Chapter: Biochemistry: Proteins
Classification of amino acids
Classification of amino acids
The amino acids are classified based on the nature
of their R groups, in particular their polarity or tendency to interact with
water at biological pH. The polarity of the R groups varies widely, from
totally non polar to highly polar.
1. Non-polar, aliphatic R-group
The R-group in this class of amino acids are
non polar (or) hydrophobic. Six amino acids come under this class, which are glycine, alanine, valine, leucine,
isoleucine and methionine.
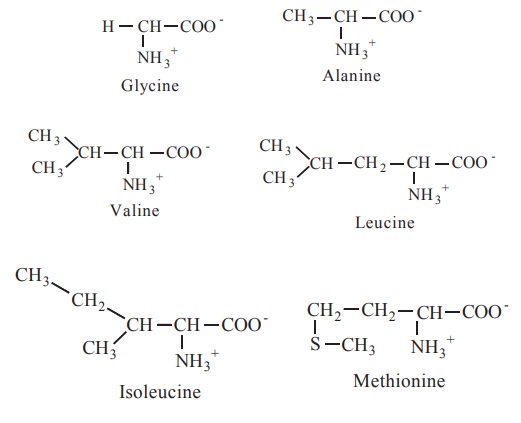
Glycine has the simplest structure. Methionine
is one of the two sulphur containing aminoacids and has a non polar thio ether
group in its side chain.
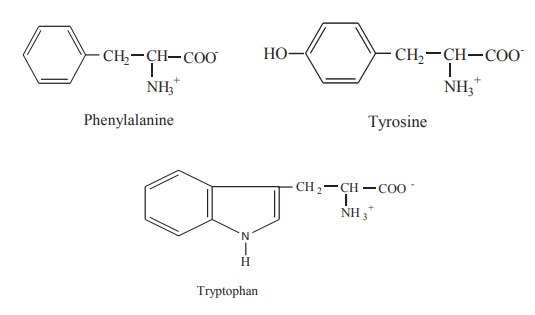
2. Aromatic R groups
Phenylalanine,
tyrosine and tryptophan, with their aromatic side chains, are relatively non-polar. All can
participate in hydrophobic interactions. The hydroxyl group of tyrosine can
form hydrogen bond with other compounds and it is an important functional group
in some enzymes. Tyrosine and tryptophan are significantly more polar than
phenyl alanine because of the hydroxyl group of tyrosine and the nitrogen of
the indole ring in tryptophan.
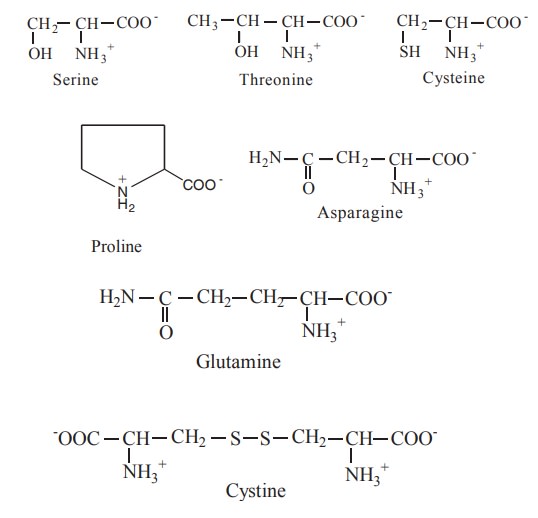
3. Polar-uncharged R groups
The R groups of these amino acids are more
soluble in water or more hydrophilic, than those of the non polar amino acids
because they contain functional groups that form hydrogen bonds with water.
This class of amino acids includes serine,
threonine, cysteine, proline,
asparagine and glutamine.
The polarity of serine and threonine is
contributed by their hydroxyl groups; that of cysteine by its sulphydryl (-SH)
group; and that of asparagine and glutamine by their amide groups. Proline has
a distinct cyclic structure and is only moderately polar. Proline has an imino
group. Cysteine is readily oxidized to form a covalently linked dimeric amino
acid called cystine, in which two cysteine
molecules are joined by a disulphide bond.
