Chapter: Medical Electronics : Electro-Physiology and Bio-Potential Recording
Bio Potential Electrodes
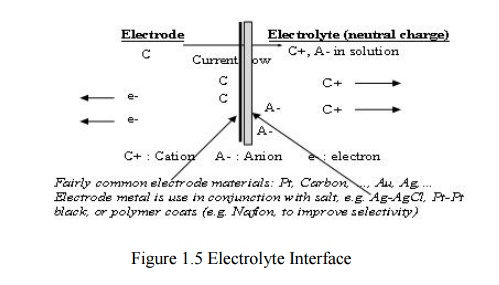
BIO POTENTIAL ELECTRODES
Electrode
– Electrolyte Interface
General
Ionic Equations
C<->Cn+
+ne-
Am-<->A +me -
• If electrode has same material as
cation, then this material gets oxidized and enters the electrolyte as a cation
a nd electrons remain at the electrode and flow in the external circuit.
• If anion can be oxidized at the
electrode to form a neutral atom, one or two electrons are given to the
electrode
The
dominating reaction can be inferred from the following :
·
Current flow from electrode to electrolyte :
Oxidation (Loss of e-)
·
Current flow from electrolyte to electrode :
Reduction (Gain of e-)
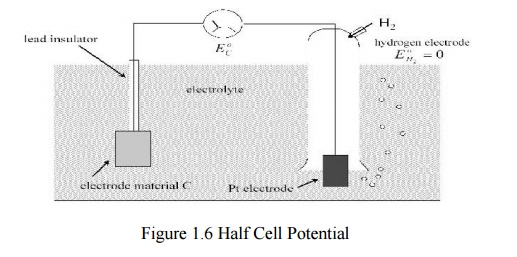
Half Cell Potential
·
A characteristic potential difference established
by the electrode and its surrounding electrolyte which depends on the metal,
concentration of ions in solution and temperature.
Half cell potential cannot be measured without a
second electrode.
·
The half cell potential of the standard hydrogen
electrode has been arbitrarily set to zero. Other half cell potentials are
expressed as a potential difference with this electrode.
Reason for Half Cell Potential : Charge Separation
at Interface
·
Oxidation or reduction reactions at the
electrode-electrolyte interface lead to a double-charge layer, similar t o
that which exists along electrically active biological cell membranes.
Measuring Half Cell Potential
Polarization
· If there is a current between the electrode
and electrolyte, the observed half cell potential is often altered due to polarization.
Nernst Equation
·
When two aqueous ionic solutions of different
concentration are separated by an ion-selective semi-permeable membrane, an
electric potential exists across the membrane.
The Nernst equation for half cell potential is E=E0
+ R T/n[acyad/ aAαaBβ]
where
E0 : Standard Half Cell Potential
E : Half Cell Potential
a : Ionic Activity (generally same as concentration)
n :
Number of valence electrons involved
Polarizable and Non-Polarizab le Electrodes
Perfectly Polarizable Electrodes: These are
electrodes in which no actual charge crosses the electrode-electrolyte interface when a current is applied. The
current across the interface is a displacement current and the electrode
behaves like a capacitor. Example : Ag/AgCl Electrode
Perfectly Non-Polarizable Electrode: These are
electrodes where current passes freely across
the electrode-electrolyte interface, requiring no energy to make the
transition.
Over
potentials. Example : Platinum electrode
Example:
Ag-AgCl is used in recording while Pt is use in stimulation
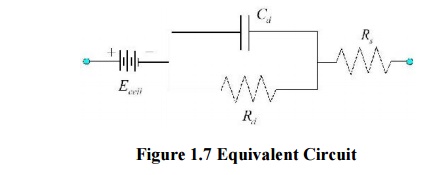
Cd :
capacitance of electrode-eletrolyte interface
Rd :
resistance of electrode-eletrolyte interface
Rs :
resistance of electrode lead wire
Ecell : cell
potential for electrode
Electrode Skin Interface
Motion Artifact
·
When the electrode moves with respect to the
electrolyte, the distribution of the double layer of charge on polarizable
electrode interface changes. This changes the half cell potential temporarily.
