Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 33 : Indirect Taxation
Differences between Direct Taxes and Indirect Taxes
Differences
between Direct Taxes and Indirect Taxes
The main differences between direct
taxes and indirect taxes are given in table.
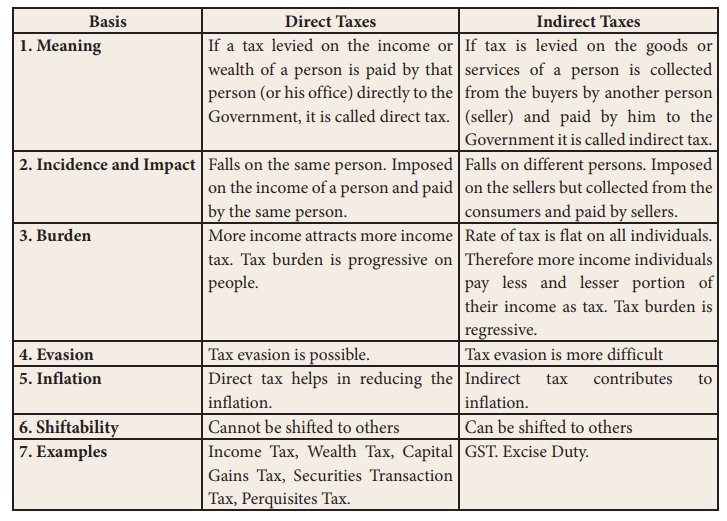
Direct Taxes Vs Indirect Taxes
1.
Meaning
Direct
Taxes: If a tax levied on the income or wealth of a person
is paid by that person (or his office) directly to the Government, it is called
direct tax.
Indirect
Taxes: If tax is levied on the goods or services of a
person is collected from the buyers by another person (seller) and paid by him
to the Government it is called indirect tax.
2.
Incidence and Impact
Direct
Taxes: Falls on the same person. Imposed on the income of a
person and paid by the same person.
Indirect
Taxes: Falls on different persons. Imposed on the sellers
but collected from the consumers and paid by sellers.
3.
Burden
Direct
Taxes: More income attracts more income tax. Tax burden is
progressive on people.
Indirect
Taxes: Rate of tax is flat on all individuals. Therefore
more income individuals pay less and lesser portion of their income as tax. Tax
burden is regressive.
4.
Evasion
Direct
Taxes: Tax evasion is possible.
Indirect
Taxes: Tax evasion is more difficult
5.
Inflation
Direct
Taxes: Direct tax helps in reducing the inflation.
Indirect
Taxes: Indirect tax contributes to inflation.
6.
Shiftability
Direct
Taxes: Cannot be shifted to others
Indirect
Taxes: Can be shifted to others
7.
Examples
Direct
Taxes: Income Tax, Wealth Tax, Capital Gains Tax,
Securities Transaction Tax, Perquisites Tax.
Indirect
Taxes: GST. Excise Duty.
Related Topics