Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Digestion, Absorption And Utilization Of Lipids
DIGESTION
ABSORPTION AND UTILIZATION
Digestion
In the mouth:
Fat digestion starts in the mouth with hard fats beginning
to melt when they reach body temperature. The salivary glands at the base of
the tongue release a lipase enzyme which digest fat to a less extent in adults.
In the stomach:
In the stomach fat floats as a layer above the others
components of swallowed food. As a result little fat digestion takes place.
In the small Intestine:
When
fat enters the small intestine, the hormone
cholescystokinin
signals the gall bladder to release bile. Bile emulsifies fat and also provides
an alkaline medium for the action of pancreatic lipase and intestinal lipase.
The triglycerides are acted upon by these lipases and hydrolyzed to
monolycerides and fatty acids.
The
cholesterol esters are hydrolyzed to give cholesterol and fatty acids.
Triglycerides
-> Monoglyceride + fatty acids
Cholesterol
esters -> Cholesterol + fatty acids
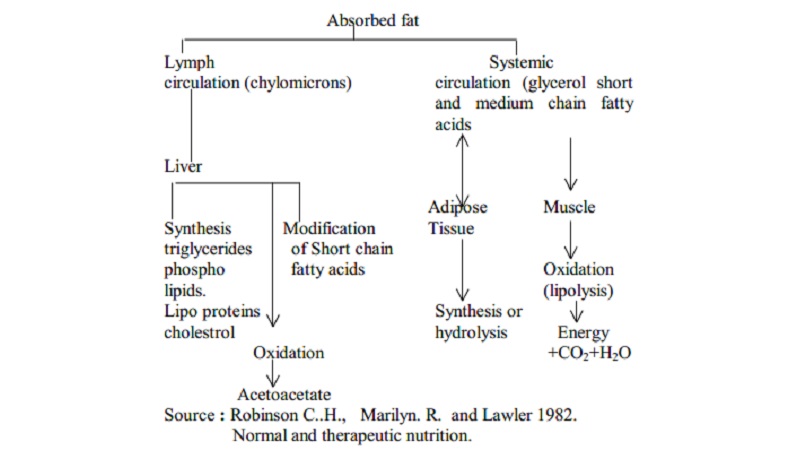
Absorption and Utilisation
Small molecules of digested triglycerides (glycerol, short
& medium chain fatty acids) can diffuse into intestinal cells and are
absorbed directly into the blood stream.
Larger
molecules(Monoglycerides, long chain fatty acids) merge into spherical
complexes known as miscelles. The lipid contents of the miscelles diffuse into
the intestinal cells. Once inside the monoglycerides and long chain fatty acids
are reassembled to new triglycerides.
Within the intestinal cells the new triglycerides and larger
lipids like cholesterol and phospholipids are placed into transport vehicle
called chylomicrons.
The intestinal cells then release chylomicrons into the
lymphatic system. The lymph circulation empties into the thoracic duct which
inturn enter the subclavian vein and subsequently into the blood stream.
The blood transport lipids to the rest of the body and cells
absorb them and utilize for energy. This breakdown of fat to yield energy is
called lipolysis.
Majority of lipids enter via the lymph to the liver where
the protein and lipid (cholesterol, triglycerides) are bound together to form
lipoproteins.
There
are four types of lipoproteins, they are:
1.
chylomicrons,
2.
very low density lipo protein (VLDL)
3.
low density lipo protein (LDL) and
4.
high density lipo proteins (HDL).
Chylomicrons, VLDL and LDL serve to transport and deposit
lipids from the intestine and liver to the tissues for absorption. Low-density
lipoprotein, which has the highest cholesterol fraction favours lipid
deposition in tissues including blood vessels and hence termed ' bad'
cholesterol. HDL cholesterol removes the lipids from the tissues and transports
it back to liver for disposal, hence it is termed as ' good cholesterol' . High
levels of LDL cholesterol indicates a high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Apart from lipoproteins, triglycerides, cholesterol and
phospholipids are synthesized in the liver. This is called lipogenesis.
Related Topics