·
If a pair of electrodes is in an electrolyte and
one moves with respect to the other, a potential difference appears across the
electrodes known as the motion artifact. This is a source of
noise and interference in biopotential measurements.Motion artifact is minimal
for non-polarizable electrodes
Body Surface Recording Electrodes
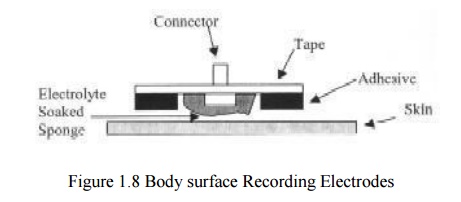
Commonly Used Biopotential Electrodes
Metal
Plate Electrodes are
1. Suction
Electrodes
2. Floating
Electrodes
3. Flexible
Electrodes
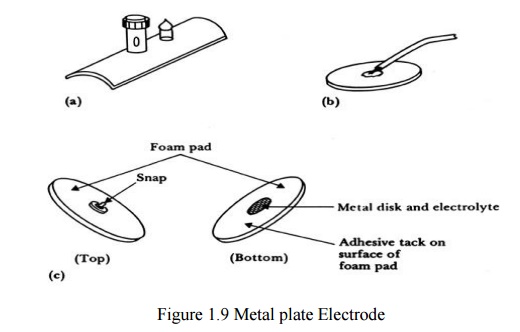
Metal plate electrodes
– Large surface: Ancient, therefore still used,
ECG
– Metal disk with stainless steel; platinum or
gold coated
– EMG, EEG
– smaller diameters
– motion artifacts
– Disposable foam-pad: Cheap!
Suction electrodes
-
No straps or adhesives required
-
precordial (chest) ECG
-
can only be used for short periods

Floating electrodes
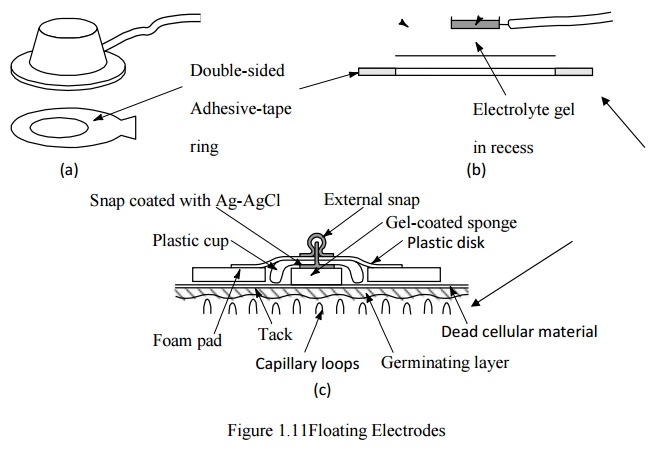
-
metal disk is recessed
-
swimming in the electrolyte gel
-
not in contact with the skin
-
reduces motion artifact
Flexible electrodes
-
Body contours are often irregular
-
Regularly shaped rigid electrodes may not always
work.
-
Special case : infants
-
Material :
- Polymer
or nylon with silver
- Carbon
filled silicon rubber (Mylar film)
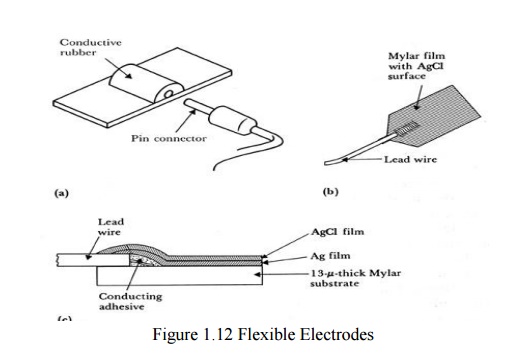
(a)Carbon-filled silicon e rubber electrode.
(b)Flexible thin-film neonatal electrode.
(c)
Cross-sectional view of the thin-film electrode in (b).
Electrodes in Biopotential Measurements
•
to make the electrode cheaper
•
more suitable for lower noise measurement for EEG
•
circumvent patents that are based on plastic/foam
electrode body
•
attractive to consumers for use with their ECG
machines at home
•
reduce artifact (minimize the motion of
skin/electrode) in ambulatory recording
In a
research laboratory, scientists want to record from single cells in a culture
dish. They want to record action potentials from single, isolated heart cells.
What kind of electrode would they need to use (describe material and design)?
Give a simplified schematic (circuit model of the electrode) described in the
notes given to you.
Neural electrodes/microelectrodes
It is
used to measure potential within asingla cell.It is small in diameter and
during insertion of microelectrode into cell will not damage to human cell.
·
It is classified into
1. Metallic
2. Non
metallic(Micropipet)
Metallic Electrode
·
It is formed by electrolytically etching the tip of
fine tungsten filament stainless wire into a minute structure.
·
Potential within the cell can be measured by using
two electrodes
1. Micro electrode, 2. Reference electrode.
Non Metallic (Micropipet)
·
It is used to measure the potential within the
single cell using non metallic material is used.
·
It is filled within an electrolyte ,that is
compatible with the cellular fluids.
Related Topics