Chapter: 11th Economics : Chapter 1 : Introduction To Micro-Economics
Economics: Its Types
Economics:
Its Types
Economics
is a rapidly growing subject and its horizon has been expanding. The basic
thrust of the subject is that there should be efficient allocation of the
available scarce resources to obtain maximum welfare to the people on a
sustainable basis. Given below are some of the major branches of the subject,
where such efficient resource allocation is made.
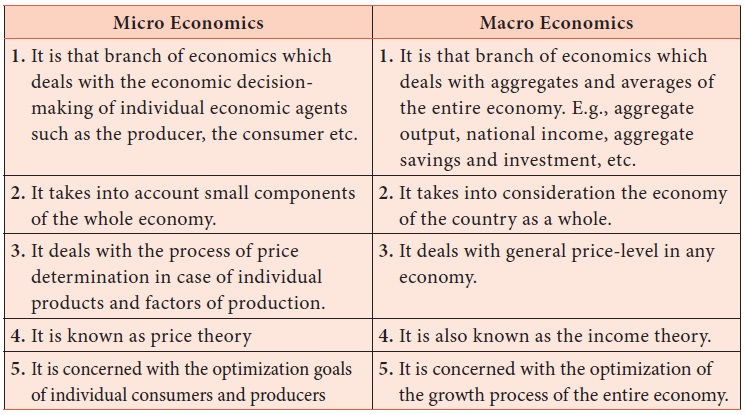
1. Micro-economics
Micro Economics is the study of the economic actions of individual units say households, firms or industries. It studies how business firms operate under different market conditions and how the combined actions of buyers and sellers determine prices. Micro economics covers
1.
Value theory (Product pricing and factor pricing)
2.
Theory of economic welfare
2. Macro-economics
Macro economics is the obverse of micro economics. It is concerned with the economy as a whole. It is the study of aggregates such as national output, inflation, unemployment and taxes. The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money published by Keynes is the basis of modern macro economics.
The terms ‘micro economics’ and ‘macro economics’ were first
used in economics by Norwegian economist Ragner Frisch in 1933. After Prof. Frisch, the terms earned popularity
when J.M. Keynes clearly distinguished between the terms through his book
entitled ‘General
theory of
‘Employment, Interest and Money’ published in 1936.

Difference between Micro Economics and Macro Economics
3. International Economics
In the
modern world, no country can grow in isolation. Every country is having links
with the other countries through foreign capital, investment (foreign direct
investment) and international trade.
4. Public Economics
Public
finance is concerned with the income or revenue raising and expenditure
incurring activities of the public authorities and with the adjustment of the
one with the other. The scope of Public Finance covers Public expenditure,
Public revenue, Public debt and financial administration.
5. Developmental Economics
The
countries have been classified into developed, developing and under developed
on the criteria of per capita income, Human Development Index and Happiness
Index. The Development Economics deals with features of developed nations,
obstacles for development, Economic and Non-economic factors influencing
development, various growth models and strategies.
6. Health Economics
Health
Economics is an area of applied economics. It covers health indicators,
preventive and curative measures, medical research and education, Rural Health
Mission, Drug Price control, Neo natal care, Maternity and Child health,
Budgetary allocation for health etc.
7. Environmental Economics
Depletion
of natural resources stock and pollution result from rapid economic
development.Hencetheneedforthestudyof Environmental Economics which analyses
the inter relationship between economy and environment. Environmental Economics
is a study of inter disciplinary tools for the problems of ecology, economy and
environment.
Related Topics