Introduction to C++ - Data type modifiers | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 9 : Introduction to C++
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 9 : Introduction to C++
Data type modifiers
Data
type modifiers:
Modifiers
are used to modify the storing capacity of a fundamental data type except void
type. Usually, every fundamental data type has a fixed range of values to store
data items in memory. For example, int data type can store only two bytes of
data. In reality, some integer data may have more length and may need more
space in memory. In this situation, we should modify the memory space to
accommodate large integer values. Modifiers
can be used to modify (expand or
reduce) the memory allocation of any fundamental data type. They are also called
as Qualifiers.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() There are four modifiers used in
C++. They are:
There are four modifiers used in
C++. They are:
(1) signed
(2) unsigned
(3) long
(4) short
These
four modifiers can be used with any fundamental data type. The following Table
9.6 shows the memory allocation for each data type with and without modifiers.
Integer type
Table 9.6 Memory allocation for Data types
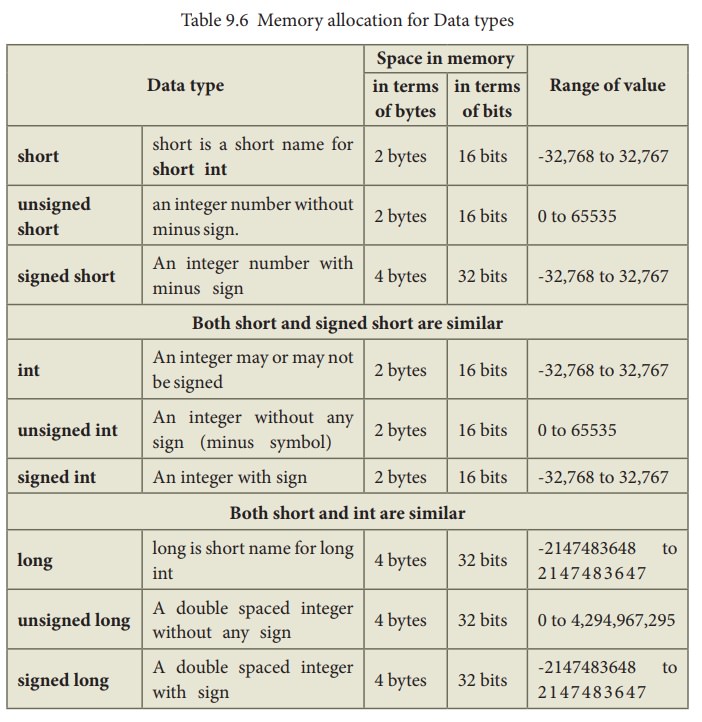
The above table clearly shows that an integer type accepts only 2 bytes of data whereas a long int accepts data that is double this size i.e., 4 bytes of data. So, we can store more digits in a long int. (long is modifier and int is a fundamental data type)
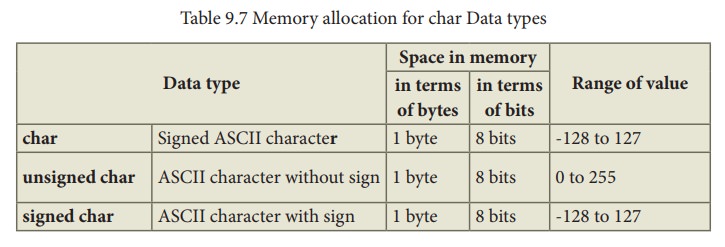
char type
Table
9.7 Memory allocation for char Data types
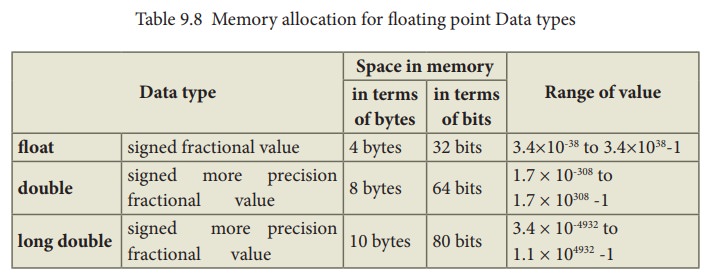
Floating point type
Table
9.8 Memory allocation for floating point Data types
Memory
allocation is subjected to vary based on the type of compiler that is being
used. Here, the given values are as per the Turbo C++ compiler. Dev C++
provides some more space to int and long double types. Following Tables 9.9
shows the difference between Turbo C++ and Dev C++ allocation of memory.
