Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Spark Ignition Engines
Factors affecting knock
Factors affecting knock
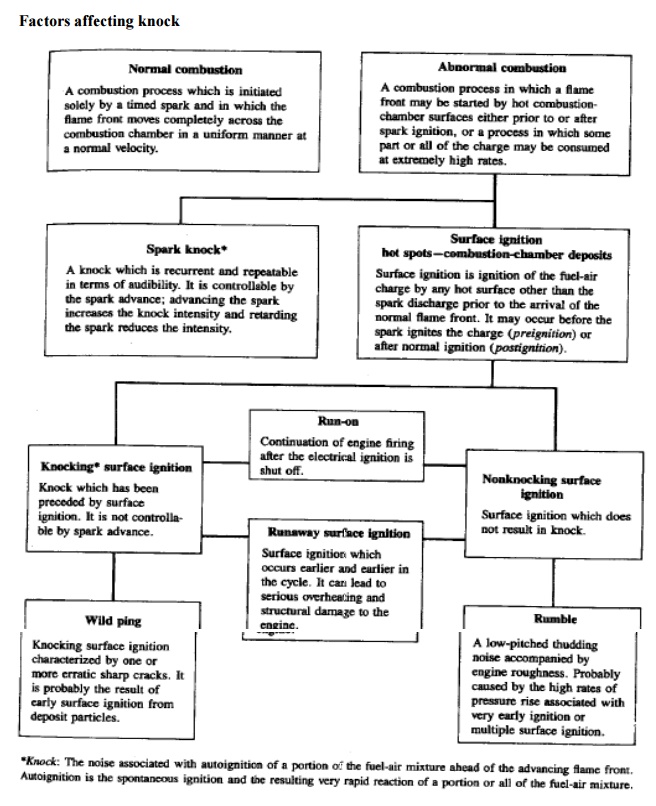
What is
Knocking?
Knock is
the name given to the noise which is transmitted through the engine structure
when essentially spontaneous ignition of a portion of the end-gas-the fuel,
air, residual gas, mixture ahead of the propagating flame occurs. When this
abnormal combustion process takes place, there is an extremely rapid release of
much of the chemical energy in the end-gas, causing very high local pressures
and the propagation of pressure waves of substantial amplitude across the
combustion chamber.
Effect of Knock:
1. Knock has
the following effects on engine operation:
2. Noise and
Roughness.
3. Mechanical
damage: increase in engine wear, cylinder head and valves may be pitted.
4. Carbon
deposits.
5. Increase
in heat transfer.
6. Decrease
in power output and efficiency.
7. Pre-ignition:
combustion Occurs before the spark.
Effect of engine variables on Knock:
To
prevent Knock in the S.I. engine the end gas should have:
A- Low
temperature.
B- Low
density.
C- Long
ignition delay.
D- Non-
reactive combustion.
When the
engine conditions are changed, the effect of the change may be reflected by
more than one of the above variables.
A- Temperature factors:
The
temperature of the unburned mixture is increased by the following factors:
1. Raising
the compression ratio.
2. Supercharging.
3. Raising
the inlet temperature.
4. Raising
the coolant temp.
5. Increasing
load.
6. Advancing
the spark.
7. Raising
the temperature of the cylinder and combustion chamber walls.
B- Density factors:
Increasing
density by any of the following methods, will increase the possibility of
Knock:
1. Increasing
load.
2. Increasing
compression ratio.
3. Supercharging.
4. Advancing
the spark.
C- Time factors:
Increasing
the time of exposure of the unburned mixture to auto-ignitions by any of the
following factors will increase tendency to knock:
1. Increasing
the distance of the flame travel.
2. Decreasing
the turbulence of mixture.
3. Decreasing
the speed of the engine.
D- Composition:
The
probability of Knock in S.I. engines is decreased by:
1. Increasing
the octane rating of the fuel.
2. Either
rich or lean mixtures.
3. Stratifying
the mixture.
4. Increasing
the humidity of the entering air.
Related Topics