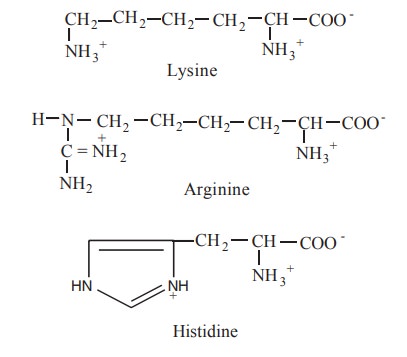
4. Positively charged (basic) R-groups
The most hydrophilic R groups are those that
are either positively (-NH3+) or negatively (-C00-) charged. The
amino acids in which the R groups have significant positive charges at pH 7.0
are lysine, arginine and histidine.
5. Negatively charged (Acidic) R groups
The two amino acids having R groups with a net
negative charge at pH 7.0 are aspartate and glutamate.
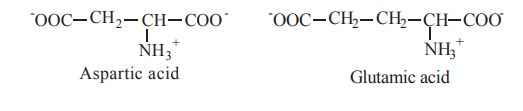
Based on their inclusion in the diet, amino
acids are classified into two groups, namely essential amino acids and
non-essential amino acids.
6. Essential amino acids
Certain amino acids can not be synthesized by
the living organisms. They must be compulsarily included in the diet for normal
health.These amino acids are called essential amino acids. For human being
about 10 amino acids are considered as essential.eg,
1. Arginine
2. Histidine
3. Isoleucine
4. Leucine
5. Lysine
6. Methionine
7. Phenyl alanine
8. Threonine
9. Tryptophan
10. Valine
7. Non-essential amino acids
Certain amino acids can be synthesized in the
cells from essential amino acids or from other compounds. So these amino acids
need not be included in the diet. They are called non-essential amino acids.
8. Non protein amino acids
Certain amino acids which do not exist in
proteins are called non protein amino acids eg.
Ornithine and b-alanine etc..
9. Peptide bonds
In proteins, amino acids are linked together by
linkages called peptide bonds. The carboxyl group of one amino acid is joined
to the α amino group of another amino acid by a peptide bond.
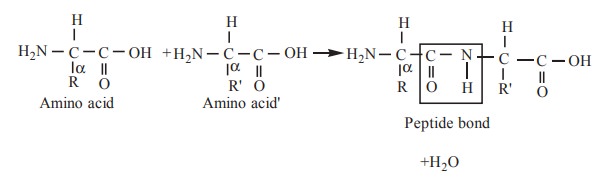
The peptide bond is also called as the amide
bond. The two amino acids, joined by a peptide bond, constitute a dipeptide.
The dipeptide is formed by simple condensation reaction.
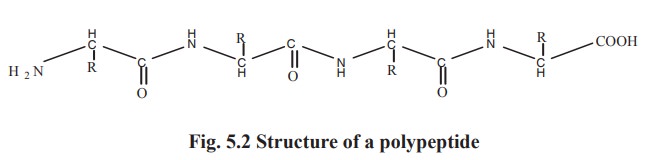
The product formed by a peptide bond is called
a peptide. The compound formed by the linking of three amino acids is called as
tripeptide. A peptide formed of less than 10 amino acids constitute an
oligopeptide. More than 10 amino acids join together to form a polypeptide
chain (Fig. 5.2).
Protein is made up of one or more polypeptide chains
Many proteins, such as myoglobin, consist of a
single polypeptide chain. Others contain two or more chains, which may be
either identical or different. For example haemoglobin is formed of 4
polypeptide chains, of which two a chains are of one kind and the other two b chains are of another kind.
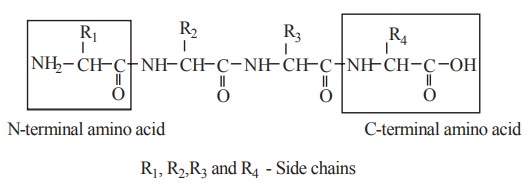
N and C terminal ends of protein
An amino acid in a polypeptide is called a
residue. A polypeptide have two ends, namely amino and carboxyl terminal end.
The end of the polypeptide chain containing amino group is called amino terminal
or N-terminal. The end of the polypeptide chain containing carboxyl group is
called carboxyl terminal or C-terminal. The terminal amino acid with the free
amino group is called N-terminal amino acid and the terminal amino acid with
the free carboyl group is called C-terminal amino acid.
Related Topics