Table
9.9 Memory allocation by Turbo C++ and Dev C++
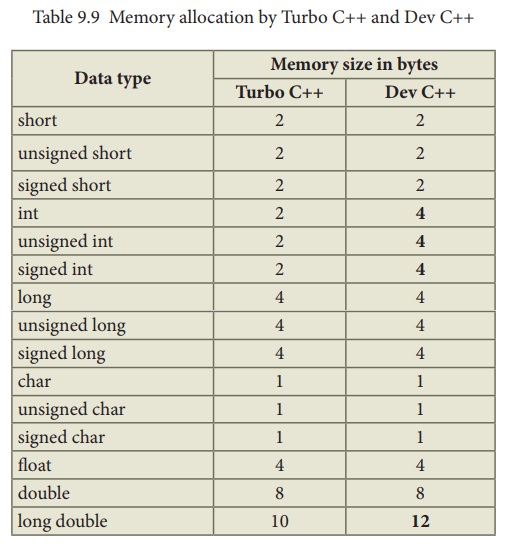
Since,
Dev C++ provides 4 bytes to int and long, any one of these types can be used to
handle bigger integer values while writing programs in Dev C++.
Note: sizeof( ) is an operator which gives
the size of a data type.
Illustration 9.5: C++ Program to find the size of data types
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
short a;
nsigned short b;
signed short c;
int d;
unsigned int e;
signed int f;
long g;
unsigned long h;
signed long i;
char j;
unsigned char k;
signed char l;
float m;
double n;
long double p;
cout <<
"\n Size of short = " << sizeof(a);
cout <<
"\n Size of unsigned short = " << sizeof(b);
cout <<
"\n Size of signed short = " << sizeof (c);
cout <<
"\n Size of int = " << sizeof(d);
cout <<
"\n Size of unsigned int = " << sizeof(e);
cout <<
"\n Size of signed int = " << sizeof(f);
cout <<
"\n Size of long = " << sizeof(g);
cout <<
"\n Size of unsigned long = " << sizeof(h);
cout <<
"\n Size of signed long = " << sizeof(i);
cout <<
"\n Size of char = " << sizeof(j);
cout <<
"\n Size of unsigned char = " << sizeof(k);
cout <<
"\n Size of signed char = " << sizeof(l);
cout <<
"\n Size of float = " << sizeof(m);
cout <<
"\n Size of double = " << sizeof(n);
cout <<
"\n Size of long double = " << sizeof(p);
}
Output : (compiled and executed in Dev C++)
Size of short = 2
Size of unsigned short = 2
Size of signed short = 2
Size of int = 4
Size of unsigned int = 4
Size of signed int = 4
Size of long = 4
Size of unsigned long = 4
Size of signed long = 4
Size of char = 1
Size of unsigned char = 1
Size of signed char = 1
Size of float = 4
Size of double = 8
Size of long double = 12
Number Suffixes in C++
There
are different suffixes for integer and floating point numbers. Suffix can be
used to assign the same value as a different type. For example, if you want to
store 45 in an int, long, unsigned int and unsigned long int, you can use
suffix letter L or U (either case) with 45 i.e. 45L or 45U. This type of declaration instructs the compiler to store the
given values as long and unsigned.
‘F’ can be used for floating point values, example: 3.14F
Related Topics