Nursing - Factors affecting body temperature | 11th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Nursing - Health Assessment and Physical Examination
Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Nursing - Health Assessment and Physical Examination
Factors affecting body temperature
Factors affecting body temperature
1) Age, 2) Exercise,
3) Hormone level, circadian rhythm 5) Stress, 6) Environment, 7) Temperature
attraction, ever, 9) Hyperpyrexia, 10) Heat stroke, Hypothermia
1.
Age: Temperature regulation
is unstable until children reach
puberty. Older adults are sensitive to temperature extremes because of
deterioration in control mechanisms, reduced sweat gland activity, reduced
amounts of subcutaneous fat and reduced metabolism
2.
Exercise: Muscle activity causes increased metabolism by increasing carbohydrate and fat
breakdown. Any form
of exercise can increase heat production and the body temperature because of
increased metabolism.
3.
Hormone level: Women generally experience greater fluctuations in
body temperature than men. Hormonal variations during menstrual cycles cause
body temperature fluctuation.
Temperature changes occur in women during menopause
(cessation of menstruation).
4.
Circadianrhythm:Bodytemperature normally changes from 0.5º to 1ºC
during 24 hours period. The temperature is usually lowest between 1.00 AM and
4.00 AM
5.
Stress: Physical and emotional stress increases body temperature through
hormonal and neural stimulation. Those physiological changes increase
metabolism, which increases heat production.
6.
Environment:Environmentinfluences body temperature because of extensive
radiant and conductive heat loss.
7.
Temperature attraction: Changes in body temperature can be related to excess heat loss, minimal heat
production, minimal heat loss or any combination of these.
8.
Fever: Hyperpyrexia or fever occurs because heat loss mechanisms are
unable to keep pace with excess heat. Production, resulting in an abnormal rise
in body temperature.
9.
Hyperpyrexia: An elevated body temperature related to the body’s
inability to promote heat loss or reduce heat production is hyperthermia. Any
disease or trauma to the hypothalamus can impair heat loss mechanisms.
10.
Heat stroke: Prolonged exposure to the sum or high environmental
temperature can overwhelm the body’s heat loss mechanisms. Heat also depresses
hypothalamic function. These conditions cause heat stroke, a dangerous
emergency condition with a high mortality rate. Patients at risk for heat
stroke are the very young, very old, cardio vascular condition, diabetes and
alcoholics.
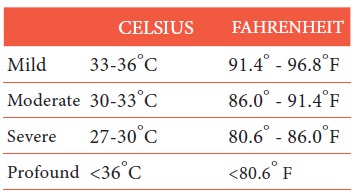
11. Hypothermia: Heat loss during prolonged
exposure to cold overwhelms the body ability to produce heat causing
hypothermia. Hypothermia is classified
as follows:
Related Topics