Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Gastrointestinal system
Dyspepsia - GI presentations
Dyspepsia
Definition
Dyspepsia is a group of symptoms that suggest disease of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Prevalence
Dyspepsia has a prevalence of between 23 and 41% in Western populations.
Aetiology/pathophysiology
Diagnoses made at endoscopy include gastritis, duodenitis or hiatus hernia (30%); oesophagitis (10–17%); duodenal ulcers (10–15%); gastric ulcers (5–10%) and oesophageal or gastric cancer (2%); however, in 30% the endoscopy is normal. Functional dyspepsia describes the presence of symptoms in the absence of mucosal abnormality, hiatus hernia, erosive duodenitis or gastritis.
Clinical features
Patients may complain of upper abdominal discomfort, retrosternal burning pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, bloating, fullness and heartburn.
Investigations and management
Current UK guidelines suggest
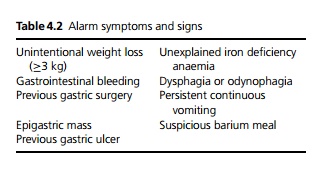
All patients over the age of 55 years with new onset of uncomplicated dyspepsia and patients of any age with ‘alarm symptoms or signs’ (see Table 4.2) should undergo an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Antisecretory drugs (i.e. H2 antagonists and proton pump inhibitors) may mask significant diagnoses at endoscopy and should be avoided for 4 weeks before investigation. At endoscopy, biopsy and urease tests should be performed.
In patients under the age of 55 years with significant symptoms but without any ‘alarm symptoms or signs’ antisecretory agents may be commenced. It is recommended that such patients should undergo Helicobacter pylori testing and where appropriate, eradication therapy.
Related Topics