Commerce - Classification of Markets | 12th Commerce : Chapter 13 : Elements of Marketing : Concept of Market and Marketer
Chapter: 12th Commerce : Chapter 13 : Elements of Marketing : Concept of Market and Marketer
Classification of Markets
Classification of Markets
On the basis of different approaches markets have
been classified on the basis of Area, Nature of Goods, and Economic view,
Transaction, Regulation, Time, Volume and importance. The detailed
classification is presented in the following chart.
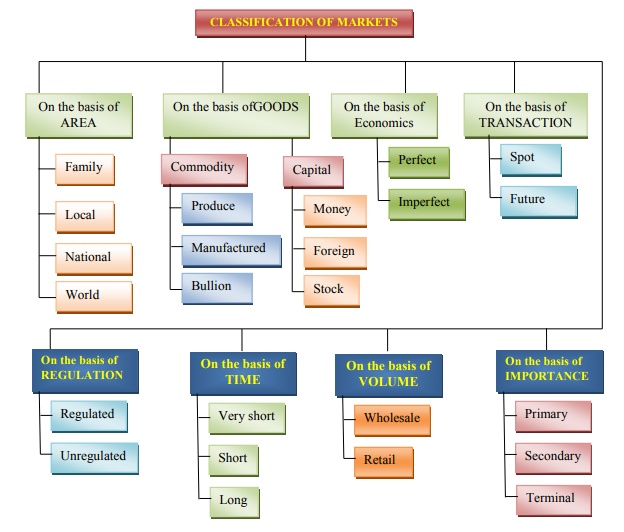
I. On the Basis of Geographical Area
a. Family Market: When exchange of
goods or services are confined within a family or close members of the
family, such a market can be called as family market.
b. Local Market: Participation of both
the buyers and sellers belonging to a local area or areas, may be a town or
village, is called as local market. The demands are limited in this type of
market. For example, perishable goods like fruits, fish, vegetables etc. But
strictly speaking such markets are disappearing because of the efficient system
of transportation and communication. Even, then, in many villages such markets
exist even today.

c. National Market: a. Certain type of
commodities has demand throughout the country. Hence it is called as a national
market. Today the goods from one corner can reach another corner with ease as
the communication and transportation facilities are developed well in India.
This creates national markets for almost all the products.
d. International Market or World Market: World or international market is one where the buyers and sellers
of goods are from different countries i.e., involvement of buyers and sellers
beyond the boundaries of a nation.
II. On the Basis of Commodities/Goods
a. Commodity Market:
A commodity market is a place where produced goods
or consumption goods are bought and sold. Commodity markets are sub-divided
into:
i. Produce Exchange Market: It is an organised market where
commodities or agricultural produce are bought and sold on wholesale basis.
Generally it deals with a single commodity. It is regulated and controlled by
certain rules. e.g. Wheat Exchange Market of Hapur, the Cotton Exchange Market
of Bombay etc.
ii. Manufactured Goods Market: This market deals with manufactured goods.
e.g., Leather goods, Manufactured machinery etc. The Leather Exchange Market at
Kanpur is an example of the same.
iii. Bullion Market: This type of market
deals with the purchase or sale of gold and silver. Bullion markets of
Mumbai, Kolkata, Kanpur etc., are examples of such markets.
b. Capital Markets:
New or going concerns need finance at every stage.
Their financial needs are met by capital markets. They are of three types:
i. Money Market: It is a type of
market where short term seurities are exchanged. It
provides short term and very short term finance to industries, banks,
governments agencies and financial intermediates.
ii. Foreign Exchange Market: It is an international market.
This type of markets helps exporters and importers, in converting their
currencies into foreign currencies and vice versa.
iii. The Stock Market: This is a market where sales and
purchases of shares, debentures, bonds etc., of companies are dealt with. It is
also known as Securities market. Stock Exchanges of Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai
etc., are examples for this type of market.
III. On the Basis of Economics
a. Perfect Market: A market is said to
be a perfect market, if it satisfies the following conditions:
i. Large number of buyers and sellers are there.
ii. Prices should be uniform throughout the market.
iii. Buyers and sellers have a perfect knowledge of
market.
iv. Goods can be moved from one place to another
without restrictions.
v. The goods are identical or homogenous.
It should be remembered that such types of markets
are rarely found.
b. Imperfect Market: A market is said to
be imperfect when
i. Products are similar but not identical.
ii. Prices are not uniform.
iii. There is lack of communication.
iv. There are restrictions on the movement of
goods.
IV. On the Basis of Transaction
i. Spot Market: In such markets,
goods are exchanged and the physical delivery of goods takes place
immediately.
ii. Future Market: In such markets,
contracts are made over the price for future delivery. The dealing and
settlement take place on different dates.
V. On the Basis of Regulation
i. Regulated Market: These are types of markets which are
organised, controlled and regulated by statutory measures.
Example: Stock
Exchanges of Mumbai, Chennai,
Kolkata etc.
ii. Unregulated Market: A market which is not regulated by
statutory measures is called unregulated market. This is a free market, where
there is no control with regard to price, quality, commission etc. Demand and
supply determine the price of goods.
VI. On the Basis of Time
i. Very Short Period Market: Markets which deal in
perishable goods like, fruits, milk, vegetables etc., are called as very short
period market. There is no change in the supply of goods. Price is determined
on the basis of demand.
ii. Short Period Market: i. In certain goods, supply is adjusted to
meet the demand. The demand is greater than supply. Such markets are known as
Short Period Market.
iii. Long Period Market: This type of market deals in durable
goods, where the goods and services are dealt for longer period usages.
VII. On the Basis of Volume of Business
i. Wholesale Market: In wholesale market goods are supplied in
bulk quantity to dealers/ retailers. The goods and services are not sold to
customers directly.
ii. Retail Market: In retail market the
goods are purchased from producer or wholesales and sold to customers in
small quantities by retailers.
VIII. On the Basis of Importance
i. Primary Market: The Primary producers of farm sell their
output or products through this type of markets to wholesalers or consumers.
Such markets can be found in villages and mostly the products arrive from
villages.

ii. Secondary Market: In this market, the semi finished
goods are marketed. Here finished goods are not sold. The commodities arrive
from other markets. The dealings are commonly between wholesalers or between
wholesalers and retailers.
iii. Terminal Market: It is a central site that serves as an
assembly and trading place for commodities in a metropolitan area. For
agricultural commodities, these are usually at or near major transportation
hubs.
Related Topics