Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Disorders of blood vessels and lymphatics
Deep vein thrombosis - Venous disease
Venous
disease
Deep vein
thrombosis
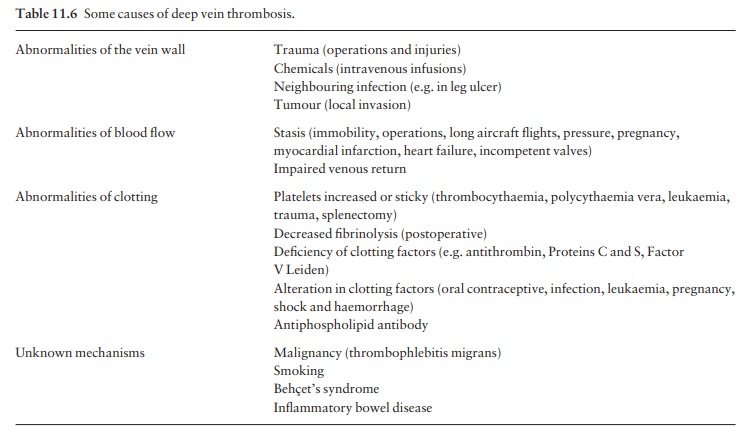
The
common causes are listed in Table 11.6.
The onset may be ‘silent’ or heralded by pain in the calf, often about 10 days after immobilization for surgery, parturition or an infection. The leg becomes swollen and cyanotic distal to the thrombus. The calf may hurt when handled or if the foot is dorsiflexed (Homan’s sign). Sometimes a pulmonary embolus is the first sign of a silent deep vein thrombosis.
Suitable
investigations include venography, Doppler ultrasonography, which can only
detect thrombi in large veins at, or above, the popliteal fossa, and 125I-fibrinogen
isotope leg scanning.
Treatment
is anticoagulation with heparin and later with a coumarin. The value of
thrombolytic regimens has yet to be assessed properly. Prevention is important.
Deep vein thrombosis after a surgical operation is less frequent now, with
early postoperat-ive mobilization, regular leg exercises, the use of elastic
stockings over the operative period and prophylaxis with low dose heparin.
Related Topics