Chapter: Medical Electronics : Electro-Physiology and Bio-Potential Recording
EMG (Electro Myograph)
EMG (ELECTRO MYOGRAPH)
It is an
instrument used for recording the electrical activity of the muscles to
determine whether the muscle is contracting or not. Study of neuromuscular
function is also possible by using EMG. Muscular contractions are caused by the
depolarization of muscle fibers. Similarly the recording of peripheral nerves
action potentials is called as electro neurography.
ELECTRODES USED FOR EMG
Two types of electrodes:
Surface electrodes- Usually
this electrode is used for EMG. But by using this electrode, it is not possible to take the deeper
potential.
Needle electrodes – These are inserted into tissue or
closer to tissue to measure the electrical
activity of muscle.
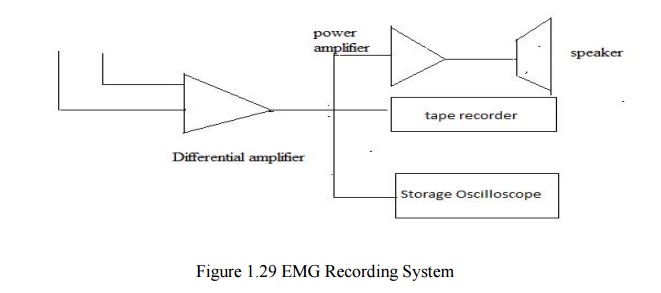
EMG RECORDING SYSTEM
EMG
potentials are taken from the tissue by using electrodes. These EMG potentials
are given to differential amplifier. This is the high gain amplifier. Its
frequency range is given as 10 Hz to 10 KHz.
Bandwidth
of EMG is large. CMRR (Common mode Rejection Ratio) of this differential
amplifier is 80 to 100 db.Input Impedance of this amplifier is 10 MΩ. Here
there is no lead
selector
switch. Because only two electrodes are available. The output of the
differential amplifier is given to loudspeaker system, tape recorder and CRO.
Before
giving the output of differential amplifier to loudspeaker, it is given to
power amplifier. Power amplifier amplifies the signal that is received by
loudspeaker.
The
amplified signal from the output of the differential amplifier is displayed by
using CRO. Here storage oscilloscope is used. Output cab be displayed and the
same can be stored in the CRO. The signal from the differential amplifier is
recorded by using tape recorder. It is used for the future purpose.
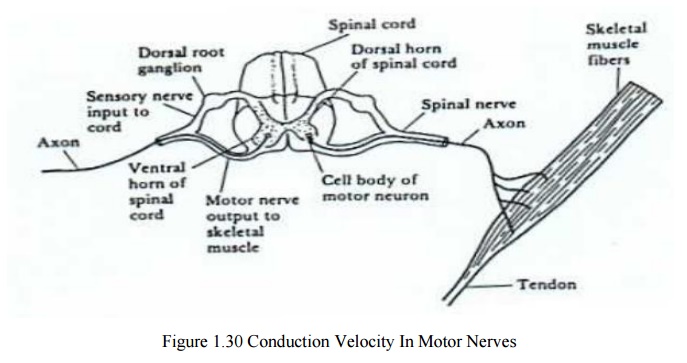
MEASUREMENT OF CONDUCTION VELOCITY IN MOTOR NERVES
In modern
EMG systems, nerve conduction time and nerve velocity are measured. For this
measurement, initially nerve is stimulated and EMG is measured.This conduction
velocity measurement is used to indicate the location and type of nerve lesion.
Steps involved in measurement of conduction
velocity
·
Stimulte is applied at point A
·
Electrical activity of muscle is measured at point
B
·
The space between A and B is noted as l1
meters.
·
The time delay between applying stimulus and
receiving action potential is known as latency. This time delay is detoned as t1
second.
·
Now change the position of A into C. Now the space
is reduced. It is noted as l2 meters.
·
The time delay noted is t2 second.
·
Usually, l2<l1 and t2
<t1.
·
Now , the conduction velocity is given as , V= l1-l2/t1-t2.
·
Usually V= 50 m/sec.
·
If V<40
m/s. It means there is some disorder in nerve conduction.
·
Thus conduction velocity is measured in motor
nerves.
·
Skeletal muscle is organized functionally on the
basis of the motor unit.
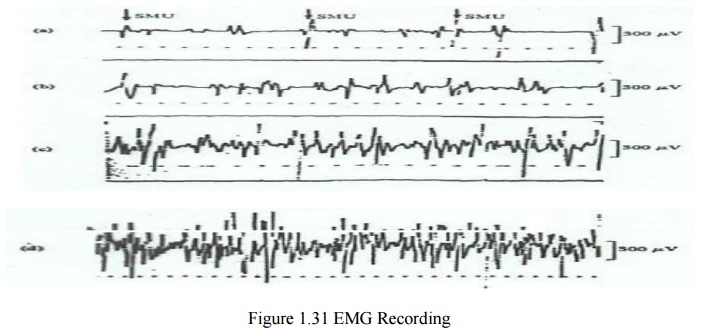
Single Motor Unit (SMU)
·
The motor unit is the smallest unit that can be
activated by a volitional effort (all constituent muscle fibers are activated
synchronously)
·
Single motor unit (SMU) consists of a single motor
neuron and the group of skeletal muscles that it innervates
·
SMU is a distributed unit bioelectric source in a
volume conductor consisting of all other muscle fibers, both active and
inactive.
·
The evoked extracellular field potential from the
active fibers of an SMU has a triphasic form of 3-15 ms duration and 20-2000 μV
amplitude depending on the size of SMU
·
The figure below shows motor unit potentials from
normal muscle under graded levels of contraction. At high levels of activity,
many sophisticated motor unit responses give rise to a complicated response
(interference pattern)
·
A variety of electrodes have been developed for EMG
recording
·
The figure below shows the needle and wire
electrodes used in recording the EMG signal
·
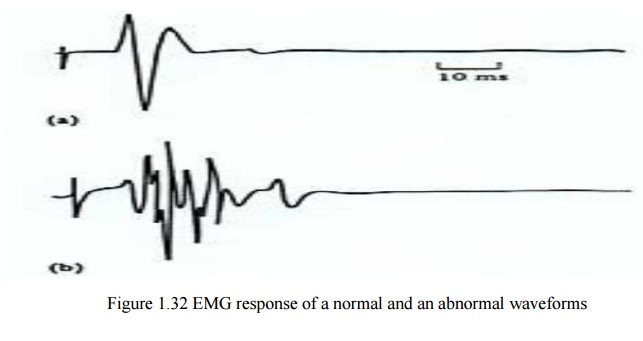
The EMG is also of considerable clinical value
·
The shape of SMU potentials is modified by disease
The
figure below shows the EMG response for a normal subject and one with
neuropathy
Applications of EMG:
EMG is
used in the field of:
·
Electrophysiological testing.
·
Clinical neurophysiology.
·
Neurology.
·
Psychiatry.
Related Topics