Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 9 : Carbohydrates and Energy
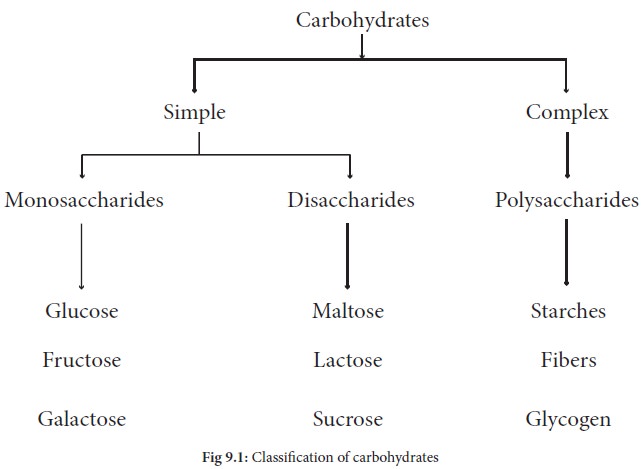
Classification of carbohydrates
Classification
of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are
classified according to the number of saccharide (sugar) groups present. They
are broadly classified as simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. The
simple carbohydrates includemonosaccharides(Singlesugar)and
disaccharides(Doublesugars). Complex carbohydrates include starch,glycogen and
fibers. The classification of carbohydrates is schematically represented below:
Simple Carbohydrates
A) Monosaccharides
They have one
saccharide group and are the simplest form of carbohydrates. All carbohydrates
are reduced to this state before absorption and utilization. They contain 3-6
carbon atoms and are accordingly termed triose, tetrose, pentose or hexose.
1. Biose: C2H4O2
(e.g.)Glycolic aldehyde
2. Triose: C3H6O3
(e.g.)Glyceraldehyde and Dihydroxyacetone. They occur in plant and animal
tissues in small amounts and are derived from the breakdown of glucose.
3. Tetroses: C4H8O4
(e.g.) Erythrose,
Threose
4. Pentoses: C5H10O5(e.g.)
Arabinose, Xylose, Ribose and Deoxyribose.
5. Hexoses: C6H12O6
.They are further sub-divided into 2 groups(i.e) Aldoses or sugars
containing aldehyde group(e.g.) Glucose,
Major monosaccharides
a. Glucose (Dextrose or grape
sugar): It serves as the main source of energy in the body. It is abundantly
found in nature. It is found in sweet fruits such as grapes, berries, oranges
in vegetables like sweet corn and carrots. It is less sweet than cane sugar. It
is the end product in the digestion of disaccharides and polysaccharides and is
the form of carbohydrate circulating in the blood.
b. Fructose(Levulose or fruit
sugar): It is much sweeter than cane sugar and is found in honey,ripe fruits
and some vegetables.It is also a product of the hydrolysis of sucrose.
c. Galactose: It does not occur in
the free state, but occurs as a constituent of lactose present in milk.
B) Disaccharides
They are formed by the
combination of 2 monosaccharides. The disaccharides of nutritional importance
are sucrose, maltose and lactose.
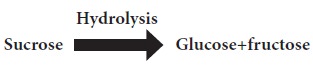
a. Sucrose(Cane sugar,
beetsugar, tablesugar): It occurs in sugarcane (10-12%) and beetroot(12-18%).In
the intestine, sucrose is broken down into monosaccharides -glucose andfructose
by the enzyme sucrase present in the intestinal juice and then absorbed.
b. Lactose(Milk sugar): It occurs
in the milk of mammals. Cow’s milk and buffalo’s milk contain 4% of lactose,
while human milk contains about 7% of lactose. Lactose is hydrolysed to glucose
and galactose by the enzyme lactase present in the intestinal juice

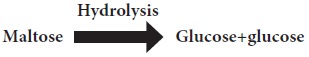
c. Maltose (Malt sugar): It is
found in all sprouted and malted products.It is an intermediate product formed
in the process of conversion of starch into glucose. Maltose is hydrolysed to 2
molecules of glucose by the enzyme maltase present in the intestinal juice.
Sprouted cereals and beer contain large amount of maltose.
Complex Carbohydrates
These are complex
compounds with high molecular weights. Their structural
formula is (C6H10O5)n
, where n>2.They are formed by a combination of more than 2 molecules of a
monosaccharide. Unlike the
sugars,which contain 3
monosaccharides – Glucose, fructose and galactose in different combinations,
the polysaccharides – Starch and Glycogen are composed entirely of glucose.
They differ from each other only in the nature of the bonds that link the
glucose units together.
1. Starch : It is a long, straight
or branched chain of hundreds of glucose units linked together. The important
sources of starch are
cereals and
millets(65-85%) and roots and tubers(19-35%). Starch is a polysaccharide formed
in nature by the condensation of large number (4000-15000) of glucose
molecules. It consists of a mixture of 2 components called amylase and
amylopectin.It is the storage form of carbohydrate in the plant kingdom.
Cooking facilitates the digestion of starch. Boiling causes swelling of the
starch granules and rupture of the cell walls, allowing better digestion. The
enzyme amylase present in the salivary and pancreatic juices, converts starch
into maltose which is subsequently broken into glucose and absorbed.
2. Dextrin: It is not found in
direct form in nature. They are polysaccharides formed by the partial
hydrolysis of starch by acids or amylase. They are composed of large number of
glucose molecules.
3. Glycogen: It is made up of
chains of glucose,which are more highly branched than starch molecules.It is
the storage form of carbohydrates in human beings and animals. It is formed by the condensation of large number (5000-10000) of
glucose molecules.When required by the body, glycogen is converted to glucose
to give energy.
Related Topics