Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Eczema and dermatitis
Eczema and dermatitis: Histology
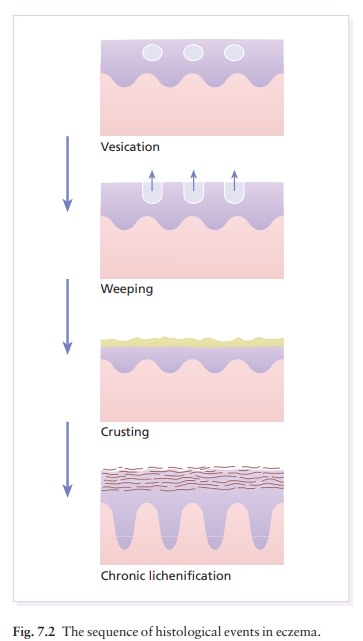
The clinical appearance of the different stages of eczema mirrors their histology.
Histology
(Fig. 7.2)
The
clinical appearance of the different stages of eczema mirrors their histology.
In the acute stage, oedema in the epidermis (spongiosis) progresses to the
formation of intraepidermal vesicles, which may co-alesce into larger blisters
or rupture. The chronic stages of eczema show less spongiosis and vesication but
more thickening of the prickle cell layer (acanthosis) and horny layers
(hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis). These changes are accompanied by a variable
degree of vasodilatation and infiltration with lymphocytes.
Study Material, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, brief detail
Clinical Dermatology: Eczema and dermatitis : Eczema and dermatitis: Histology |
Related Topics
Clinical Dermatology: Eczema and dermatitis