Chapter: Biochemistry: Carbohydrate Metabolism
Degradation of glycogen (Glycogenolysis)
Degradation
of glycogen (Glycogenolysis)
When the blood sugar level falls (Hypoglycemia),
glycogen stored in the tissues specially glycogen of liver and muscles may be
broken down and this process of breakdown of glycogen is called glycogenolysis.
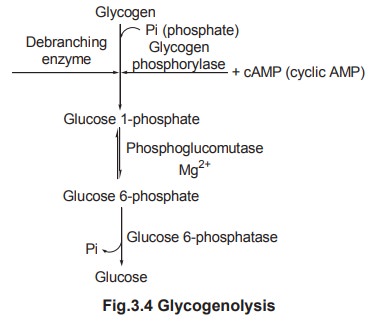
The following are the various steps of glycogenolysis.
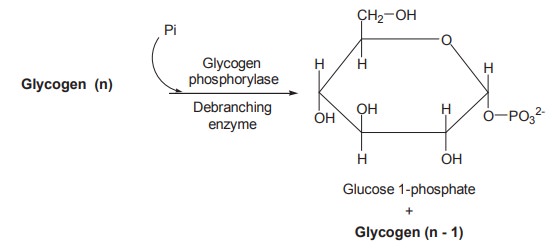
Step 1
The first step in the breakdown of glycogen is
catalyzed by two enzymes which act independently.
The first enzyme, namely glycogen phosphorylase
with inorganic phosphate catalyses the cleavage of a terminal a 1-4 bond of
glycogen to produce glycogen with one molecule less and a molecule of glucose
1-phosphate. The enzyme glycogen phosphorylase cannot cleave a 1-6 linkage.
This is carried out by another enzyme called the debranching enzyme (a 1-6
glucosidase) which hydrolyses these bonds and thus make more a 1-4 linkage
accessible to the action of glycogen phosphorylase.
The combined action of glycogen phosphorylase
and the debranching enzyme converts glycogen to glucose 1-phosphate.
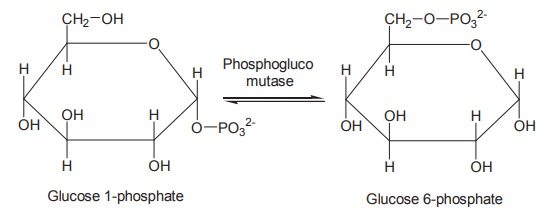
Step 2
The glucose 1-phosphate is then reversibly
converted to glucose 6-phosphate by the action of the enzyme
phosphoglucomutase.
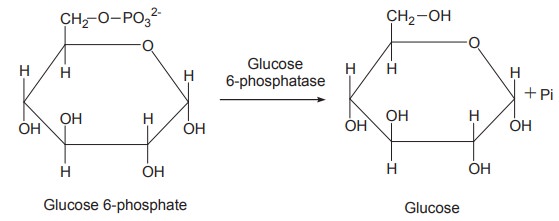
Step 3
The next reaction namely the conversion of
glucose 6-phosphate to glucose takes place in the liver and kidney by the
action of the enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase.
Glucose 6-phosphatase removes phosphate group
from glucose 6-phosphate enabling the free glucose to diffuse from the cell
into the extra cellular spaces including blood. This reaction does not occur in
the muscles because muscles lack the enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase.
Related Topics