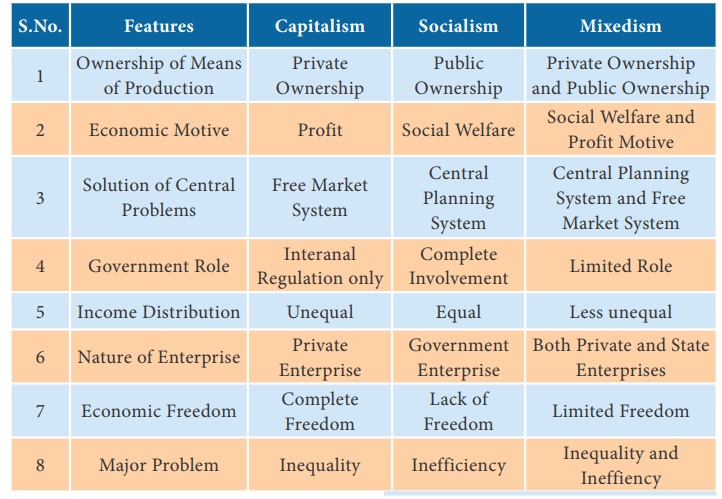
Features, Merits, Demerits of Capitalistic Economy (Capitalism)
Capitalistic Economy (Capitalism)
Adam Smith is the ‘Father of Capitalism’. Capitalistic economy is
also termed as a free economy (Laissez faire, in Latin) or market economy where
the role of the government is minimum and market determines the economic
activities.
The means of production in a capitalistic economy are privately
owned.


Manufacturers produce goods and services with profit motive. The
private individual has the freedom to undertake any occupation and develop any
skill. The USA, West Germany, Australia and Japan are the best examples for
capitalistic economies. However, they do undertake large social welfare
measures to safeguard the downtrodden people from the market forces.
Features of Capitalistic Economy
1. Private Ownership of Property and Law of Inheritance: The basic feature of capitalism
is that all resources namely, land, capital, machines, mines etc. are owned by
private individuals. The owner has the right to own, keep, sell or use these
resources according to his will. The property can be transferred to heirs after
death.
2. Freedom of Choice and Enterprise: Each individual is free
to carry out any occupation or trade at any place and produce any commodity.
Similarly, consumers are free to buy any commodity as per their choice.
3. Profit Motive: Profit is the driving force behind all
economic activities in a capitalistic economy. Each individual and organization
produce only those goods which ensure high profit. Advance technology, division
of labour, and specialisation are followed. The golden rule for a producer
under capitalism is ‘to maximize profit.’
4. Free Competition: There is free competition in both product
and factor market. The government or any authority cannot prevent firms from
buying or selling in the market. There is competition between buyers and
sellers.
5. Price Mechanism: Price mechanism is the heart of any
capitalistic economy. All economic activities are regulated through price
mechanism i.e, market forces of demand and supply.
6. Role of Government: As the price mechanism regulates economic
activity, the government has a limited role in a capitalistic economy. The
government provides basic services such as, defense, public health, education,
etc.
7. Inequalities of Income: A capitalist society is divided into two
classes – ‘haves’ that is those who own property and ‘have-nots’ who do not own
property and work for their living. The outcome of this situation is that the
rich become richer and poor become poorer. Here, economic inequality goes on
increasing.
Merits of Capitalism
1. Automatic Working: Without any government intervention, the
economy works automatically.
2. Efficient Use of Resources: All resources are put into optimum use.
3. Incentives for Hard work: Hard work is encouraged and entrepreneurs
get more profit for more efficiency.
4. Economic Progress: Production and productivity levels are
very high in capitalistic economies.
5. ConsumersSovereignty:Allproduction activities are aimed at
satisfying the consumers.
6. Higher Rates of Capital Formation: Increase in saving and
investment leads to higher rates of capital formation.
7. Development of New Technology: As profit is
aimed at, producers invest on new technology and produce quality goods.
Demerits of Capitalism
1. Concentration of Wealth and Income: Capitalism causes
concentration of wealth and income in a few hands and thereby increases
inequalities of income.
2. Wastage of Resources: Large amount of resources are wasted on
competitive advertising and duplication of products.
3. Class Struggle: Capitalism leads to class struggle as it
divides the society into capitalists and workers.
4. Business Cycle: Free market system leads to frequent
violent economic fluctuations and crises.
5. Production of non essential goods: Even the harmful goods
are produced if there is possibility to make profit.
Related Topics