Nutrition and Dietetics - Energy | 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 9 : Carbohydrates and Energy
Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 9 : Carbohydrates and Energy
Energy
Energy
Energy is the capacity
to do work. Energy must be supplied regularly to meet the needs of the
body’s survival. The body needs energy for maintaining body temperature,
metabolic activity, supporting growth, for physical work, to maintain constant
body weight and good health.
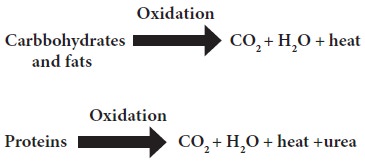
Energy yielding food factors
The energy yielding
food factors are
(i) carbohydrates (ii)
fats and(iii) proteins. Within the body, these are oxidised in the cells. The
process is one of continuous
utilization of O2
and production of CO2 H2O and heat.
Units of energy – calorie and joule
The energy value of
foods can be expressed in terms of kilocalories(KCal) or megajoules(MJ).The
International Union of Nutritional Sciences has suggested the use of megajoule
as the energy unit in place of
Kcal. These units are
defined as follows:
Kilocalorie: One
kilogram calorie is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1
kg of water through 1° C.
Joule: A joule is
defined as the energy required to move 1kg mass by 1 metre by a force of 1
Newton acting on it.
Newton: One Newton is
the force needed to accelerate 1 kg mass by less than a second.
1 Kcal
= 4.184 KJ
1000Kcal = 4.184 Megajoule(MJ)
1 MJ = 240Kcal
Energy value of foods
The energy in various
foods is measured by calorimetry. Calorimetry is the measurement of heat
loss.The energy value of foods is determined using the instrument called Bomb
calorimeter.
Gross Energy value of foods
When samples of
carbohydrate, fat, protein are burned, the amount of heat produced is always
the same for each of these nutrients. The average gross energy value of carbohydrates,fats
and proteins determined with bomb calorimeter is as follows:
1g of Carbohydrate =
4.1 kcal
1g of fat = 9.45 kcal
1g of protein = 5.65 kcal
Physiological energy value of foods
In the utilization of
carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body a certain percentage of these
nutrients is lost in digestion and the nitrogen of protein is excreted in urine
as urea which still contains some energy value.The average losses in digestion
in human subjects have been estimated to be 2.0% for carbohydrates,5.0% for
fats and 8.0% for proteins. The loss of energy in urea is estimated to be
1.2kcal per gram of protein oxidised. The physiological energy values of foods
calculated from the gross energy values after allowing for the losses in
digestion and metabolism are as follows: Carbohydrates 4.0;fats 9.0 and
proteins 4.0.
These values are known
as ‘Atwater Bryant factors’ or physiological fuel values.
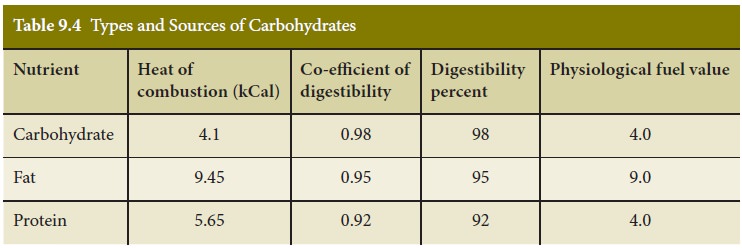
Coefficient of digestibility
The coefficient of
digestibility is used to express the proportion of an ingested nutrient that
ultimately becomes available to the body cells. The coefficient of
digestibility for carbohydrate, fat and protein are 0.98,
0.95 and 0.92
respectively. It is observed that carbohydrate and fat are metabolized almost
completely, whereas protein metabolism is incomplete due to the presence of
nitrogen.
The physiological fuel
value, Co- efficient of digestibility and digestibility percent of
carbohydrate, fat and proteins is presented in table 9.4.
Related Topics